
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
CORROSION # 1
Important Points
Galvanic list
etihparG
tiaairar
ravlGt
022 aekGv
dGiL
rehhGt
naa
eliis lliM
liioss oMMiswoL
elits oMMi
milAlmllA
clml
eMiml llA
+ 0.25v
0.0 v
- 0.1 v
- 0.15 v
- 0.2 v
- 0.35 v
- 0.35 v
- 0.4 v
- 0.7 v
- 0.7 v
- 0.9 v
- 1.0 v
- 1.6 v
More noble metals
Less noble metal
Factors that influence the rate of corrosion as follows.
1. Variation in oxygen content on the steel surface (wet/dry)
2. R.H % (Above 60% is critical)
3. Presence of impurities in the air (acid, alkalis, salt etc.)
4. Higher nobility metals in contact with the steel. (Mill scale)
1|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
Corrosion is defined as
a) Rusting of Cathode
b) Oxidation of iron in contact with water
c) Degradation of a material by chemical or electrochemical means
d) Breakdown of metal by hydrogen
2.
What is an electrolyte?
a) It is a mixture of Salts and water
b) A substance which will conduct electricity and cause rusting
c) Oxidation liquid which will attack steel.
d) A substance which will conduct a current and be broken down by it.
3.
The degradation of material by chemical or electrochemical means is
a) Pickling followed by passivation
b) Acid cleaning
c) Corrosion
d) An Electrolyte
4.
Is the electrical circuit in a corrosion reaction?
a)AC
b)DC
c) Negative charge
d) Positive charge
5.
Hydrogen is evolved at
a) The anode at all times.
b) The Cathode at all times.
c) The cathode as a byproduct of the corrosion reaction
d) The Anode as corrosion takes place
6.
Positively charged area
a) Anode
b) Cathode
c) Electrolyte
d) Electron
2|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Negatively charged area
a) Anode
b) Cathode
c) Electrolyte
d) Electron
8.
What are three elements needed for corrosion to occur?
a) Hydrogen, Oxygen, Water
b) Electron, Proton, Neutron
c) Anode, Cathode, Electrolyte
d) Temperature, Salt, Acid
9.
Water will be drawn through the film and the resulting solution builds up a pressure under the
film forced to form
a) Blister
b) Micron
c) Sulphates
d) Chloride
10.
Hygroscopic blisters are called
a) Sulphates
b) Chlorides
c) Pinhead size water filled
d) Corrosion
11.
Presence of oxygen into the Cathodic reaction the Number of Hydroxyl ions doubles
a) Sulphates
b) Double the corrosion rate
c) Pinhead size water filled
d) Corrosion not occur
12.
Another name for the Galvanic List, is
a) The Corrosion list
b) Electro Negative List
c) Electrical Corrosive properties series
d) Electromotive Forces Series
3|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
Two examples of hygroscopic salts would be
a) Iron phosphates and Iron Chromates
b) Iron Chordates and Iron Oxides
c) Iron Sulphates and Iron Chlorides
d) Iron Sulphates and Iron Silicates
14.
If Zinc and Aluminium were in close contacts, in the presence or electrolyte
a) Aluminium would corrode
b) They would corrode equally.
c) Zinc would corrode
d) None of the above
15.
MEM’s are also known as
a) Moisture Enriched Mat2erials
b) Metal Eating Microbes
c) Maximum Evolved Moistures
d) Material Electron Mobility
16.
SRB’s are also known as
a) Salts Reducing Bacteria
b) Substrate Reducing Bacteria
c) Solid Reducing Bacteria
d) Sulphur Reducing Bacteria
17.
The factors which can affect the rate corrosion are
a) Temperature, Time and Coating system
b) Bi-Metallic contact, Hygroscopic Salts and Bacteria
c) Coating system, Pipe diameter and Ultra Violet Light
d) Blasting Grades, Rust Grades and surface profile
18.
The thickness of Mill scale is
a) 25 m to 100 m
b) 100 to 150 m
c) Zero
d) Dependent upon the material thickness
4|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
The three compressed oxides which from Mill scale are
a) Iron Oxide, Rust and Iron Sulphate
b) Wusite (FeO), Hematite (Fe3O4) and Magnetite (Fe2O3)
c) Iron sulphate, Iron Chloride and Iron Phosphate
d) RSC, RSJ and RSA
20.
Name of sub atomic particles
a) Proton, Neutron, Electron
b) Micron, poron, Moron
c) Wusite, Hematite and Magnetite
d) Anode, Cathode, Electrolyte
21.
Which of the following is the best noble metal?
a) Magnesium
b) Tungsten
c) Mill scale
d) Zinc
22.
Which is cathode in corrosion?
a)Water
b)Oxygen
c)Substrate
d)Electrons released
23.
Which one is more noble?
a)Silver
b)Steel
c)Magnesium
d)Zinc
24.
Fe++ is ______________
a)An atom
b)Molecule
c) Iron Ion
d)Iron Substrate
5|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
25.
2013
Which one is not a compound in mill scale?
a) FeO
b) Fe2O3
c) Fe2 O4
d) Fe3O4
26.
Which metal corrode fast according to bimetallic principle?
a) Less electronegative
b) More Electropositive
c) More noble
d) Less Noble
27.
Which one of the following is more noble?
a) Zinc
b) Steel
c) Millscale
d) Aluminium
28.
The corrosion will takes place at
a) The Anode
b) The Cathode
c) The electrolyte
d) Anode first than cathode
29.
The by production of corrosion reaction is
a) Iron oxide
b) Iron sulphates
c) Iron chromate
d) Iron chloride
30.Aerobic condition would refer to?
a) Hydrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Nitrogen
d) Moisture
6|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
31.
2013
Which of the following is the highest known potential value?
a) Mill scale
b) Tin
c) Copper
d) Iron
32.
The chemical composition of Hematite?
a) Fe2 O3
b) Oxygen
c) Nitrogen
d) Moisture
33.
Which two materials are commonly used as sacrificial anodes?
a) Copper and Tungsten
b) Aluminium and Graphite
c) Zinc and Aluminium
d) Lead and Tin
34.
Which of the following could be classified as a major cause of microbial corrosion?
a) Sulphur Eating Metal
b) Sulphur Reducing Bacteria
c) Rust inhibitive salts
d) Iron phosphates
35.
Which is the more noble metal?
a) Steel
b) Aluminum
c) Magnesium
d) Tin
36.
Which of the element will corrode quickly as per bimetallic principle?
a) Steel-Magnesium
b) Steel – Zinc
c) Steel - Aluminium
d) Carbon
7|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
37.
2013
Bi metallic corrosion causes
a) Causes a material of a higher nobility to corrode faster
b) Causes a material of the same nobility to corrode faster
c) Causes a material of lower nobility to corrode faster
d) Causes a material containing carbon to corrode faster
38.
Molecular freedom of steel metal increases when
a) substrate contains salt
b) presence of oxygen
c) temperature increases
d) Bacteria Affected
39.
Which is more electropositive?
a) silver
b) steel
c) mill scale
d) magnesium
40.
Mill scale is formed during steel rolling manufacturing operations in temperature at
a) Below 580oC
b) Excess 580oC
c) up to 580oC
d) on 580oC
41.
