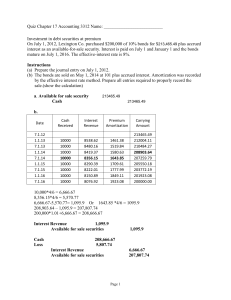
MODULE OF INSTRUCTION Module 1 Introduction to Business Finance Welcome to the first module of Business Finance. Are you excited to learn things about finance? Let’s first tackle the basic concepts. In this lesson you should be able to Business Finance Explain the major role of financial management and the different individuals involved Enumerate the various functions of the Financial Manager Compare and contrast the basic types of financial instruments Distinguish a financial institution from financial market Classify institutions as banking and non-banking financial institutions Enumerate and distinguish the different types of financial institutions and financial markets Explain the flow of funds 1 X.X Business Finance 1.1 Definition of Business Finance Finance is the art and science that describes the management, creation and study of money, banking, credit, investments, assets and liabilities. Finance is needed in business because financing decisions often involve large financial amounts that are very significant to the business and once made, such decision is not easily reversed. Financial management decision function includes areas such as investment, financing, and asset management decisions. 1.2 Objectives of Financial Management The goals of business finance may be broadly divided into two parts which includes profit maximization and wealth maximization. Profit Maximization The main aim of any kind of economic activity is to earn profit. When we say profit, we usually refer to the financial benefit that is realized when the amount of revenue gained from a business activity exceeds the expenses, costs and taxes needed to sustain the activity. Profit maximization is a traditional and narrow approach where business entities determine the best output and price levels in order to maximize its return. The company will usually adjust influential factors such as production costs, sale prices, and output levels as a way of reaching its profit goal. Wealth Maximization Wealth maximization is a modern concept which deals with the increase of the value of a business in order to increase the share of stockholders or the owners. It is widely accepted as the ultimate goal of a business. The concept requires the management team to continually search for the highest possible returns on funds invested in the business, while mitigating any associated risk of loss. This calls for a detailed analysis of the cash flows associated with each prospective investment, as well as constant attention to the strategic direction of the organization. 2 MODULE OF INSTRUCTION 1.3 Key Individuals in Business Finance In a typical business organization, there are three key role players in financial management. They are the financial manager, the controller and the treasurer. Financial Manager- he is in charge of the overall finance functions of a business. He develops strategies and plans to achieve the financial goals of the organization. In large companies, this position is usually termed as Chief Financial Officer. The financial manager is to whom the controller and the treasurer reports. Controller – he is the one responsible for managing the accounting staff that provides managerial accounting information used for internal decision making, financial accounting information for external reporting purposes, and tax accounting information to meet tax filing requirements. The controller is usually the head accountant of the company. Treasurer- his primary duties include asset safekeeping and cash management. He is also responsible for obtaining investment capital as well as obtaining loans and credit from outside sources. 1.4 Functions of Financial Manager The finance manager plays a very big role in the finance function which requires him to have possessed knowledge in the area of accounting, finance, economics and management. He is responsible for the performance of the accountant and the treasurer since he is the head of that department. His position is highly critical and analytical to solve various problems related to finance. He performs the following major functions Forecasting Financial Requirements The financial manager is responsible to estimate the financial requirement of the business. He the one who should estimate how much resources are required to acquire fixed assets and forecast the amount needed in order to have a continuous business operation. Business Finance 3 X.X Business Finance Acquiring Necessary Capital Financial managers are also in charge of the acquisition of the necessary capital to be used in the business. He should concentrate on how, where and when to obtain finances. Investment Decision The finance manager must carefully select best investment alternatives and consider the reasonable and stable return from the investment. He must be well versed in the field of capital budgeting techniques to determine the effective utilization of investment. The finance manager must concentrate to principles of safety, liquidity and profitability while investing capital. Cash Management The financial manager must see to it that the entity has enough cash for its business operations as well as for the payment of debts or liabilities. Furthermore this deals with the proper management of cash on hand and cash in bank. Interrelation with Other Departments The finance manager must maintain a good relationship with all the functional departments of the business organization. He should have sound knowledge not only in finance related area but also in other areas as well. 4 MODULE OF INSTRUCTION 1.5 The Financial System Financial System is a framework which collectively describes the financial markets, financial institutions, borrowers and lenders within the economy. The functions