Personality Theories: Psychodynamic, Humanistic, Trait, Biological
advertisement

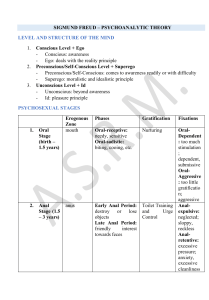
INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A THEORY? A set of related assumptions that allows scientist to use logical deductive reasoning to formulated testable hypothesis. Not a fact or truth but accepted as if it is. FIVE MAJOR THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVE 1. P SY C HO DY N AM IC P r i ma r y A s s u mp t i o n s First 5 years of life most shape personality. Unconscious forces are most important. Neurosis result from unhealthy moving toward, against, or away from others. Focus/Key Terms: Unconscious Early recollections Collective Unconscious Archetypes Object-relations Identity Crises Relatedness Key Figures: Sigmund Freud Alfred Adler Carl Jung Melanie Klein Karen Horney Erick Erikson Erich Fromm 2. HUM AN I ST IC - EX I ST E NT I AL P r i ma r y A s s u mp t i o n s People strive to live meaningful, happy lives People are motivated by growth and psychological health Personality is shaped by freedom of choice, response to anxiety, and awareness of death. Focus/Key Terms: Meaningful life Psychological Well-being and growth Key Figures: Abraham Maslow Carl Rogers Rollo Reese May 3. DI S PO SIT IO N AL / T R AIT P r i ma r y A s s u mp t i o n s People are predisposed to behave in unique and consistent ways; they have unique traits There are five trait dimensions in human personality Focus/Key Terms: Traits Motives Key Figures: 4. Gordon Allport Raymond Cattell Robert McCrae Paul Costa B I O L O G I C AL - E V O L U T I O N A R Y P r i ma r y A s s u mp t i o n s The foundation of thought and behavior is biological and genetic forces. Human thought and behavior have been shaped by evolutionary forces (natural and sexual selection) Focus/Key Terms: Brain structures, neurochemicals and genes Adaptive mechanism Key Figures: Hans Eysenck David Buss