Chemical name of rust
a) Hygroscopic salts
b) Hydrous iron oxide
c) mill scale
d) Hygroscopic blisters
42.
Hygroscopic slats cause
a) Rash rusting
b) Pinholes
c) Rogue peak
d) Blisters
8|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
43.
2013
In the corrosion circuit, electron travel from
a) Anode to Cathode
b) Cathode to Anode
c) Electrolyte to both Cathode to Anode
d) None of the above
44.
In the corrosion circuit, electron flow from
a) Anode to Cathode, via Electrolyte
b) Positive to Negative
c) Electrolyte to both Cathode to Anode
d) Anode to Cathode, via metallic path
45.
In which salts would be found in Marine environment?
a) Potassium
b) Chloride
c) Sulphate
d) Zinc sulphate
46.
In which salts would be found in Agricultural environment?
a) Sulphate
b) Potassium
c) Chloride
d) Potassium chloride
48.
An Anode becomes positively charged by
a) Releasing proton to the cathode
b) Releasing electrons to the cathode
c) Receiving atoms from the cathode
d) None of the above
49.
In the galvanic list, which of the following materials has the highest known potential values?
a) Mill scale
b) Copper
c) Al
d) Graphite
9|Page
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
50.
2013
AnSteel becomes positively charged by
a) Releasing proton to the cathode
b) Releasing electrons to the cathode
c) Receiving atoms from the cathode
d) None of the above
51.
In the galvanic list, which of the following materials has the lowest known potential values?
a) Mill scale
b) Copper
c) Aluminium
d) Graphite
52.
Atom acquire the electric charged are
a) Atomisation
b) Solaration
c) Polarisation
d) Electromation
10 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SURFACE PREPARATION METHODS & STANDARDS # 2
Types Of Abrasive Blasting
a) Dry Abrasive Blast Cleaning
b) Water Blasting
c) Hand and Power Tool Cleaning
d) Flame Cleaning
e) Pickling
f) Vapour Degreasing
g) Weathering
Types of Abrasive ( BS 7079 pt E)
None metallic (Mineral) expendable
Copper Slag, Nickel Slag, Garnet, Sand.
Metallic (Recyclable)
Steel Grit, Steel Shot, Grit and Shot Mix, Garnet
Agricultural by-product
Walnut Shell , Coconut Shell
Grit cuts the profiles; shot controls the peak (so uniform profile)
Digital gauges (measuring methods)
Surface Profile Needle Gauge
Dial Micrometers and Replica Tape.
Dial Micrometer and Replica Tape (Mylar tape)
trade name Testex
corn plaster method
method provides a permanent record
Steel surface
Rust Grades. BS 7079 Pt A, ISO 8501, SS 05 59 00
Rust Grade A
Rust Grade B
Rust Grade C
Rust Grade D
- largely covered with adherent mill scale
- begun to rust / which the mill scale has begun to flake.
- mill scale has rusted away /can be scraped / slight pitting
- mill scale has rusted away / general pitting
11 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Abrasive Blasting Grades
Sa 1
Sa 2
Light Blast Cleaning
Thorough Blast Cleaning
Sa 2 ½
Very Thorough Blast Cleaning
Sa 3
Blast Cleaning to Visually Clean Steel
Poorly adhering mill scale, rust
Most of the mill scale, rust Any residual
contamination shall be firmly adhering
Mill scale, rust and show only as slight
stains in the form of spots or stripes
Uniform metallic colour / White Metal
Hand and Power Tool Grades
St2
St3
Thorough hand and power tool cleaning
Very thorough hand and power tool cleaning
poorly adhering mill scale rust
metallic sheen arising from the metallic
substrate
Rust Grade:
A - Covered in Mill scale with little or no rust
B - A Mixture of Mill scale and rust.
C - Mill scale gone, rusted with slight surface pitting.
D - Heavily rusted and pitted.
Grades of wire brushing
St 2- Thorough hand and power tool cleaning
(manual)
St3 - Very thorough hand and power tool cleaning (Mech.)
12 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
The British standard for preparation of steel substrate?
a) BS 3900
b) IGE SR 21
c) BS 7079
d) ISO 8501
2.
The two factors to consider when inspecting a surface preparation
a) Degree of cleanliness and time taken
b) Surface profile and material condition
c) Surface profile and degree of cleanliness
d) Dependent upon the material thickness
3.
Which is nota surface preparation cleaning methods in before paint application?
a) Dry abrasive blast cleaning
b) Hand and power tool leaning
c) Flame cleaning
d) Light blast cleaning
4.
Which pressure suitable for dry blasting?
a)20psi
b)100psi
c)220psi
d)450psi
5.
When using a Venturi Nozzle at 100 psi the abrasive exits at approximately what speed?
a) 200 mph
b) 450 mph
c) 1200 mph
d) 100 mph
6.
Sand is not permitted as a dry blast abrasive, as directed by
a) BGC/PS/CW5
b) BS 7079 Part A
c) COSHH
d) BS 410
13 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Which standard is not permitted as a Sand blast abrasive?
a) BS 4800
b) BS 7079 Part A
c) SI 1657
d) BS 410
8.
Which one is non-metallic abrasive?
a) Iron Silica
b) Steel Shot
c) Steel Grit
d) Grit-Shot Mix
9.
Copper slag is a
a) Metallic
b) None metallic
c) Agriculture product
d) Dry sand
10.
Copper slag is a
a) Metallic
b) Mineral
c) Agriculture product
d) Dry sand
11.
Copper slag is a
a) Recyclable
b) Expendable
c) Reuse
d) Angular chilled iron
12.
Which abrasive shattering on impact release silica?
a)Sand
b) Garnet
c)Copper
d) Angular chilled iron
14 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
Which is grit form?
a) Random
b) Sharp
c)Amorphous
d) All the above
14.
Metallic abrasive are
a) Expendable
b) Recyclables
c)Silica free
d) None of the above
15.
Copper slag is also known as
a) Garnet
b) Black sand
c) Iron silica
d) Steel Grit
16.
Colour of Copper slag is
a) Black shining
b) Brown
c) Red
d) Yellow
17.
The most common type of abrasive used for British Gas site work is
a) Copper slag
b) Grit & Shot mix
c) Garnet
d) Angular Chilled Iron
18.
Abrasive used on site for British Gas projects must be
a) Mixed with sand, to reduce cost
b) Stored correctly prior to use
c) Expendable
d) Used up to a Maximum of three times only
15 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
How many times can Garnet be used as abrasive for BGas site use?
a) Upto 3 times
b) None
c) It must be expendable
d) 20 times
20.
Angular chilled iron isformed from
a) Metallic shot
b) Metallic grit
c) Metallic gritand Metallic shot
d) Garnet
21.
Metallic shot is
a) Shatters
b) Spherical
c) Random
d) Cutting Edges
22.
Irregular profile are given
a) Girt
b) Shot
c) Girt and shot
d) Garnet
23.
Which type of abrasive give more uniform profile?
a) Metallic Shot
b) Steel Grit
c) Copper Slag
d) Metallic Shot & Grit Mixed
24.
