Communicative Competence & Skills Course Material
advertisement

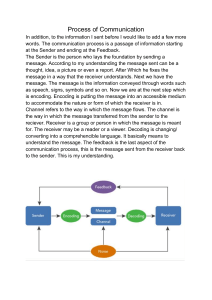
Communicative Competence - students ability to use language correctly and appropriately to accomplish communicate goals. Self - Confidence - it must be boost so that you can share your idea in front of many people. AREAS OF COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE ( These must be develop after studying this course). 1. Linguistic Competence - mastery of linguistic. - ability to use grammar correctly. 2. Sociolinguistic Competence - understanding of the social context. - words and phrases must fit this setting. - be aware of information you are sharing and know what to say / not to say. 3. Discourse Competence - mastery to combine grammatical forms and meaning to able write spoken and written text. - ability to interpret series of sentence 4. Strategic Competence - mastery of verbal and non-verbal communication - ability to communicate even there are presence of noises/ hindrance / roadblocks. COMMUNICATION SKILLS Effective Communication Skill - are critical element in your career and personal lives. - we all must be use our communicative skill to understand and understood. (Goal of Effective Communication) Enrich - that skill to possess. Effective Communication ( results in) 1. Productive Relationship 2. A better perspective in life. Communication - in every aspect of our lives , this is presence and very essential. - the act of giving, receiving, and sharing information. Effective Communication - the receiver able to give a feedback and the communication is go on and so on until ends with a period. Communication Gap - when the meaning intended by the speaker or sender is not what is understood by the recipient ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION 1.Sender - the person who initiates the communication and sends the message. 2.Message - information or idea that the sender wants to convey to the receiver. 3.Encoding - process of converting the message into a form that can be transmitted through a communication channel. 4.Channel - medium through which the message is transmitted. Examples. Face-to-face conversation. Social media. Email Phone call 5.Decoding - process of interpreting the message by the receiver. 6.Receiver - person who receives the message and interprets it. 7.Feedback - response or reaction of the receiver to the message. - it can be verbally or non-verbally( body language). 8.Noise - any interference or disturbance that affects the clarity or accuracy of the message. 9.Context - situation or environment in which the communication takes place, including the cultural, social, and psychological factors that influence the communication process. • Social Relation= communicating to workmates , family or friends. 10.Medium -technology or platform used to transmit the message, such as text message, video call, or social media platform. COMMUNICATION IS CLASSIFIED BASED ON 1. Communication Channels a. Verbal Communication - it can be written / oral . b. Non-verbal Communication - body language and sign language. 2. Style / Purpose a. Formal Communication - includes specific formats, language conventions, and professional etiquette. Ex : business communication and meetings b. Informal Communication / Casual Communication - unrestrained communication , no rules and regulations , you can express everything you want without specific format. Ex: friends , family or relatives LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION 1. Intrapersonal Communication - talking to one self. 2. Interpersonal Communication - communicate relatively to small number of people. 3. Public Communication - communicate to large number of people - you are the speaker( sender)and they are the audience ( receiver). 4. Mass Communication - practiced through various channels known as mediums, which include radio, television, social networking, billboards, newspapers, magazines, books, film, and the Internet. - large scale to a wide range of people. 5. Organizational / Business Communication - communication that takes place between people who are working towards common goals. 2 types of Organization Communication a. Horizontal Communication - communication that takes place between workers in an organization that are at the same level. b. Vertical Communication - information flowing between superiors to lower-levels. Two types of Vertical Communication I. Downward - superiors to subordinates. II. Upward - subordinates to superiors.