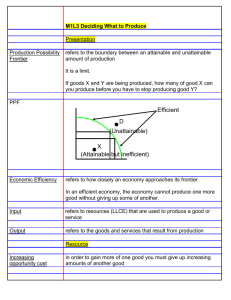
lOMoARcPSD|20901920 Econ C.2 PPF - Textbook notes Principles Economics (Tufts University) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Hoàng TRí (trihoang1510@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20901920 Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) ● Shows maximum output allocation society can produce by given technology and input of resources ● Assumptions of PPF ○ 1. Society only produces two outputs ○ 2. There is only one input ○ 3. Technology is fixed ○ 4. Individual workers are identical in skill, education, and ability ● Productivity measures: ratio of how much input is put in in order to yield an output ○ Use this to find amount of output produced when given amount of input ● Y-axis good #1 v. x-axis good #2 ○ Points of PPF are efficient b/c this means society is fully utilizing resources to produce goods ○ Points under PPF curve are possible but inefficient b/c not fully utilizing resources ■ I.e unemployment ○ Points above PPF curve are not possible because this amount of output requires more input that exceed society’s current avaliable resources ● Calculate Whether a Point is Possible on PPF ○ 1. Identify coordinates of point (x,y) ○ 2. Use equation (x)(productivity measure good #1) + (y)(productivity measure good #2) = total input ● ● ■ x is amount of output of good #1 ■ y is amount of output of good #2 ○ If value is less than or equal to total input, then it is possible Slope of PPF represents opportunity cost of shifting resource for one good in order to gain a quantity of another good ■ b/c resources are limited in the society —> scarcity ○ This represents there is a tradeoff when producing more goods b/c give up another good ○ Opportunity cost of good #1 and good #2 are inverses ■ Original slope is opportunity cost of good #1 is (##quantity) of good #2 ● This means in order to produce one more of good one, z more of good #2 is sacrificed ■ Inverse of original slope is opportunity cost of good #2 is (##quantity) of good #1 ● This means in order to produce one more of good two, z more of good #1 is sacrificed PPF line shifts outward in times of economic growth ○ Includes additional resources or input value and improvement in technology, ○ Points may shift inside our onto PPF when decreased unemployment ■ Decrease in unemployment itself doesn’t shift the curve out. It may shift points from under PPF to on PPF b/c now fully utilizing resources ○ In either industries will increase production of PPF ○ When assumption #2 no longer holds Downloaded by Hoàng TRí (trihoang1510@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20901920 ● Shape of PPF ○ Linear— constant opportunity cost ○ Bowed outward— increasing opportunity cost ■ b/c slope of tangent becomes larger ■ A.k.a opportunity cost for producing good #1 becomes greater because more resources of good #2 is being shifted ○ PFF bowed outwards when… ■ 1. Different workers have different skills ■ 2. Different opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of the other ■ 3. There’s a mix of resources with varying opporunity cost ○ When there is better technology in only one industry, that ONLY end of PPF will shift up or right ■ There’s a shift because improved technology allowed less labor hours with the same resulting output Downloaded by Hoàng TRí (trihoang1510@gmail.com)