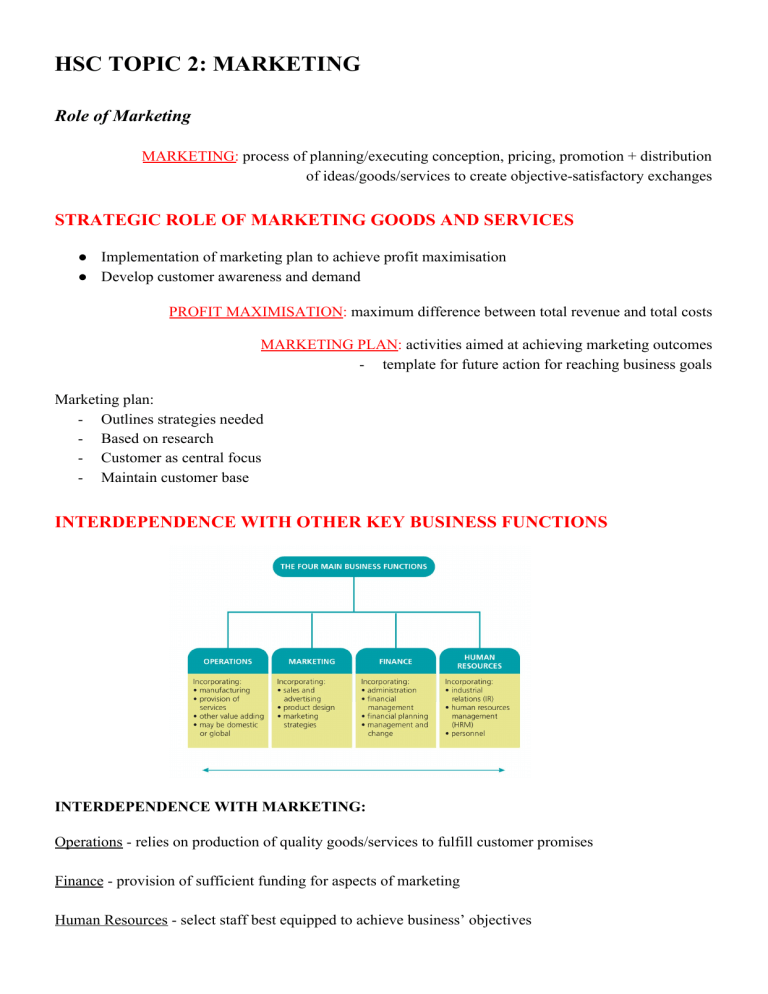
HSC TOPIC 2: MARKETING Role of Marketing MARKETING: process of planning/executing conception, pricing, promotion + distribution of ideas/goods/services to create objective-satisfactory exchanges STRATEGIC ROLE OF MARKETING GOODS AND SERVICES ● Implementation of marketing plan to achieve profit maximisation ● Develop customer awareness and demand PROFIT MAXIMISATION: maximum difference between total revenue and total costs MARKETING PLAN: activities aimed at achieving marketing outcomes - template for future action for reaching business goals Marketing plan: - Outlines strategies needed - Based on research - Customer as central focus - Maintain customer base INTERDEPENDENCE WITH OTHER KEY BUSINESS FUNCTIONS INTERDEPENDENCE WITH MARKETING: Operations - relies on production of quality goods/services to fulfill customer promises Finance - provision of sufficient funding for aspects of marketing Human Resources - select staff best equipped to achieve business’ objectives PRODUCTION, SELLING, MARKETING APPROACHES PRODUCTION APPROACH SALES APPROACH - 1820s - 1920s - 1920s - 1960s - Industrial Revolution - Emphasises selling - Focused on production - Increased competition → - Marketing = taking orders attempt to stimulate demand + delivering products - Marketing still secondary to production + finance MARKETING APPROACH - 1960s - present - Customer becomes focus - Market research - Stage two: adds CSR + relationship marketing - Customer orientation SELLING: activities undertaken to assist customer’s buying decisions CUSTOMER ORIENTATION: every aspect of business operations = aimed at achieving highest standards of customer service TYPES OF MARKETS RESOURCE ➢ Primary production (e.g. mining, agriculture) INTERMEDIATE ➢ Purchase finished products + resell to make profit MASS ➢ Mass-production, mass-distribution, mass-promotion (one product to all buyers) INDUSTRIAL ➢ Purchase products to use in further production CONSUMER ➢ Individuals who plan to use/consume products they buy NICHE ➢ Concentrated/micro market → narrow target market segment Influences on Marketing FACTORS INFLUENCING CUSTOMER CHOICE CUSTOMER CHOICE: (buying behaviour) decisions/actions of customer regarding evaluation/selection/purchase of goods/services PSYCHOLOGICAL ➔ Influences within affecting choice - Perception - Motives - Attitudes - Personality SOCIOCULTURAL ECONOMIC ➔ External influences by people/groups - Social class - Culture - Family - Friends ➔ Capacity to compete + customer’s to spend - Boom - Recession GOVERNMENT ➔ Policy measures - Economic policy - Laws/regulations (CCA 2010) - Regulatory bodies (ASIC + ACCC) CONSUMER LAWS ❖ Competition and Consumer Act 2010 (Cth) ➢ Replaced Trade Practices Act 1974 (Cth) ■ Protect consumers ■ Regulate trade practices that restrict competition Australian Competition and Consumer Commission UNCONSCIONABLE CONDUCT: practice by business deemed unreasonable (often illegal) DECEPTIVE AND MISLEADING ADVERTISING EXAMPLES: Fine print - important conditions written in small print → difficult to read Before and after advertisements - misleading comparison (distorted ‘before’, enhanced ‘after’) Tests and surveys - making unsubstantiated claims e.g. stating ‘9 out of 10 people’ without survey BAIT AND SWITCH ADVERTISING: advertising few products at reduced prices → ‘run out’ = directed to higher priced products DISHONEST ADVERTISING: claim product has quality it doesn’t have GREENWASHING: misleading/deceptive claims about environmental benefits of product PRICE DISCRIMINATION PRICE DISCRIMINATION: setting different prices in separate markets Possible due to: - Markets geographically separated (e.g. city vs country) - Product differentiation within one market (e.g. electricity prices for domestic/business users) ● Prohibited if substantially reduces competition ● Business cannot favour some customers over others IMPLIED CONDITIONS IMPLIED CONDITIONS: unspoken/unwritten terms of a contract CONSUMER GUARANTEES: comprehensive rights/remedies for defective goods/services ACCEPTABLE QUALITY: (‘merchantable quality’) product fit for purpose - safe, durable, no defects WARRANTIES WARRANTY: promise by business to repair/replace faulty products ● Clearly stated terms and conditions of warranty for product ● Business required by law to provide refund ○ If product is faulty ○ If product does not match description ○ If product fails to do job it is designed to do ETHICAL MATERIALISM: individual desire to constantly acquire possessions PRODUCT PLACEMENT: inclusion of advertising in entertainment 1. 