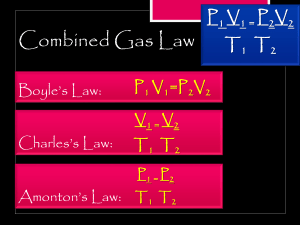
Gas Laws Worksheet Overview/Introduction In this assignment, you will perform calculations using the various gas laws. This will help you understand the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature in the gaseous state. Directions Complete the problems for each section. If you used steps to complete the calculations or determine the answer, please include them with your answer. All answers and work shown should be neat, clear, and legible. Equations 1 atm = 760.0 mmHg = 101.3 kPa = 14.7 lbs/in2 1 mole gas = 22.4 L at STP 1. If 34.7 L of nitrogen at 748 mmHg are compressed to 725 mmHg at constant temperature, what is the new volume of nitrogen? P1V1=P2V2 748mmHgx3.7L=725mmHgxV2 25955.6LxmmHg=725mmHgxV2 25955.6/725=V2 V2=35.800827 L 2. A gas with a volume of 5.0 L at a pressure of 210 kPa is allowed to expand to a volume of 12.0 L. What is the pressure in the container if the temperature remains constant? P1V1=P2V2 (same formula as Question 1) P2=87.5 kPa 3. A gas occupies 700.0 mL at a temperature of 27.0 °C. What is the volume of gas at 120.0 °C assuming pressure did not change? V1/T1=V2/T2 Convert units to Kelvin. 700mL/300K=V2/393K V2=917 mL 4. A container of 5.00 L of gas is collected at 93 K and then allowed to expand to 25.0 L. What must the new temperature be assuming pressure is constant? Using Charles’s Law again V1/T1=V2/T2 No need to convert units. T2=465 K 5. On a 26 °C summer day, the pressure in Tony Cousteau’s backup oxygen tank read 900 mmHg before he dove into the ocean. He dove to a depth where the temperature was -23 °C. What is the pressure in Jacques’s backup tank at that temperature? P1/T1=P2/T2 Convert C to Kelvins. P2= 752.51 mmHg 6. A paint spray can has a pressure of 30 lbs/in2 at a temperature of 27 °C. If the gasses in the can reach a pressure of 90 lbs/in2, the can will explode. What temperature must the gasses in the spray can be at in order for the spray can to explode? (Assume constant volume) P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 Volume is constant we can eliminate from the equation. Convert C to Kelvins, plug in and solve: 30 psi/300K=90 psi/T2 T2=627 C 7. What is the density of carbon monoxide at STP? CO is the formula. STP=Standard Temp and Pressure Temp=273.15 K Pressure=1 atm R=0.0821 Density =MP/RT M=Molar mass=28.01 g/mol 28.01 (g/mol) x 1 (atm)/0.0821 (Latm/molK) x 273.15 (K) =1.25 g/L 8. 50 g of nitrogen gas (N2) has a volume of ____ liters at STP. Set up equation for using Ideal Gas Law 50 g N2/1 X 1 mol N2/28 g X 22.4 L/1 mol Volume = 40 L 9. A gas is heated from 263.0 K to 298.0 K and the volume is increased from 24.0 liters to 35.0 liters by moving a large piston within a cylinder. If the original pressure was 1.00 atm, what would the final pressure be? Combined gas law P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 1x24/263=P2x35/298 P2=0.78 atm 10. A gas balloon has a volume of 90.0 liters when the temperature is 39 °C and the pressure is 740.0 mmHg. What would its volume be at 15.0 °C and 780.0 mmHg? Combined gas law P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 Convert temps to Kelvin by adding 273 and plug in all known values. V2=78.82 L