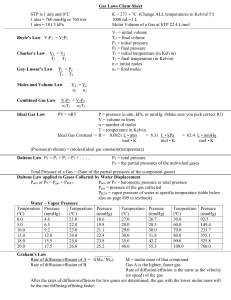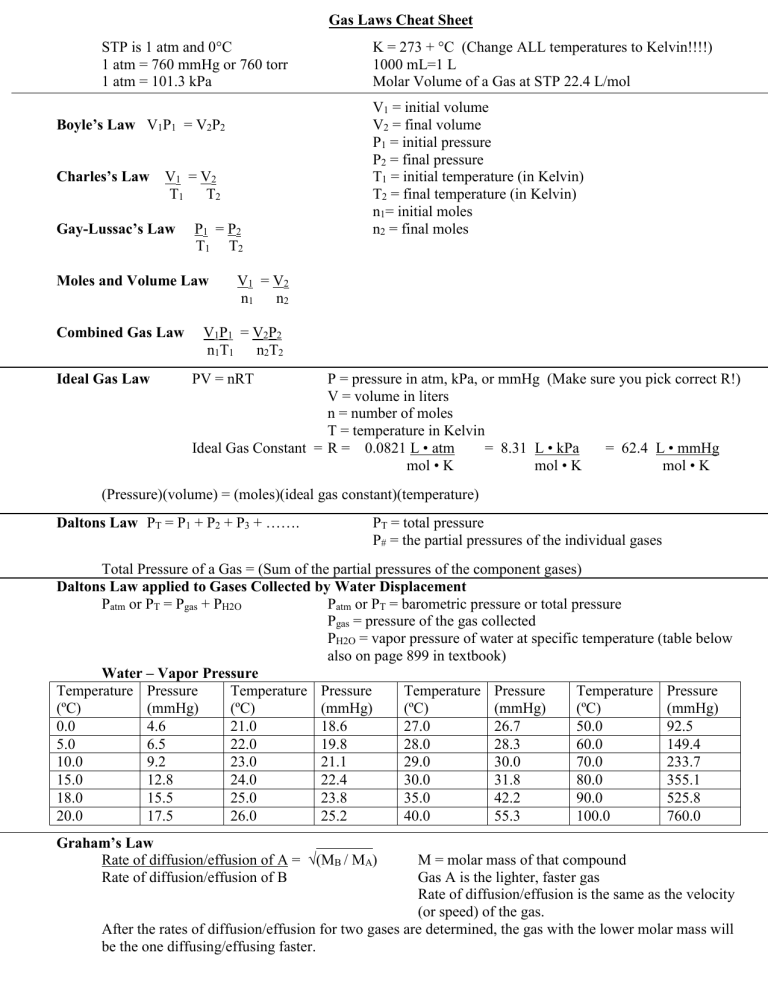
Gas Laws Cheat Sheet STP is 1 atm and 0C 1 atm = 760 mmHg or 760 torr 1 atm = 101.3 kPa Boyle’s Law V1P1 = V2P2 Charles’s Law V1 = V2 T1 T2 Gay-Lussac’s Law P1 = P2 T1 T2 Moles and Volume Law Combined Gas Law Ideal Gas Law K = 273 + C (Change ALL temperatures to Kelvin!!!!) 1000 mL=1 L Molar Volume of a Gas at STP 22.4 L/mol V1 = initial volume V2 = final volume P1 = initial pressure P2 = final pressure T1 = initial temperature (in Kelvin) T2 = final temperature (in Kelvin) n1= initial moles n2 = final moles V1 = V2 n1 n2 V1P1 = V2P2 n1T1 n2T2 PV = nRT P = pressure in atm, kPa, or mmHg (Make sure you pick correct R!) V = volume in liters n = number of moles T = temperature in Kelvin Ideal Gas Constant = R = 0.0821 L • atm = 8.31 L • kPa = 62.4 L • mmHg mol • K mol • K mol • K (Pressure)(volume) = (moles)(ideal gas constant)(temperature) Daltons Law PT = P1 + P2 + P3 + ……. PT = total pressure P# = the partial pressures of the individual gases Total Pressure of a Gas = (Sum of the partial pressures of the component gases) Daltons Law applied to Gases Collected by Water Displacement Patm or PT = Pgas + PH2O Patm or PT = barometric pressure or total pressure Pgas = pressure of the gas collected PH2O = vapor pressure of water at specific temperature (table below also on page 899 in textbook) Water – Vapor Pressure Temperature Pressure Temperature Pressure Temperature Pressure Temperature Pressure (ºC) (mmHg) (ºC) (mmHg) (ºC) (mmHg) (ºC) (mmHg) 0.0 4.6 21.0 18.6 27.0 26.7 50.0 92.5 5.0 6.5 22.0 19.8 28.0 28.3 60.0 149.4 10.0 9.2 23.0 21.1 29.0 30.0 70.0 233.7 15.0 12.8 24.0 22.4 30.0 31.8 80.0 355.1 18.0 15.5 25.0 23.8 35.0 42.2 90.0 525.8 20.0 17.5 26.0 25.2 40.0 55.3 100.0 760.0 Graham’s Law Rate of diffusion/effusion of A = √(MB / MA) Rate of diffusion/effusion of B M = molar mass of that compound Gas A is the lighter, faster gas Rate of diffusion/effusion is the same as the velocity (or speed) of the gas. After the rates of diffusion/effusion for two gases are determined, the gas with the lower molar mass will be the one diffusing/effusing faster.