2. 3. 4. Creation of needs → appeal to materialism Stereotypical images of males/females Use of sex to sell products → overuse of sexual themes/connotations Product placement → concealed nature TRUTH, ACCURACY AND GOOD TASTE IN ADVERTISING ADVERTISING: paid, non-personal message communicated through mass medium ● Untruths from concealed facts ○ Purposely omitted information → harms customer trust ● Exaggerated claims ○ Puffery → exaggerated praise (especially in promotions) that no one would take as factual ○ E.g. ‘$13 million lawsuit proves Red Bull doesn’t give you wings’ ● Vague statements ○ Ambiguous wording so customers assume intended message ○ E.g. ‘helps to …” ● Invasion of privacy ○ Data collection resold for target advertising purposes - Ad Standards - Ensure acceptable advertising standards are followed Dispute resolution mechanism (lacks authority to enforce guidelines) PRODUCTS THAT MAY DAMAGE HEALTH ● ‘Responsible Children’s Marketing Initiative’ ○ Fast food companies can advertise products to children that meet nutritional guidelines ● Digital advertising (e.g. Facebook, Twitter) of junk food to children ENGAGING IN FAIR COMPETITION CONSUMER EXPLOITATION: rights of consumers = ignored ● E.g. high pressure sales tactics ● Development + adoption of ethical marketing policy SUGGING SUGGING: selling under guise of a survey Marketing Process SITUATIONAL ANALYSIS SWOT PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE INTRODUCTION - Increase consumer awareness - Build market share - Product: brand established - Price: often lower than competitors - Promotion: directed at early buyers - Distribution: selective - GROWTH Pursuit of brand acceptance and market share Product: maintain quality Price: per unit maintained Promotion: seek wider audience Distribution: channels increased MATURITY Sales plateau Market saturated Product: try to differentiate - Price: may go down - Promotion: continue quality image - Distribution: offer incentives - - DECLINE Sales decline Business faces options Product: maintained with improvements Price: reduced Promotion: discontinued Distribution: channels reduced MARKET RESEARCH MARKET RESEARCH: process of systematically collecting/recording/analysing information of specific marketing problem ● Information about needs and wants of consumers Steps of market research process: 1. Determine information needs → relevant to issue/problem 2. Collect data from primary/secondary sources 3. Analyse/interpret data MARKETING DATA: information relevant to defined marketing problem PRIMARY DATA: facts/figures collected from original sources for purpose of problem SECONDARY DATA: already collected by other person/organisation Gathering primary data: 1. Survey method 2. Observation method 3. Experiment method (test marketing) Secondary data: - Types of secondary data - Internal data: already collected inside of business - External data: published data outside business - E.g. census data, household surveys - Gathered by government + private organisations STATISTICAL INTERPRETATION ANALYSIS: focusing on data representing average or deviations from patterns ESTABLISHING MARKET OBJECTIVES MARKETING OBJECTIVES: realistic/measurable goals achieved through marketing plan 1. Increasing market share 2. Expanding product mix 3. Maximising customer service PRODUCT MIX: total range of products offered by business ● E.g. QANTAS/Jetstar combined goal to maintain domestic market share of 63% IDENTIFYING TARGET MARKETS TARGET MARKET: present + potential customers business intends to sell to PRIMARY TARGET MARKET: market segment most of marketing resources are directed SECONDARY TARGET MARKET: smaller/less important market segment ● Mass marketing