Which type of abrasive used for controlling Rash Rusting?
a) Metallic Shot
b) Steel Grit
c) Copper Slag
d) Metallic Shot & Grit Mixed
16 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
25.
2013
Which of the effect produce when rogue peaks are concentrated areas?
a) Rash Rusting
b) Flash Rusting
c) Rust Staining
d) Rust Blooming
26.
What is the cause of rash rusting?
a) Mill scale contamination
b) Hygroscopic salts
c) Rogue Peaks
d) Contaminated blast abrasive
27.
What is the reason for spot rusting?
a) Surface contamination
b) Millscale
c) Rogue peak
d) Hygroscopic salt
28.
The correct ratio of a working mix would be
a) 70-80% Grit : 20-30% Shot
b) 50% Grit : 50% Shot
c) 70-80% shot : 20-30% Grit
d) 20-25% Sand : 75-80% Copper Slag
29.
Metallic Shot also has which affect upon the material?
a) Stress relieves
b) Physically deforms
c)Work hardens
d) Causes Slivers
30.
What are the properties of an abrasive?
a) Size ,Hardness,Density,shape
b) Velocity, Impingement, Time spend, Shape
c) Rash, Rust rashing, Rust spotting, Rust blooming
d) Rogue peak, Key, Amplitude, Peak to through
17 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
31.
2013
Degree of cleanliness not depends
a) Time spent on area
b) Angle of impingement
c) Velocity of the particles
d) Substrate rust grade
32.
The standard for sizing of abrasives is
a) BS 7079
b) BS 410
c) BGC/PS/PA10
d) SI 1657
33.
The force required to separate two surfaces in touch.
a) Profile
b) Adhesion
c) Anchor pattern
d) Amplitude
34.
The two theories of adhesion are
a) Molecular interference and molecular attraction
b) Molecular integration and molecular connection
c) Molecular cross linking and molecular coalescence
d) Microscopic interaction and microscopic collaboration
35.
Another names of profile is?
a) Anchor pattern
b) Key
c) Amplitude
d) All of the above
36.
Amplitude refers to what?
a) The peak to through height of a blast profile
b) The height required for scaffolding prior to blast cleaning
c) The velocity of abrasive particles
d) The roughness of an abrasive particle
18 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
37.
2013
Anchor pattern, key, peak-to-through height and amplitude are names given to what?
a) The abrasive properties
b) The cross section of a blasted area
c) The total area of blasted substrate
d) The potential of adhesion
38.
Degree of roughness related to
a)Abrasive blasting
b)Hand and power tool
c) Anchor pattern
d)Abrasive hardness
39.
Flash Rust
a) Due to rogue peak
b) Due to Moisture
c)Due to air temperature
d) Due to steel temperature
40.
Profile thickness as per BGAS
a) 30-75 microns
b) 25-100 microns
c) 30-70 microns
d) 25-70 microns
41.
Blasting in one area for too long, produces what?
a) Hackles
b) Rogue Peaks
c) Silvers
d) Laminations
42.
Longitudinal crack is called
a) Laminations (slivers)
b) Hackles
c) Rogue peaks
d) Amplitude
19 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
43.
2013
Surface profile thickness is measured by?
a) Comparators
b) Digital profile needle gauge
c) Surface profile needle gauge
d) Dial micrometer with replica tape
44.
Surface needle gauge calibrated by
a) Blasted surface
b) Smooth piece of glass
c) Bare metal
d) Coated metal
45.
Replica tape supplied in grades
a) Coarse and Extra Coarse
b) Coarse and fine coarse
c) Extra coarseand mediumcoarse
d) Coarse and below coarse
46.
Trade name of Replica tape
a) Mylar
b) Paper
c) Testex
d) Polyester
47.
Testex also called
a) Mylar
b) Paper
c) Polyester
d) Corn plaster
48.
Thickness of Replica tape
a) 20 microns
b) 40 microns
c) 50 microns
d) 30 microns
20 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
49.
2013
What is the material used in surface replica tape, used to measure profile?
a) Mylex
b) Testrex
c) Mylar
d) Mylon
50.
What is the minimumNumber of readings required for a dial micrometer?
a) Minimum of 101
b) Minimum of twelve
c) One only
d) As many as you wish, but the average reading must be measured
51.
Transparent layer in replica tape is ____________
a)Milar
b)Mylex
c)Mylar
d)Testex
52.
When checking surface profiled using X-Course replica tape :
a) 50 microns must be added to the final reading
b) The average Number of readings must be taken
c) 50 microns must be deducted from the reading
d) A minimum of ten readings must be taken.
53.
______________ not suitable for profile measurement.
a)Dial micrometer
b) Surface profile needle gauge
c) Surface comparator
d)Corn plasters method
54.
What is the main advantage of using Testex papers for surface profile measurement?
a) It also measures cleanliness
b) Most accurate over a large area
c) Easy to use
d) Permanent record
21 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
55.
2013
When using replica tape 50µm deducted because _________
a) Thickness of paper
b) Thickness of transparent layer
c) Thickness of Testex
d) Dial micrometer Criteria
56.
Coarse grade for measuring profile range is
a) 30-50 µm
b) 37-115µm
c) 20-50 µm
d) 30-75 µm
57.
Extra Coarse grade for measuring profile range is
a) 30-50 µm
b) 37-115 µm(40-115µm)
c) 20-50 µm
d) 30-75 µm
58.
1000 µm =
a) 1cm
b) 1mm
c) 10mm
d) 0.1mm
59.
1mill (thou) =
a)24.5 microns
b)25.4 mm
c)25.4 microns
d)24.4 mm
60.
Dial position gives the Number of complete full revolutions of needle gauge on the scale
a)2 µm scale is 100µm
b)5 µm scale is 500µm
c) 2 µm scale is 200 µm
d)5 µm scale is 250µm
22 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
61.
2013
Assess the roughness
a)Naked eye
b)Visual aid
c)Tactile
d)All of the above
62.
Size of comparators diameter hole in the middle
a) 4 cm square with 2 cm
b) 8 cm square with 2 cm
c)6 cm square with 2 cm
d)10 cm square with 3 cm
63.
Any profile below the lower limit for fine grading is referred to
a) Coarser than fine
b) Coarser than Coarse
c) Finer than fine
d) Finer than Coarse
64.
Any profile above the upper limit for fine grading is referred to
a) Coarser than fine
b) Coarser than Coarse
c) Finer than fine
d) Finer than Coarse
65.
Preparation of steel substrate before application of paints and related products
a) BS 7079 Pt C
b) BS 7079 Pt. A
c) BS 7079 Pt B
d) BS 7079 Pt D
66.
Rust Grade A can be described as
a) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with evident heavy pitting
b) Clean white metal
c) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with no apparent corrosion
d) Mill scale which has begun to flake, or can be scraped away
23 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
67.
2013
Rust Grade B can be described as
a) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with evident heavy pitting
b) Clean white metal
c) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with no apparent corrosion
d) Mill scale which has begun to flake, or can be scraped away
68.
