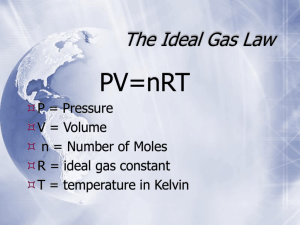
SCH 3U1 ... The volume of a gas depends upon: V
advertisement
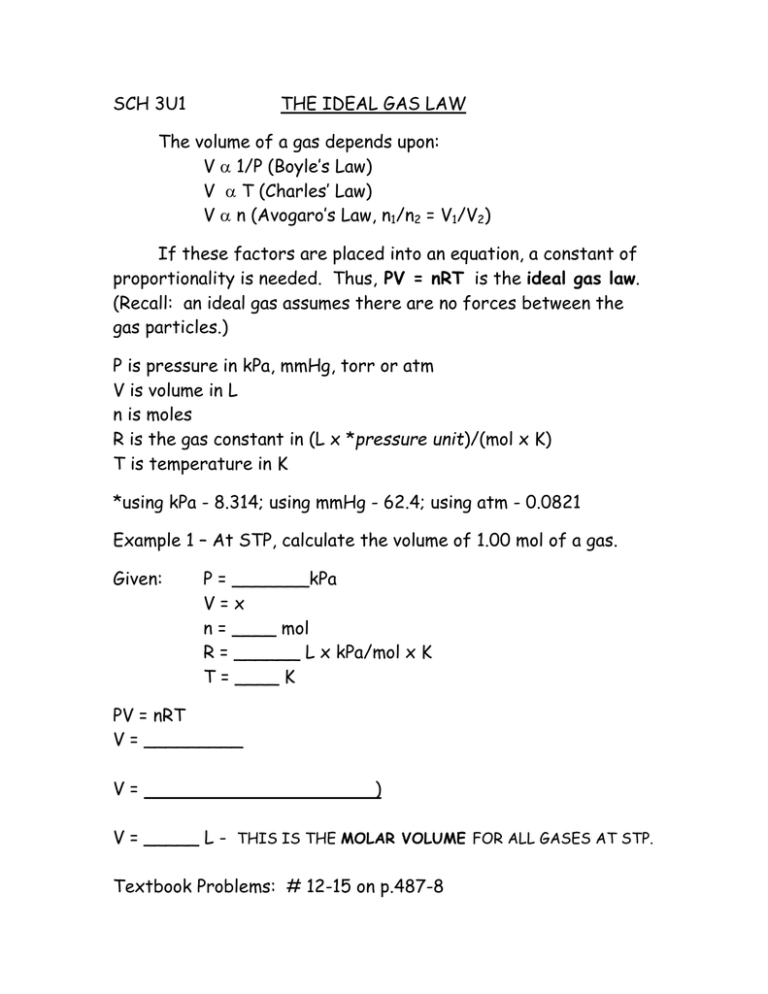
SCH 3U1 THE IDEAL GAS LAW The volume of a gas depends upon: V 1/P (Boyle’s Law) V T (Charles’ Law) V n (Avogaro’s Law, n1/n2 = V1/V2) If these factors are placed into an equation, a constant of proportionality is needed. Thus, PV = nRT is the ideal gas law. (Recall: an ideal gas assumes there are no forces between the gas particles.) P is pressure in kPa, mmHg, torr or atm V is volume in L n is moles R is the gas constant in (L x *pressure unit)/(mol x K) T is temperature in K *using kPa - 8.314; using mmHg - 62.4; using atm - 0.0821 Example 1 – At STP, calculate the volume of 1.00 mol of a gas. Given: P = _______kPa V=x n = ____ mol R = ______ L x kPa/mol x K T = ____ K PV = nRT V = _________ V= ) V = _____ L - THIS IS THE MOLAR VOLUME FOR ALL GASES AT STP. Textbook Problems: # 12-15 on p.487-8