Nationalist Revolutions Powerpoint
advertisement

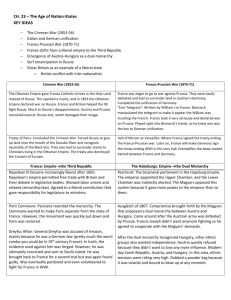
Text Chapters 24.2-24.3 Stage for nationalist movements was set by the Congress of Vienna: Met from 1814-1815 to establish rules for a European peace following the defeat of Napoleon 5 “Great” European powers: Russia, Prussia, Austria, GB, France Dominated by Prince Metternich of Austria Restore the balance of power in Europe by reestablishing Europe’s Monarchs to their old thrones (& old borders). Limit the spread of the ideas championed by the French Revolution, mainly democracy and popular government. Europe was split largely along it’s pre-French Revolution borders, and ruled by it’s old nobles The nobles carved up the continent without regard to growing ethnic desires among people in Italy, Germany, Poland, Greece, etc. Conservatives: Rich & Nobility. Europe should remain under traditional monarchies Liberals: Middle class. Wanted to give more power to elected bodies, but only educated & landowners could vote. Radicals: All people should share in a democracy. Believed in the ideas of the F.R. (Liberty, Equality, Brotherhood) Greeks, fueled by nationalist pride in their Hellenic culture, gain independence from the Ottoman Empire— 1821 Unsuccessful nationalist uprisings occur in Belgium (against the Dutch), and Poland (against Russia)—1830’s French radicals force King Charles X to flee the country after he tries to stage a return to absolute monarchy (1830). Louis-Napoleon (Napoleon’s nephew) is eventually elected president after a bloody conflict that lead to a moderate constitution. (1848) Austrian empire is broken up into AustroHungarian Empire after pressure from Hungarians (1860’s) Czars of Russia lose power (Russification) Ottoman Empire is weakened when they are pressured by British and French to recognize all their citizens as equal (1850-1860) Italy unites under Camillo di Cavour (prime minister of Sardinia working for its king Victor Emmanuel II) Di Cavour annexes all of Northern Italy from Austria He also supports the efforts of rebel Giuseppe Garibaldi (Red Shirts) to unite southern Italy & Sicily. 1870—Last of the Italian territory is acquired after the Papal States are conquered. Rome becomes Italy’s capital (Except for Vatican City) Otto Von Bismarck (Prime Minister of Prussia) unites the German Confederation under the Prussian King Wilhelm (1871) Realpolitik Seven Weeks war with Austria stokes Prussian Nationalism, and increases Prussian territory (1867) Franco Prussian War ignites feelings of German nationalism in southern Germany (they accept Prussian leadership) (1870) King Wilhelm names himself Kaiser of the Second Reich (1st was Holy Roman Empire) Russia’s elimination of the feudal system and attempts to modernize after the Crimean war (p 691)