Rust Grade C can be described as
a) Tightly adhering mill scale, this can be brushed clean
b) Loosely adhering mill scale, with no evident pitting
c) Mill scale almost totally removed, visible rust, slight pitting
d) Heavy pitting visible, heavy corrosion
69.
Rust Grade D can be described as
a) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with evident heavy pitting
b) Mill scale rusted away, generalpitting, clearvisible.
c) Tightly adhering Mill scale, with no apparent corrosion
d) Mill scale which has begun to flake, or can be scraped away
70.
Corrosion begins on the metal and mill scale begins of flake away?
a) Rust Grade A
b) Rust Grade B
c) Rust Grade C
d) Rust Grade D
71.
Thorough Blast Cleaning
a) poorly adhering mill scale, rust
b) most of the millscale, rust and residual contamination shall be firmly adhering
c) millscale, rust, slight stains in the form of spots or stripes
d) free from mill scale, have a uniform metallic colour
72.
Very Thorough Blast Cleaning
a) poorly adhering mill scale, rust
b)most of the millscale, rust and residual contamination shall be firmly adhering
c) millscale, rust, slight stains in the form of spots or stripes
d) free from mill scale, have a uniform metallic colour
24 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
73.
2013
Blast cleaning to visually clean steel
a) poorly adhering mill scale, rust
b) most of the millscale, rust and residual contamination shall be firmly adhering
c) millscale, rust, slight stains in the form of spots or stripes
d) free from mill scale, have a uniform metallic colour
74.
Which blasting Grade best describes light blast cleaning?
a) Sa 2
b) Sa 21/2
c) Sa3
d) Sa1
75.
Which blasting Grade best describes Thorough blast cleaning?
a) Sa 2
b) Sa 21/2
c) Sa3
d) Sa1
76.
Very thorough blast cleaning is refers to
a) Sa1
b) Sa2
c) Sa2½
d) Sa3
77.
Blast cleaning to visually clean steel is refers to
a) Sa1
b) Sa2
c) Sa2½
d) Sa3
78.
How many photographs of Rust grade are in BS 7079 part A?
a) 4
b) 14
c) 8
d) 16
25 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
79.
2013
How many Abrasive Blast Cleaning Photographs are in BS 7079 part A?
a) 4
b) 14
c) 8
d) 16
80.
How many photographs of flame cleaning standards are in BS 7079 part A?
a) 4
b) 14
c) 8
d) 16
81.
How many photographs available by using tools according to BS 7079?
a) 14
b) 6
c) 4
d) 16
82.
BS 7079 does not contains
a) Rust Grades
b) Blast Grades
c) Hand and Power tool Grades
d) Salt tests on Substrate
83.
Wheelabrators sometimes called as
a) Centrifugal blast unit
b) Dry abrasive blasting
c) Wheel jetting
d) Water blasting
84.
____________ Abrasive is preferred for Wheelabrators
a) Steel Grit
b) Steel Shot
c) Grit and Shot Mixed
d) Copper Slag
26 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
85.
2013
What is the approximate speed of the abrasive particles exiting a Wheelabrators?
a) 450 mph
b) 220 mph
c) Mach 3
d) 100 psi
86.
Air pressure measured by
a) Pound per square inch
b) Pound per square feet
c) Cubic feet per min
d) Cubic feet per inch
87.
Air pressure delivered through
a) Pound per square inch
b) Pound per square feet
c) Cubic feet per min
d) Cubic feet per inch
88.
Which blasting use is removal for soluble salts?
a) Wet abrasive blasting
b)Dry abrasive blasting
c) Solvent / with water
d) Water wash
89.
Which blasting use are removal for Sulphate and chloride?
a) High pressure water blasting
b)High pressure water plus abrasive
c) Low pressure water plus abrasive
d) Water wash
90.
Which blasting use is removal for toxic materials?
a) Wet abrasive blasting
b)Dry abrasive blasting
c) Solvent / with water
d) Water wash
27 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
91.
2013
How many photographs totally covered as per BS 7079?
a) 32
b) 24
c) 28
d) 30
92.
Another name for a Vapour Trap is?
a) Air wash cup
b) Dry out pot
c) Knock out pot
d) Pressure regulator
93.
One of the most important safety items of equipment in abrasive blasting is
a) Dry abrasive mix
b) The banana gauge
c) Dead means handle
d) 100 psi compressor
94.
Miser Valve ___________________ in dry blasting
a) Controls the Air Pressure
b) Controls the flow of abrasives
c) Removes oil and water
d) Avoids leakage
95.
The optimum pressure to achieve 100% efficiency in abrasive blast cleaning is?
a) 75 psi
b) 450 psi
c) 100 psi
d) 220 psi
96.
Reccova valve is ____________
a)Control abrasive transfer
b)Stores abrasives
c)Removes water
d)Control air from compressor
28 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
97.
2013
With every 11 degree rise in temperature, the air’s ability to hold water
a) Would rise by 11%
b) Would half
c) Would double
d) Would decrease by 11%
98.
Carbon Impregnated hoses are used to
a) Conduct Electricity
b) Prevent static electricity
c) Reduce friction
d) Discharge static electricity
99.
_______________ can be used to check air pressure
a) Hygrometer
b) Surface profile needle gauge
c) Hypodermic needle gauge
d) Touch pyrometer
100.
Why steam cleaning is not conducive the oil and gas industry?
a) Require electricity
b)Need more water
c) Require heat source
d) Highly expensive
101.
Air/Abrasive stream is using water approx.
a) One and a half litre /min
b)Need more water
c) Two litre/min
d) Three litre / min
102.
Sometimes use flame cleaning at site, what should be followed?
a) Approval site engineer
b) Once get approval from client
c) Using wire brushing grades
d) Not to be used oil and gas industry
29 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
103.
2013
The blasting hose should be carbon impregnated?
a) Under direct operator control for his/her own safety
b) To reduce the chance of the operator getting shock form static
c) Black color gives good look
d) Carbon hose increase the speed of abrasive speed
104.
How much air supplied, if nozzle size is ½ inch
a)450 cfm
b)413cfm
c)100 cfm
d)220 cfm
105.
Which of the recommended stand-off distance and speed at which the abrasive leaves a
Venturi Nozzle?
a) 450 mm and 200 mph
b) 220 mm and 450 mph
c) 220 mm and 220 mph
d) 450 mm and 450 mph
106.
Compared to a Venturi Nozzle, a straight bore nozzle would give
a) Better paint application
b) More speed
c) Larger area coverage
d) Greater accuracy
107.
Operating pressure at
a) 200 psi
b) 450 psi
c) 100 psi
d) 220 psi
108.
What safety requirement covered for blasting equipment used?
a) HASAWA
b) COSHH
c) EPA
d) IGE/SR21
30 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
109.
2013
IGE SR 21 is associated with
a) Gas Plant Manufacture
b) Handling of Methanol
c) Abrasive Blasting Safety
d) Using of Sand Abrasive
110.
Burnishing will produce by
a) Needle gun
b) Wire brush
c) Emery cloth
d) Grinders
111.
Which one is not associated with wet blasting?
a) Spark free
b) Profile roughness
c) Remove Toxic contents
d) Remove Soluble Salts
112.