of the financial system is to channel the funds from lenders to the borrowers, provide a medium of exchange, provide a mechanism for risk sharing and provide a channel through which the central bank can influence the economy. Financial Instruments These things are crucial to the operation of the economy. A financial instrument is the written legal obligation of one party to transfer a thing of value, usually money, to another party at some future date, under certain conditions. According to the Philippine Accounting Standards 32, a financial instrument is any contract that gives rise to both a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity. With this definition, we can also consider currency bills and coins as financial instruments because they are financial assets of the person holding the money and a financial liability of the government issuing it. In business, when we say financial instruments, we basically refer to stocks bonds and notes. Stocks This is a type of security that signifies ownership in a corporation and represents a claim on part of the corporation's assets and earnings. Stocks are issued by companies in order to raise funds for the business. Generally, this can be classified as common and preferred stock. This is a financial asset of the stockholder and an equity instrument of the issuing company. Bonds A bond is a debt security in which an investor lends his money to an entity which borrows the funds for a defined period of time at defined interest rate. Bonds are usually issued by companies, municipalities, states and sovereign governments to raise money and finance their economic activities. A bond is a financial asset of the investor – reflected as Bonds Receivable and a financial liability of the issuing company –reflected as Bonds-Payable. Notes This is a debt security obligating repayment of a loan with a corresponding interest within a defined period of time. Notes are being issued by the borrower to signify its indebtedness. A note is the Business Finance 5 X.X Business Finance financial liability of the debtor - reflected as Notes Payable and a financial asset of the creditor - reflected as Notes Receivable. Financial Markets A financial market is where stocks, bonds and other financial securities can be purchased or sold. Funds are transferred in financial markets when one party purchases financial assets previously held by another party. Financial markets facilitate the flow of funds and thereby allow financing and investing by households, firms, and government agencies. Financial markets may be classified into two namely the money market and the capital market. The money market is where debt securities with an original maturity of one year or less are traded as well as long-term securities having at least six months left to maturity. The capital market is where securities with maturity of more than one year are traded. The capital market is subdivided into bond market, stock market and mortgage market. Some financial markets may exist but have few activities. In the country, the large financial markets are those being regulated by the Banko Sentral ng Pilipinas. These are the foreign exchange market, the fixed income exchange market and the stock market. The BSP upholds and maintains the efficient and safe operations of these financial markets. Foreign Exchange Market In the country, the Foreign Exchange is where participants can be able to buy, sell, exchange and speculate on currencies. The BSP maintains a floating exchange rate system. Exchange rates are determined on the basis of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. The role of the BSP in the foreign exchange market is principally to ensure orderly conditions in the market. The market-determination of the exchange rate is consistent with the Government’s commitment to market-oriented reforms and outward-looking strategies of achieving competitiveness through price stability and efficiency. Fixed Income Exchange Market The Fixed Income Exchange is the country’s first centralized electronic infrastructure for trading of fixed-income securities. The FIE is a comprehensive financial market infrastructure that aims to provide an electronic platform for trading, clearing and settlement, and 6 MODULE OF INSTRUCTION depository and custodianship fixed-income securities and its derivatives. When we say fixed-income securities, these are investments that provide return in the form of fixed periodic payments and the eventual return of principal at maturity. This may include treasury bonds and certificate of deposits. Stock Market The Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) is a private organization created to provide and maintain a fair, efficient, transparent and orderly market for the purchase and sale of stocks and other securities. Financial Intermediaries A financial intermediary is an entity that acts as the middleman between two parties in a financial transaction. Financial intermediaries are businesses which move money from the individual into the markets. With this statement, we can say that those who are borrowing in financial intermediaries are said to be engaged in indirect financing. Financial institutions are considered as the financial intermediaries. A financial institution is an establishment that provides financial services such as investments, loans and deposits. Typically, these are the key entities that control the flow of money in the economy. Financial institutions may either be a banking institution or nonbanking institution. Banking Institutions A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates credit which is being supervised by a regulatory agency. Commercial Bank This is a financial institution that provides various financial services, such as accepting