NATO and Warsaw Pact
advertisement

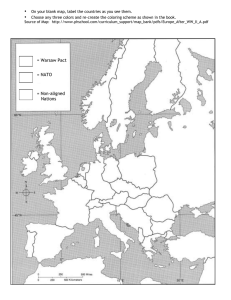
NATO 1949 NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization Partly to counter Soviet influence after World War II, Western leaders encouraged regional economic and political cooperation. 12 Original members~1949 US Canada Iceland Norway Denmark The Netherlands Belgium Luxemburg Great Britain France Portugal Italy Later (1952) Greece and Turkey also joined NATO 1955 (West) Germany joined NATO 1982 Spain also joined NATO All of the countries agreed to come to each other’s aid if attacked. An attack on one is an attack on all. The alliance’s goal was the eventual integration of the national armed forces of the member nations into a unified military command. In reality, NATO was dominated by the American military establishment. A US general (beginning with Eisenhower) was always the supreme commander. NATO was the first peacetime alliance joined by the United States. On April 4, 1949, President Truman and diplomats from the US and 11 other countries signed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization pact. 1955The Warsaw Pact In 1955 , the USSR with its own fears of a rearmed Germany created a competing military alliance system, the Warsaw Pact. It integrated the armed forces of Eastern Europe into a unified command under the USSR In addition, the USSR recognized East Germany as an independent state. Thus, by 1955, Germany had become two separate nations, each integrated into the sphere on influence of a superpower. It was formally called the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance. The treaty was signed in Warsaw, Poland on May 14, 1955. It was established to counter the alleged threat from the NATO alliance. The creation of the Warsaw Pact was prompted by the integration of a "remilitarized" West Germany into NATO on May 9, 1955. Members of the Warsaw Pact: Soviet Union Poland East Germany Czechoslovakia Bulgaria Hungary Romania Albania The communist states of Central and Eastern Europe were signatories except Yugoslavia. The members of the Warsaw Pact pledged to defend each other if one or more of the members were attacked. The treaty also stated that relations among the signatories were based on mutual noninterference in internal affairs and respect for national sovereignty and independence. The noninterference rule would later be violated with the Soviet interventions in Hungary (Hungarian Revolution1956) and Czechoslavakia (Prague Spring, 1968). In both cases the intervening forces claimed to have been invited, and thus the rules were not considered formally violated. Albania stopped supporting the alliance in 1961 as a result of the Sino-Soviet spit in which the hard-line Stalinist government in Albania sided with China, and officially withdrew from the pact in 1968.