High pressure water blasting operates up to which pressure?
a) 100 psi
b) 10,000 psi
c) 250 psi
d) 30000 psi
113.
High pressure water plus abrasive injection operates up to which pressure?
a) 100 psi
b) 20,000 psi
c) 250 psi
d) 30000 psi
114.
Low pressure water plus abrasive injection operates up to which pressure?
a) 100 psi
b) 20,000 psi
c) 250 psi
d) 30000 psi
31 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
115.
2013
Which type of the cleaning not allowed in the Oil and Gas industry?
a) Dry abrasive
b) Water jetting
c) Steam cleaning
d) Hand and power tool
116.
Which application not in hand and power tool?
a) wire brushing
b) needle gunning
c) grinding
d) None of the above
117.
Wire brushes used for BGas hand & power tool cleaning, must be made from which
material?
a) Tungsten or Stainless steel
b) Copper or Brass
c) Beryllium Bronze or Phosphor Bronze
d) The same material as the pipe
118.
A typical remedy for burnishing would be.
a) Power brushing
b) Emery paper or similar
c) Needle gun
d) Addition of thinners
119.
Very coarse profile will occurs when
a)High pressure Water blasting
b)Flame cleaning
c)Dry Abrasive blasting
d)Needle Gunning
120.
Phosphor Bronze/Beryllium Bronze refers to
a) Sparking Alloys
b) Non Sparking Alloys
c) Alloys of Nickel
d) Ferroalloys
32 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
121.
2013
Which of the hand and power tool equipment not allowed in the Gas industry?
a) Phosphor bronze
b) Beryllium bronze
c) Grinding wheel
d) Emery cloth
122.
Which grade is not having photographs in wire brushing?
a) Rust Grade B
b) Rust Grade C
c) Rust Grade A
d) Rust Grade D
123.
Which one factor is not flame cleaning?
a) Expansion
b) Dehydration
c) Heat penetration
d) Passivation
124.
Phosphate process of steel structure is termed as
a) Expansion
b) Passivation
c) Cathodic protection
d) Salt Detection
125.
Which of the following do not belong to the Footners Duplex System?
a) Chromic Acid or Phosphoric acid
b) Sulphuric Acid
c) Iron Sulphates and IronChloride
d) Iron fillings
126.
Chemical cleaning is another name for
a)Silver nitrate test
b)Potassium ferry cyanide test
c) Pickling
d)Copper sulphate test
33 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
127.
2013
Concentration and temperature of sulphuric acid in pickling process
a) 5-10% , 65-70 oC and 5-25 minutes
b) 65-70% , 5-10oC and 5-20 minutes
c) 2%, 80oC and 5-25 minutes
d) 80%, 65-75 oC and 5-20 minutes
128.
Concentration and temperature of phosphoric/chromic acid in pickling process
a) 5-10% , 65-70 oC and 5-25 minutes
b) 2% , 80 oC and 1-2 minutes
c) 2%, 80oC and 5-25 minutes
d) 80%, 65-75 oC and 5-20 minutes
129.
What is pH?
a) Percentage of Hydrogen
b) Percentage of Helium
c) Potential of Hydrogen
d) Potential of Helium
130.
Which pH range covers Acids?
a) 7 to 14
b) 0 to 7
c) 0 to 14
d) 5 to 10
131.
Which pH range covers Alkalinity?
a) 7 to 14
b) 0 to 7
c) 0 to 14
d) 5 to 10
132.
When measuring acidity, alkalinity, distilled water has a pH value is?
a) 1
b) 3.5 to 4.5
c) 0 to 14
d) 7
34 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
133.
2013
Which PH range is required after chemical cleaning of steel substrate?
a) 7
b) 7 - 14
c) 4.5 – 7
d) 0
134.
What is the neutral figure on the pH scale?
a) 7
b) 7 - 14
c) 4.5 – 7
d) 0
135.
What is the main cause of flash rusting on a substrate?
a) Rogue Peaks
b) Moisture
c) Hackles
d) Hygroscopic salts
136.
Inclusion is defect related to
a)Rogue peak
b)Lamination
c)Hackle
d)High thickness profile
137.
If Profile thickness is higher than specified, result will be
a) Rash rusting
b) Cause Paint adhesion
c) Blisters
d) Mill scale
138.
Where would you normally use a comparator gauge?
a) At CP system reference point
b) To determine surface roughness
c) Check for correct pre-heat prior to application of FBE
d) To assess the rust Grade of a material.
35 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
139.
2013
Wet abrasive blast cleaning of a surface should be followed by dry abrasive blast
cleaning?
a) Only as directed by the engineer
b) To remove the surface profile created by the wet process
c) Because the immediate oxidation of the substrate after wet blasting must be removed
d) Does not required
140.
Un fused area in steel is _____________
a)Sliver
b)Rogue Peak
c)Hackle
d)Pinhole
141.
Lamination found must referred to
a) Engineer
b) Site inspector
c) Contractor
d) Project Manager
142.
Which of the recommended stand-off distance and speed at which the abrasive leaves a
Straight bore Nozzle?
a) 450 mm and 200 mph
b) 220 mm and 450 mph
c) 220 mm and 220 mph
d) 450 mm and 450 mph
143.
Surface profile thickness assets by
a) The Comparators
b) Dial micrometer and needle gauge
c) Dial micrometer with replica tape
d) Digital surface needle gauge
144.
Every 1psi drop in pressure results in an efficiency drop of
a) 2 psi
b) 1 ½ psi
c) 3 psi
d) None
36 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
145.
2013
Enclosed blasting chambers are used because
a) They protect other people and equipment from blast scatter
b) They are cheap to set up
c) They provide adequate surface profile
d) They normally use expendable abrasives
146.
Burnishing needs to be treated by
a) Needle gun
b) Wire brushes
c) Grinders
d) Emery cloth
147.
Enclosed system is
a) Water blasting
b) Wheelabrators
c) Flame cleaning
d) Hand and power tool
148.
Open blasting system is
a) Water Jetting
b) Wheelabrators
c) Flame cleaning
d) Chemical process
149.
Mill scale removed by
a) Use needle gun
b) Bristle on the brushes
c) Water Jetting
d) Dry blasting
150.
Which type of nozzle given greater control?
a) Venture Nozzle
b)Short bore Nozzle
c) Straight bore Nozzle
d) Angled Nozzle
37 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
151.
2013
Copper Slag is
a) Shatters
b) Does not shatters
c) Spherical
d) None of the above
152. Limits for Testex Tape use Coarse
a) 0.8 to 2.0 mil
b) 0.6 to 2.0 mil
c) 0.8 to 4.0 mil
d) 0.6 to 4.0 mil
153. Limits for Testex Tape use X - Coarse
a) 0.8 to 2.0 mil
b) 0.6 to 2.0 mil
c) 1.5 to 4.5 mil
d) 1.6 to 4.0 mil
38 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SURFACE CONTAMINANTS AND TESTS FOR DETECTION # 3
Qualitative test
Test for soluble iron salts
Potassium Hexa-cyanoferrate Test
Test to detect soluble chlorides
Silver Nitrate Test
Copper Sulphate Test
Test to detect the presence of mill scale
Test to detect the presence of dust on a substrate
Test to detect the presence of moisture on a substrate
Test to detect the presence of oil or grease
01.