deposits, offering savings and checking account services, and issuing loans for both private individuals and businesses. Furthermore, it may also provide safety deposit boxes, mortgages, debit and credit cards, automated teller machines, online banking and other financial services. A commercial bank also has the power to accept drafts and issue letters of credit; discount and negotiate promissory notes, drafts, bills of exchange, and other evidences of debt; accept or create demand deposits; receive other types of deposits and deposit substitutes; buy and sell foreign exchange and gold or Business Finance 7 X.X Business Finance silver bullion; acquire marketable bonds and other debt securities; and extend credit. Investment Banks Unlike commercial banks, investment banks do not take deposits. Their focus is assisting individuals, corporations, and governments in raising capital by underwriting or acting as the client's agent in the issuance of securities. An investment bank may also assist companies involved in mergers and acquisitions. Non-Banking Financial Institutions A non-banking financial institution is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by a national or international banking regulatory agency. Credit Unions These are non-profit financial cooperatives owned by and operated for the benefit of its members. These member-owned financial cooperatives are democratically controlled by its members, and operated for the purpose of offering its members economical financial services. Membership is available through affiliation with an employer, a union, religious organization, community organization, or some other group. Savings and Loan Associations These are also known as thrift banks, these are financial institutions that specialize in savings type deposits, mortgages and other loans. They provide dividends to their depositors. Today savings and loan associations offer most of the services commercial banks do. They can also serve both consumers and businesses. However, by law, they can have no more than twenty percent of their lending in commercial loans. Insurance Companies These are corporate entities that insure people against loss. The client pays a fee, known as a premium, in exchange for the promise of the company to protect the client financially in the event of certain potential misfortunes. The common types of insurance include health, life and property insurances. 8 MODULE OF INSTRUCTION 1.6 Flow of Funds The figure below shows how the funds flow from the participants in the financial system. As you can see we have the direct and the indirect finance. In indirect finance, a financial institution stands between lender and borrower. For example, a bank receives money from its savers or depositors. The bank has now the money on hand. Then, a spender decides to borrow funds from the bank to buy a car. The bank lends out the money of the saver to a borrower. In direct finance, the borrowers sell securities directly to lenders in the financial markets. There are no intermediaries involved. For example a corporation offers its stocks to the stock exchange and the investor acquires it by paying the required amount. In exchange of the corporation issues a stock certificate to the investor which is now considered as the stockholder. Business Finance 9 X.X Business Finance Glossary Financial Manager- the one in charge of all the organization’s finance and accounting functions and typically reports to the chief executive officer. Controller –the one responsible for managing the accounting staff that provides managerial accounting information used for internal decision making, financial accounting information for external reporting purposes, and tax accounting information to meet tax filing requirements. Finance - is the art and science that describes the management, creation and study of money, banking, credit, investments, assets and liabilities Financial institution is an establishment that provides financial services such as investments, loans and deposits. Financial market – this is where financial securities such as stocks and bonds can be purchased or sold. Financial system - a framework for describing set of markets, organizations, and individuals that engage in the transaction of financial instruments, as well as regulatory institutions. Profit – the difference between income and expenses Treasurer- the one responsible for obtaining sources of financing for the organization, projecting cash flow needs, and managing cash and short-term investments. Wealth – the true value or net worth of business References C. Paramasivan and T. Subramanian. (2005). “Financial Management”, New Age International Ltd., Publishers. J. Van Horne and J. Wachowics (2008). “Fundamentals of Financial Management”, Pearson Education Limited. Investopedia, (2016). 10 MODULE OF INSTRUCTION Supplemental Resources Videos The American Dream (2011), “Understanding Money and the Banking System”, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k6zpfE7WjHI Oracle (2015). “Modern Finance in Digital Age” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=saijnZMQueo Oracle (2015). “A Day in the Life of A Modern CFO”, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X-U9RTt4x-o Online Readings Investopedia (2016). “Finance”. http://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/finance.asp S. Chand (2015). “Difference Between Profit Maximization and Wealth Maximization”, http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/difference/difference-betweenprofit-maximization-and-wealth-maximization-financialmanagement/29378/ Investopedia (2015). “Types Of Financial Institutions And Their Roles”, http://www.investopedia.com/walkthrough/corporatefinance/1/financial-institutions.aspx Business Finance 11