Boyle*s Law
advertisement

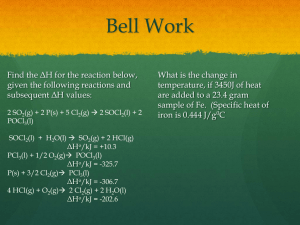
Dalton’s Law & Boyle’s Law Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure • The total pressure in a system is equal to the sum of the pressures of each gas inside. • Ptotal= P1 + P2 + P3 + …Pn Remember me? In a closed system, the partial pressures of three gases were 1.5 atm., 2.0 atm., and .75 atm. What is the pressure of the system? Ptotal= P1 +P2 + P3 Ptotal= 1.5atm + 2.0 atm + .75 atm Ptotal= 4.25atm In a closed system, there are four gases present. The pressure of the first gas is 796 mmHg. The Second gas has a pressure of 755 mmHg; and the third gas has a pressure of 760 mmHg. What is the pressure of the fourth gas if the total pressure of the system is 3000 mmHg? Ptotal= P1 +P2 + P3 + P4 3000mmHg= 796mmHg + 755mmHg + 760mmHg + P4 3000mmHg = 2311mmHg + P4 689mmHg= P4 Boyle’s Law • Pressure and volume have an inverse relationship • Can be explained with Kinetic Molecular Theory – Decreasing volume increases the number of molecules per unit volume, leading to more collisions P1V1= P2V2 • • • • P1 = initial pressure V1= initial volume P2= final pressure V2= final volume A sample of neon to be used in a neon sign has a volume of 1.51 L at a pressure of 635 torr. Calculate the volume of the gas after it is pumped into the glass tubes of the sign, where it shows a pressure of 785 torr. P1V1= P2V2 1.51x635= 785V2 958.85= 785V2 785 785 1.22L= V2 A sample of oxygen that occupies 1.00 × 106 mL at 575 mm Hg is subjected to a pressure of 1.25 atm. What will the final volume of the sample be if the temperature is held constant? 1atm= 760 mmHg P1V1= P2V2 760mmHg = 575mmHg 1atm x 0.76x1.00x106= 1.25V2 575= 760 x 760 760 0.76atm= x 7.60x105= 1.25V2 1.25 1.25 6.08x105 mL= V2 A gas has a pressure of 1.26 atm and occupies a volume of 7.40 L. If the gas is compressed to a volume of 2.93 L, what will its pressure be, assuming constant temperature? P1V1= P2V2 1.26x7.40= P2x2.93 9.32= P2x2.93 2.93 2.93 3.18L= V2