Quantitative test
Merkoquant
Bresle sample patch
Salt contamination meters
dolly test
A procedure to test for the presence of Hygroscopic salts, is the
a) PotassiumHexa-cyanoferrate test
b) Copper sulphate test
c) Footners Duplex test
d) Hegman Grind test
02.
The test for detecting soluble chloride salts?
a) The silver Nitrate Test
b) The Copper Sulphate Test
c) Ford Flow cup test
d) The ultra violet test
03.
Which of the following is not a test for contaminants?
a) Silver Nitrate Test
b) Gold leaf test
c) Copper sulphate test
d) Powdered chalk or Talcum powder test
04.
Which one is not quantitative test?
a)Silver nitrate test
b)Dolly test
c)Bresle sample patch test
d)Banana gauge test
39 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
05.
2013
___________ can be used to detect the presence of oil or grease
a) Copper sulphate
b) Transparent Sticking Paper
c) UV Light
d) Bresle Sample Patch
06.
Colour of Mill scale
a) Dark Blue
b) Dark Grey
c) Black
d) No Colour
07.
Colour of Blasted Steel
a) Dark Blue
b) Dark Grey
c) Black
d) No Colour
08.
Which test are measure the resistivity and conductivity?
a) Bresle sample patch
b) Salt contamination meters
c) The potassium hexa-cyanoferrate test
d) The wolf will born Test
09.
Which test cannot detect hygroscopic salts?
a) Potassiumferricyanide
b) Silver nitrate
c) Bresle sample patch
d) Copper Sulphate
10.
Which of the following is a quantitative test to detect chloride salts?
a) Silver nitrate test
b) Potassium test
c) Bresle Sample test
d) All of the above
40 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
11.
2013
Which of the following test to use marine environment?
a) Silver nitrate test
b) Potassium test
c) Bresle Sample test
d) copper sulphate test
12.Test to find out the presence of Mill scale in SA 3 finish?
a) Silver nitrate test
b) Merkoquant test
c) Bresle sample test
d) Copper sulphate solution
13.
The test for soluble iron salts (ferrous) is important because
a) these salts may be present because of active corrosion cells.
b) these salts may be present because of improper manufacturing procedures at the steel
rolling mill.
c) these salts will mix with the coating and improve adhesion.
d) these salts will leach out and create an acidic surface.
14.
Which of the following are quantitative test?
a) PotassiumHexa-cyanoferrate
b) Copper sulphate
c) Silver Nitrate Test
d) Bresle Sample Patch
15.
Which of the following is not a test for contaminants?
a) Sellotape
b) Banana gauge
c) Talcum Powder
d) Solvent
16.
Why a painting inspector keep potassium ferry cyanide solution
a) For checking mill scale
b) For checking hygroscopic salts
c) For detecting oil and grease
d) For pickling process
41 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
17.
2013
Mill scale test done, which Blast grade is
a) Sa1
b) Sa2 and Above
c) Sa2½ and Above
d) Sa3
18.
___________ can be used to detect the presence of moisture
a) Copper sulphate solution
b) Transparent Sticking Paper
c) UV Light
d) Talc powder
19.
What type of test is used in photographic developer?
a) Potassium hexa-cyanoferrate test
b) Copper sulphate test
c) Silver nitrate test
d) Merkoquant test
20.
The text for detecting soluble sulphates and chloride salts on the steel substrate is
a) The Xylene salt solution
b) The copper sulphate solution
c) The potassiumhexa-cyanoferrate test
d) The wolf Wilborn Test
42 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT CONSTITUENTS AND BASIC TECHNOLOGY # 4
Basic ingredients in Paints
1. Binder
2. Pigments and other additives
3. Solvent (where applicable)
Paints are supplied as either liquids or solids in powder form.
Binder;
Binds the particles together and holds them in suspension
Gives the paint its finish
Makes the coating adhere in to the surface
Gives flexibility to the paint film.
Converts the coating to a solid dry film.
Gives resistance to water, chemical, and abrasion.
Pigment:
Gives colour to the paint.
Gives opacity to the paint.
Gives resistance to acids, alkalis and light.
Solvent:
Forms the evaporative part of the drying process.
Thins the paint so it can be applied easily.
Washes out the brushes and equipment.
Acts as a degreasing agent if approved.
43 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Types of Binder
Acrylic
Alkyd
Asphaltic bitumen’s
Cellulose resins
Chlorinated rubber
Emulsions
Epoxies
Ethyl and Methyl Silicates
Phenolic resins
Polyurethane’s
Silicones
Styrene
Vinyl
Natural oils
Linseed Oil, Tung Oil (also known as China Wood Oil), Soya Oil, Tall Oil and Safflower Oil.
Natural resins
Copals, dammars and Coumarones
Binder solvent combinations
Solvent
Common name
Combination binder
Strength
Solvent
Common name
Combination binder
water
nil
Emulsions PVC/PVA, Vinyl’s,
Acrylics , Polyurethane
Low → compare to aliphatic HC
Strength
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
White sprit
Natural oil, natural resins , alkyds,
phenolic
Low → compare to aromatic HC
Solvent
Common name
Combination binder
Strength
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Xylene
Chlorinated rubber
Low → compare to ketones
Solvent
Common name
Combination binder
Strength
Ketones
Acetone
epoxy
high→ compare to others
Don’t use binder with strong solvent over a weak solvent. ( Existing coat )
44 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Example: Chlorinated Rubber coated over an Alkyd would result in lifting, and wrinkling,
Would it be acceptable practice to apply an Alkyd over Chlorinated Rubber?
Advisable
Would it be acceptable practice to apply Chlorinated Rubber over Phenolic?
Not Advisable
Would it be acceptable practice to apply Phenolic Resin over Chlorinated Rubber?
Advisable
Would it be acceptable practice to apply Epoxy over linseed oil base?
Not Advisable
Would it be acceptable practice to apply Chlorinated Rubber over Epoxy?
Advisable
Would it be acceptable practice to apply Epoxy Resin over Alkyd Resin?
Not Advisable
Polymers
Liner Polymer
Non-convertible or reversible material
Thermoplastic
Binders:
Acrylics, Vinyl’s, Chlorinated Rubber, Asphalt and Coal Tars and Cellulosic Resins.
Branched Polymer
Non-reversible or convertible coatings
Thermosetting.
Binders:
Natural Oils and Natural Resins, and isomers such as Alkyds and Phenolic.
Cross linked Polymer
Non-reversible or convertible coatings
Thermosetting.
Binder:
Epoxies
Oils
Natural oils (vegetable oils)
Linseed, castor, olive, coconut, soya and Tung oil.
Saturated oil (Non-drying oil) cannot be used
Ex: Castor oil, coconut oil, palm oil
Used only plasticisers
Non-Saturated oil (Drying oil) can be used
Ex: Linseed oil, Tung oil, china wood oil, olive oil, safflower oil.