approach → large range of customers ● Market segmentation approach → total market divided into groups with common characteristics ● Niche market approach → narrowly selected customer base DEVELOPING MARKETING STRATEGIES MARKETING STRATEGY: actions to achieve marketing objectives - Through marketing mix EMPHASIS ON MARKETING MIX | PRODUCT PRICE PROMOTION DISTRIBUTION Outcomes: ● Efficiency ○ Cost effective + time efficient ● Effectiveness ○ Tailoring to customer needs more effectively ● Specificity ○ Develop understanding of buying behaviours + needs of target market segment IMPLEMENTATION, MONITORING AND CONTROLLING IMPLEMENTATION: putting strategies into operation - Daily, weekly, monthly decisions Implementation questions: - Plan integrated with all other sections of business? - Effective lines of communication (marketing + other dep.)? - Best people for tasks needed? - Employees familiar with objectives + strategies? MONITORING: checking/observing actual progress of marketing plan ➔ Market share analysis/ratios - strategy effectiveness to competitors + effect of external factors CONTROLLING: marketing plan revised through corrective action to achieve objectives DEVELOPING A FINANCIAL FORECAST - Costs + revenues for each strategy - Measuring sales potential + revenue forecasts - Comparing against anticipated expenditure (cost-benefit analysis) COMPARING ACTUAL AND PLANNED RESULTS - Key performance indicators - Sales analysis - Market share analysis → evaluate strategies compared to competitors - Marketing profitability analysis SALES ANALYSIS: comparing actual sales with forecast sales MARKETING PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS: business breaks down total marketing costs into specific activities REVISING THE MARKETING STRATEGY - Based on findings - Whether marketing plan needs to be revised/modified - Changes in marketing mix - Product → continually upgrade for competitive advantage - Price → fluctuate according to external business environment - Promotion → change according to product life cycle - Place → expand distribution channels for growing market - New product development (natural life span of product = 5-10 years) - Product deletion → when outdated, in decline stage Marketing Strategies MARKET SEGMENTATION, PRODUCT/SERVICE DIFFERENTIATION AND POSITIONING MARKET SEGMENTATION: dividing into specific segments - aiming to increase sales, market share + profits DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION: dividing according to features of population - occupation, age, sex, income, cultural background GEOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION: dividing according to geographic location - climate, city, rural PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION: dividing according to personality characteristics - motives, opinions, socioeconomic aims, lifestyle BEHAVIOURAL SEGMENTATION: dividing according to customer relationship with product - purchasing habits, users/non-users, heavy/moderate/light PRODUCT/SERVICE DIFFERENTIATION: developing/promoting differences between competitors - e.g. adopting ‘green’ philosophy, customer service PRODUCT/SERVICE POSITIONING: create image/identity compared to competitors - e.g. Ferrari = high socioeconomic value PRODUCTS - GOODS AND/OR SERVICES PRODUCT: good/service offered in exchange for satisfying need/want BRANDING BRANDING: name, term, symbol, design identifying specific product Allows customers to: - Identify liked products - Evaluate quality of product - Reduce level of perceived risk Allows businesses to: - Gain repeat sales - Introduce new products customers trust - Create reputation PRIVATE/HOUSE BRAND: owned by retailer/wholesaler GENERIC BRAND: no brand name at all PACKAGING ● ● ● ● ● ● Preserves product Protects from damage/tampering Attracts attention Divides into units Assists display Makes transportation/storage easier PRICE - INCLUDING PRICING METHODS PRICE: amount of money customer is prepared to offer in exchange for product COST-BASED PRICING: cost of producing/purchasing + markup MARKET-BASED PRICING: according to interaction between levels of supply/demand ● High supply = drop price ● Low supply = raise price ● High demand = raise price ● Low demand = drop price COMPETITION-BASED PRICING: cover costs + compare to competitor’s price - Below competitor → undercut competition Equal to competitor → follow established price leader Above competitor → for consumers to perceive superiority PRICING STRATEGIES PRICE SKIMMING: charging highest possible price during introduction PRICE PENETRATION: lowest price possible to quickly increase market share LOSS LEADER: sold at/below cost price (hope made up for with other purchases) PRICE POINTS: selling at predetermined prices PRICE AND QUALITY INTERACTION ● General assumption ● Better quality products = more expensive/lower quality products = cheaper PROMOTION PROMOTION: methods used to inform/persuade/remind target market about products ● ● ● ● Attract new customers Increase brand loyalty Reinforce brand image Encourage existing customers to purchase more ELEMENTS OF THE PROMOTION MIX ADVERTISING ADVERTISING: paid, non personal message communicated through mass medium E.g. TV advert, leaflets, posters SALES PROMOTIONS SALES PROMOTION: use of activities/materials as direct inducement E.g. coupons, premiums, refunds PERSONAL SELLING AND RELATIONSHIP MARKETING PERSONAL SELLING: activities of sales representative directed to customer RELATIONSHIP MARKETING: development of long term, cost-effective relationships with customers E.g. reward/loyalty programs PUBLICITY AND PUBLIC RELATIONS PUBLICITY: free news story about product PUBLIC RELATIONS: creating/maintaining favourable relations E.g. speeches, attention-seeking gestures THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS OPINION LEADERS ● Person who influences others (actors, athletes, musicians) WORD OF MOUTH ● Influence through personal conversations PLACE/DISTRIBUTION PLACE: make products available to customers + where they want to purchase from DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS: routes taken to get product from business to customer 1. 2. 3. 4. Producer → customer Producer → retailer → customer Producer → wholesaler → retailer → customer Producer → agent → wholesaler → retailer → customer NON-STORE RETAILING: conducted away from store - e.g. e-marketing CHANNEL CHOICE INTENSIVE DISTRIBUTION: saturate market with product (sold everywhere) SELECTIVE DISTRIBUTION: moderate proportion of outlets EXCLUSIVE DISTRIBUTION: use only one retail outlet in large area PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION ISSUES TRANSPORT: rail, road, sea, air WAREHOUSING: central organising point for delivery INVENTORY: high stock = high cost PEOPLE, PROCESSES AND PHYSICAL EVIDENCE 1. People → quality of interaction between customer and business 2. Processes → flow of activities that business follows in delivery of service 3. Physical Evidence → environment that service will be delivered + materials needed E-MARKETING E-MARKETING: using internet for marketing activites ● E.g. web pages, podcasts, SMS, blogs ● Social media advertising GLOBAL MARKETING ● Marketing plans must adapt to suit overseas markets GLOBAL BRANDING GLOBAL BRANDING: worldwide use of name/term/symbol/logo to identify seller ● Cost effective ● Uniform worldwide image ● Successful brand name linked to new products STANDARDISATION ● Global marketing strategy ● The way product is used + needs it satisfies = same worldwide ● Marketing mix = similar/identical worldwide CUSTOMISATION ● Global marketing strategy ● Local approach → way product is used + needs it satisfies = different between countries ● Marketing mix varies greatly worldwide GLOBAL PRICING GLOBAL PRICING: how businesses coordinate pricing policy across different countries CUSTOMISED PRICING: consumers in different countries charged different prices for same product - cost-plus method → cover added costs of exportation (taxes, tariffs) MARKET CUSTOMISED PRICING: prices according to local market conditions COMPETITIVE POSITIONING COMPETITIVE POSITIONING: how business differentiates product ● ● ● ● Avoid competing only on price Develop product leadership Create positive customer relationships Sustain operational excellence