Chemical Kinetics
advertisement

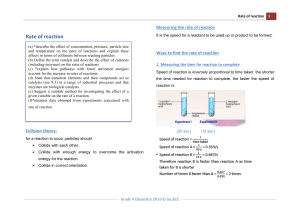
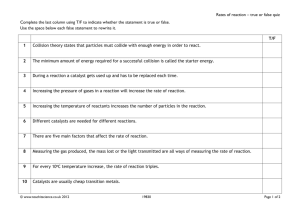
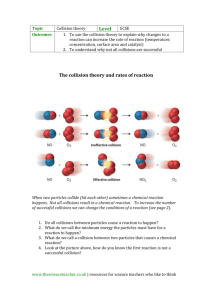
1 2 GOALS 1. Explain the role of activation energy and degree of randomness in chemical reactions 3. Investigate the effects of a catalyst on chemical reactions and apply it to everyday examples. 4. Experimentally determine indicators of a chemical reaction specifically precipitation, gas evolution, water production, and changes in energy to the system. 5. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. GOAL: Explain the role of activation energy and degree of randomness in chemical reactions 3 Reaction Directions • Physical and Chemical systems attain the lowest possible energy. • Law of disorder: the natural tendency is for systems to move in the direction of maximum disorder (or randomness)- 2nd law of thermodynamics – Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. • An increase in entropy favors spontaneous chemical reactions; decrease favors the nonspontaneous reaction. 4 Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. • Rxns are favorable when they result in a decrease in energy and an increase in entropy (disorder) • Rxn can proceed if products have more order IF energy is supplied. 5 2nd Law of thermodynamics: The total Entropy of the universe is constantly increasing. The state of maximum entroy is the most stable state. 6 Chemical Reactions and Energy • All chemical reactions release or absorb energy. – Heat, light, sound • Chemical reactions are the making and breaking or bonds. Enthalpy (ΔH): Heat Energy of the System 7 1. Exergonic • Chemical reactions that releases energy are called exergonic. – Glow sticks • If heat is released, it is called exothermic – Combustion – Decease in Enthalpy (ΔH) of the system Ch 17 2. Endergonic • Chemical reactions that require energy are called endergonic. – Ex: Cold Packs • If heat is absorbed, it is called endothermic • Increase in Enthalpy (ΔH) of the system 8 Ch 17 9 10 Intro Clip Goals: Investigate the effects of a catalyst on chemical reactions and apply it to everyday examples. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. Rates of Chemical Reactions Collision theory - For a chemical reaction to occur, the reactant particles must collide. But collisions with too little energy do not produce a reaction. - The particles must have enough energy for the collision to be successful in producing a reaction. - The rate of reaction depends on the rate of successful collisions between reactant particles. The more successful collisions there are, the faster the rate of reaction Collision Theory (Youtube) Clip 11 Measuring the Rates of Chemical Reactions • Rate: Expressed as the amount of reactant 12 changing per unit of time. • What are some ways that you might be able to measure the rate of a reaction? – Amount of a product produced over time – Amount of reactant used up over time. Factors Affecting Reaction Rates 1. Temperature 2. Concentration 3. Particle Size (surface area) 4. Pressure 5. Catalysts (“the match maker”) 13 1-Temperature • Particles can only react when they collide. If you heat a substance, the particles move faster and so collide more frequently. That will speed up the rate of reaction. increase the temp, more molecules are able to move faster, so more of them will have the minimum energy for the reaction to take place. 14 2- Concentration • Increasing the concentration, increases the probability of a collision between reactant particles because there are more of them in the same volume and so increases the chance of a successful collision forming products. 15 3-Particle Size Smaller in size means larger in surface area and hence a faster rate of reaction. 16 No so fun fact: On Feb. 7, 2008 a huge explosion and fire occurred at the Imperial Sugar Refinery in Georgia, USA causing 14 deaths and seriously injuring 38 others. The explosion was caused by accumulated sugar dust in the packaging facility 17 4-Pressure • Increasing the pressure on a reaction involving reacting gases increases the rate of reaction. • Changing the pressure on a reaction which involves only solids or liquids has no effect on the rate. 5-Catalysts • A catalyst is a substance which speeds up a reaction, but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction. Increases the frequency of collisions Changes orientation of molecules Can reduce intramolecular forces within reactants 18 Activation Energy • To understand what catalysts do, we need to go back and talk about reactions and energy….. • Collisions only result in a reaction if the particles collide with enough energy to get the reaction started. – This minimum energy required is called the activation energy for the reaction. 19 Activation Energy • The minimum energy that colliding particles must have in order to react is called activation energy. – energy can be used to stretch, bend, and ultimately break bonds, leading to chemical reactions 20 Catalysts A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction by lowering its activation energy so more particles will have enough energy to react. 21 Catalysts Biological Catalyst: Enzymes Inorganic catalyst… Metals… . – Catalysts are not used up in the reaction. 22 Catalysts and Inhibitors Some reactions proceed too fast. • They can be slowed down by inhibitors. – EX: Preservatives in food 23 “Everyday examples of Rates of Reactions 1. Enzymes 2. Catalytic converters Catalytic converters change poisonous molecules like carbon monoxide and various nitrogen oxides in car exhausts into more harmless molecules like carbon dioxide and nitrogen. They use expensive metals like platinum, palladium and rhodium as the heterogeneous catalyst. The metals are deposited as thin layers onto a ceramic honeycomb. This maximises the surface area and keeps the amount of metal used to a minimum. Taking the reaction between carbon monoxide and nitrogen monoxide as typical: Reversibility of Reactions • Some reactions are reversible • Chemical Equilibrium – When the rates of the forward rxn and the reverse rxn are equal – Dynamic state • Rxn still continues to happen • Funny Review Clip