Used as a binder
45 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
Long oil paint
Medium oil
paint
Short oil paints
more than
60%
between 45 –
60%
less than 45%
2013
slower drying / domestic applications, decorative
materials
oil to resin
faster drying / shorter over coating time / steel
work
Pigments
Rust inhibitive pigments - anti-corrosive
a) Red lead * Red
b) Calcium plumbate * White
c) Coal tar * Black
d) Zinc chromate * Yellow
(Asterisk is toxic and restricted in use)
e) Zinc phosphate (most commonly used)white.
f) Barium metaborate
g) Zinc phosphosilicate Yellow
Metallic Pigments
Zinc, Aluminium
Opaque pigments
Opaque pigments are given covering power, (opacity) and colour.
Carbon
Compound of Cobalt
Compound of Chromium
Compound of Iron
Compound of Calcium
Titanium Dioxide
Black
Blue
Greens Yellows and Oranges
Browns Reds and Yellows
Reds and Yellows
White
Extender pigments
Properties
adhesion
cohesion
film strength
durability
46 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
Materials used
Clays
Chalk
Talcum
Slate flour
2013
Kaolin, China clay
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium silicate
Aluminium silicate
Laminar pigments
Plate like pigments are MIO (Micaceous Iron Oxide), Aluminium Flake, Glass Flake, Mica and
Graphite
PVC (Pigment Volume Concentration)
CPVC, Critical Pigment Volume Concentration
Below CPVC
Too much of binder
good gloss properties
poor covering power (opacity)
low cohesive strength
Above CPVC
the film would be porous
low cohesive strength
Poor adhesion
Near CPVC (good pigment to binder ratio)
lower gloss properties
greater cohesive strength
enough resin to encapsulate each particle
good resistance to water permeation.
Solvents
Solvent strength
Evaporation rate
Flash point
Toxicity
Anti-settling agents or Thixotropic agents
bentones and waxes
47 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Plasticisers
A plasticizer is a paint reduces the brittleness of the dried film by allowing the molecules of
the paint to move more easily. There by making it more plastic.
Driers or catalyst
Driers added to accelerate the drying process. Drier consists of compound of metal e.g.
Napthenats of cobalt, zirconiµm Manganese.
Octoic Acid and Naphthanic Acid
Stabilisers
Holds modern synthetic film formers intact and helps to prevent flocculation occurring in tin.
Anti-skinning
Methyl Ethyl Ketoxime.
48 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
A barrier type paint system, must be capable of providing?
a) Good capacity
b) Low permeability
c) High permeability
d) Low opacity
2.
Example for paint involving barrier principle
a) Zinc rich epoxy
b) Zinc or Aluminium
c) Urethane
d) Rust inhibitive primers
3.
Rust inhibitive primers operate by?
a) Oxidation to protect the substrate
b) Pigmentation
c) Zinc phosphate
d) Passivation
4.
Cathodic protection using pigmentation?
a) Rust inhibitive primers
b) Zinc in Zinc rich primers
c) Zinc phosphate
d) Urethane
5.
Paint is constructed of which 3 basic ingredients?
a) Polymers, Epoxy, and Colourant
b) Natural Oils, Dyes and Hardeners
c) Oil, Color and extenders
d) Binder, Solvent, Pigments & other Additives
6.
Which term is not relate with binder
a) VOC
b) Film former
c) Vehicle
d) Non volatile
49 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Vehicle is
a) pigments
b) binder
c) solvent
d) MLC
8.
Major considerations of a binder are:
a) Flow properties or viscosity
b) Resistance to chemical attack according to environment.
c) Cohesive strength and Dialectric strength.
d) All the above
8.
Which is not a property of binder?
a)Cohesive strength
b) Leafing effect
c)Resist water
d) Hold pigments in suspension
9.
Alcohol –Acid are derived
a) Acrylic
b) Alkyd
c) Asphaltic bitumen
d) Cellulose resins
10.
The paint which prone chalking in top coat?
a) The Epoxy
b) The polyurethane’s
c) The Chlorinated rubber
d) The acrylic
11.
Which of the following binders are reversible?
a) Epoxy
b) Urethane
c) Chlorinated Rubber
d) Silicone
50 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
12.
2013
Which of the following is not a commonly used binder?
a) Epoxy
b) Zinc
c) Urethane
d) Vinyl
13.
Which of the following is natural oil?
a) Dammar
b) Alkyd
c) Castrol
d) Xylene
14.
Which of the following is natural oil?
a) Copals
b) Amber
c) Olive
d) Dammars
15.
Which of the following is not natural oil?
a) Castor
b) Amber
c) Olive
d) Linseed
16.
Natural oils are
a) Slow drying properties
b) Hot drying oil
c) Fast drying
d) Non-drying oil
17.
Natural oils are
a) Linseed oil
b) Tung oil
c) Soya oil
d) All the above
51 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
18.
Natural oils are
a)
b)
c)
d)
19.
China wood oil
Tall oil
Safflower oil
All the above
Natural oils are
a)
b)
c)
d)
20.
2013
Linseed oil
Castor oil
Coconut oil
All the above
China wood oils known as
a) Linseed oil
b) Tung oil
c) Tall oil
d) All the above
21.
Which of the following is not a natural resin?
a) Copal
b) Amber
c) Dammar
d) Linseed
22.
Examples for natural resin
a) Amber, Laq
b) Soya Oil, Tung Oil
c) Bitumen , Coal tar
d) Phenolic resin, Cellulosic resin
23.
Examples for natural resin
a) Copals
b) Coumarones
c) Dammars
d) All the above
52 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
24.
Oleoresinous known as
a)
b)
c)
d)
25.
A mixture of oil and resin
A mixture of oil and water
A mixture of resin and acid
A mixture of water and resin
Natural resins are
a)
b)
c)
d)
26.
2013
Slow drying properties
Hot drying oil
Fast drying
Semi-drying oil
Hot drying oils are
a) Phenolic resins
b) polyurethanes
c) Cellulose resins
d) Styrene
27.
Metal sprayed surfaces can be sealed with
28.
a) Phenolics
b) Silicones
c) Cellulose Resins
d) Vinyl
Which one is convertible?
a) CR
b) Vinyl
c) Natural Resin
d) Emulsion
29.
Which binder has no problem to overcoat on white spirit based binder?
a) Alkyds
b) Epoxy
c) CR
d) Natural Resin
53 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
30.
2013
Which solvent group is suitable for chlorinated rubber paints?
a) Xylene
b) Ketones
c) Water
d) White Spirit
31.
Example for aliphatic HC solvents
a) Water
b) Xylene
c) Turpentine
d) Acetone
32.
Which one is more suitable for CR paint to increase flexibility
a) Alkyd resin
b) Linseed oil
c) Bentones
d) Coconut oil
33.
What will happen when applying strong solvent binder paint over a week solvent binder paint?
a) Strong solvent will dissolved into weak solvent & cause of wrinkle or lifting
b) Nothing happen
c) Paint appearance more glossy
d) Viscosity of paint will reduce
34.
Which paint from below, can be applied over Phenolics?
a) CR
b) Epoxy
c) Alkyd
d) None of these
35.
Which paint from below, can be applied over CR?
a) Phonelics
b) Epoxy
c) Alkyd
d) None of these
54 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
36.
