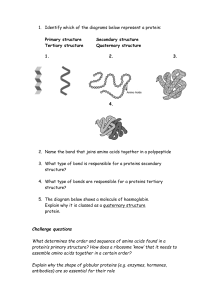
Class IX IGCSE Biological molecules Carbon is an element present in all biological molecules and carbon can form a ring structure, hence biological molecules are very large. When molecules are made up of monomers held together by a chemical bond they are called polymers Carbohydrates These may be simple sugars, or complicated materials like starch and cellulose. All carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only. Sugars with single rings are called a monosaccharide, like glucose and fructose and sugars with 2 carbon rings are called disaccharide eg maltose and sucrose. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are readily soluble in water Glucose is the form in which carbohydrates are transported around the human body. Glucose dissolve in blood plasma which delivers to every cell. A carbohydrate that is stored as energy store in plant cells. In plants the glucose molecules are linked in a slightly different way to make starch. Starch is found in the plant cell and it breaks down to form glucose. A carbohydrate that is used as an energy store in animal cells Glucose molecule can link up together to form larger molecules. In animals the larger molecule is glycogen. Plant cell wall are made up of long interconnected cellulose fibres Test for starch A solution of iodine in potassium iodide turns the orange-brown solution to blueblack when mixed with starch Benedict's test for reducing sugars Most of the sugars can be detected using Benedict's solution. Benedict's solution is blue and it changes colour when heated with reducing sugars such as glucose. Fats and oils are made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Fat is made of 3 molecule of fatty acid , joined with one molecule of glycerol. They form a part of cell membrane or the nuclear membrane. Fats also form the source of energy in the cytoplasm. Mammals often have a layer of cells containing fat droplets beneath the skin, this is both an energy resource and heat insulating layer Fats Fats and oils do not dissolve in water however, they do dissolve in ethanol. We can use this test to detect their presence in food. The food is cut into small pieces and shaken with ethanol. Any fats in the food will dissolve in the ethanol. Then the ethanol is poured into clean tube containing water which gives a milky appearance. This mixture is called emulsion. Proteins Some proteins form part of structures in the cell like the cell membranes, mitochondria, ribosomes and cytoplasm. Enzymes are proteins. Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulphur. They are made up of long chains of acids called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids. Each kind of protein has different amino acids linked in a precise order. If the amino acid is changed. There are almost infinite number of different proteins that can be made. Functions Proteins have different functions. All enzymes are proteins. Antibodies which help to protect our body from pathogens are proteins, Haemoglobin the red pigment that transports oxygen in the mammalian cells is a protein. Proteins are present in cell membranes. In Humans hair and fingernails are made up of a protein called keratin. A protein molecule is made up of long chains of amino acids arranged in a special sequence. Why there are larger number of proteins than polysaccharides ? Proteins are biomolecules made up of 20 types of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, and many thousands of different proteins are known. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates made up of long chains of the same type of sugar molecule, called monosaccharides, linked by a chemical bond. The prefix "poly" means "many", and the root word "saccharide" means "sugar". Biuret test for proteins The compounds with proteins undergo this test. Proteins are polypeptides of amino acids linked together by chemical bonds. The blue color biuret reagent turns violet when mixed with proteins. Test for vitamin C In a test tube take DCPIP solution (Blue dye). DCPIP solution is used to test Vitamin C. Add Lemon juice in it. The solution will turn colourless. Repeat the experiment with orange juice. Nutri present Elements Examples Sub-units Carbohydrates Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Starch, glycogen, cellulose, sucrose Glucose Fats/Oils Carbon, Hydrogen Oxygen (but low oxygen content than carbohydrates Vegetable oils eg olive oil, animal fats eg. Cod liver oil and waxes Fatty acids and Glycerol Protein Carbon, Hydrogen Oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulphur and phosphorus Enzymes, muscle, haemoglobin, cell membranes Amino acids (about 20 different forms Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are large, complex molecules that carry genetic information and are essential for the growth, development, and reproduction of all living organisms. A DNA molecule is made up of long chains of nucleotides formed into 2 strands A nucleotide is a 5-carbon sugar molecule joined to a phosphate group (-PO3) and an organic base. The nucleotide are joined by their phosphate groups to form a long chain. The phosphate and the sugar molecule are the same all the way down the chain. However, the bases can be any one of the four listed. Now the DNA is made up of two strands held together by chemical bonds between the bases. A always pairs with T , G always pairs with C and the sequence i.e. Cytosine, Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Thymine is a part of the genetic code. The double strand is twisted to form a helix. Chargaff found out that Adenine = Thymine Cytosine = Guanine C A T T C T Watson and crick Schematic diagram of a part of a DNA molecule G