2013
Which paint frombelow; can be applied over Natural resins?
a) CR
b) Acrylics
c) Epoxy
d) None of these
37.
Which paint from below, cannot be applied over Alkyd?
a) Acetone
b) Epoxy
c) Chlorinated Rubber
d) None of these
38.
Which paint from below, cannot be applied over CR?
a) Phonelics
b) Epoxy
c) Alkyd
d) None of these
39.
Which one material is used on operating temperature?
a) Epoxy
b) Xylene
c) Silicone
d) China Clay
40.
Cobwebs happened
a) Brush application
b) Spray application
c) Roller application
d) None of the above
41.
Solution polymer as a
a) Branched polymer
b) Crossed link polymer
c) Linear polymer
d) None of the above
55 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
42.
2013
Backbone of the structure in form of the polymerisation
a) Hydrogen
b) Carbon
c) Chlorine
d) Nitrogen
43.
Example for linear polymerisation?
a) Acrylics
b) Vinyl’s
c) Chlorinated rubber
d) All the above
44.
Which is not a linear polymerisation?
a) Asphalt
b) Coal tars
c) Cellulosic resins
d) Alkyds
45.
Which of the following are said to be reversible?
a) Cross linked polymer
b) Branched polymer
c) Linear polymer
d) Convertible coating
46.
Which of the following are said to be non-convertible?
a) Cross linked polymer
b) Branched polymer
c) Linear polymer
d) Convertible coating
47.
Which of the following are said to be thermoplastic?
a) Cross linked polymer
b) Branched polymer
c) Linear polymer
d) Convertible coating
56 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
48.
2013
Which of the following are said to be non-reversible?
a) Branched polymer
b) Linear polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) None of the above
49.
Which of the following are said to be convertible?
a) Branched polymer
b) Linear polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) None of the above
50.
Which of the following are said to be thermosetting?
a) Branched polymer
b) Linear polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) All of the above
51.
Example for Branched polymerisation?
a) Alkyds
b) Isomers
c) Phenolics
d) All the above
52.
Example for not Branched polymerisation?
a) Natural oils
b) Natural resins
c) Phenolics
d) Epoxies
53.
Which of the following are said to be non-reversible?
a)Linear polymer
b) Cross linked polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) None of the above
57 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
54.
2013
Which of the following are said to be convertible?
a)Linear polymer
b) Cross linked polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) All of the above
55.
Which of the following are said to be thermosetting?
a)Linear polymer
b) Cross linked polymer
c) Convertible coating
d) None of the above
56.
Example for Cross linked polymerisation.
a) Acrylics
b) Alkyds
c) Isomers
d) Epoxy
57.
By which polymerisation method a two pack epoxy paint dry
a) Cross linked Polymer
b) Branched Polymer
c) Solution Polymer
d) Linear Polymer
58.
A paint drying by chemical reaction is said to be
a) Linear polymer
b) Convertible
c) Non-convertible
d) Reversible
59.
Which polymerisation done in oxidation drying paints?
a) linear
b) Solution
c) Branched
d) Cross linked
58 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
60.
2013
Which one is saturated oil?
a) Linseed oil
b) Tung oil
c) Palm oil
d) China wood oil
61.
Which one is unsaturated oil?
a) Linseed oil
b) Tung oil
c) Olive oil
d) All the above
62.
A saturated oil can be used in binder for
a) Fast drying
b) Shelf life
c) Flexibility
d) Anti-skinning
63.
Which one is rapid drying oil?
a) Linseed oil
b) Tung oil
c)China wood oil
d) All the above
64.
Non- drying oils can be used in paints, for __________
a) Fast drying
b) Slow drying
c) Activate Chemical reaction
d) Flexibility
65.
Saturated oil as a
a) Drying oil
b) Semi drying oil
c) Non-drying oil
d) All the above
59 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
66.
2013
Which one is suitable for steel work?
a) Short oil paint
b) Medium oil paint
c) Long Oil paint
d) Full Oil paint
67.
Which one is long oil paint?
a) Less than 45% oil to resin
b) Between 45-60% oil to resin
c) More than 60% oil to resin
d) None of the above
68.
Which one is medium oil paint?
a) Less than 45% oil to resin
b) Between 45-60% oil to resin
c) More than 60% oil to resin
d) All of the above
69.
Which one is short oil paint?
a) Less than 45% oil to resin
b) Between 45-60% oil to resin
c) More than 60% oil to resin
d) None of the above
70.
Which one is suitable for domestic or decorative purpose?
a) Short oil paint
b) Medium oil paint
c) Long Oil paint
d) Full Oil paint
60 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
71.
2013
What are the properties of pigment?
a) Cohesively strength
b) Abrasive resistance
c) Impermeability
d) All the above
72.
Pigment particle size is
a)
b)
c)
d)
73.
Which one is a non-toxic pigment?
a)
b)
c)
d)
74.
75.
Zinc Phosphate
Zinc Chromate
Read Lead
Coal tar
What is the color of most common used Rust inhibitive pigment?
a) Grey
b) Black
c) Red
d) White
Pigment, which dissolve in a binder called
a)
b)
c)
d)
76.
¼ th micron
½ th micron
1/10 th micron
1/5 th micron
Lacquer
Dye
Varnish
Solute
Rust inhibitive pigment are added to primer to protect the steel substrate by
a)
b)
c)
d)
Passivation
Evaporation
Cathodic protection
UV protection
61 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
77.
2013
Which one is give galvanic protection?
a) Aluminum
b) Zinc
c) Glass flake
d) China Clay
78.
Which one is give solar protection?
a) Aluminum
b) Zinc
c) Glass flake
d) China Clay
79.
An additive that gives a point material its hiding power?
a) A plasticizer
b) A thyrotrophic
c) A drier
d) A pigment
80.
Properties of opaque pigment
a) Hiding power
b) Colour
c) Opacity
d) All the above
81.
Which one is opaque pigment?
a) Cobalt
b) Chromium
c) Calcium
d) All the above
82.
Which of the following is an opaque pigment?
a) Graphite
b) Compound of Chromium
c) Zirconium Octoate
d) Zinc Phosphate
62 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
83.
2013
Which one is Carbon?
a) Blue
b)Red
c) Black
d) Yellow
84.
Which one is Titanium dioxide?
a) Blue
b)Red
c) Black
d) White
85.
Which one cannot be used for yellow colourpaint?
a)Chromium
b)Cobalt
c)Calcium
d)Iron
86.
Which is not a property of extender pigments?
a) Increase Gloss
b) Increase Adhesion
c) Increase Cohesion
d) Increase film strength
87.
Which of the following is an extender?
a) Calcium carbonate
b) Magnesium Silicate
c) Aluminium silicate
d) All the above
88.
Which of the following is an extender?
a) Graphite
b) Mica
c) Glass Flake
d) China Clay
63 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
89.
2013
Which one is not a laminar pigment?
e) MIO
f) Aluminium flake
g) Glass flake
h) China Clay
90.
Which of the following is a laminar pigment?
a) Graphite
b) Mica
c) Glass Flake
d) All the above
91.
PPM
a) Parts per million
b) Per parts million
c) Parts per Micron
d) None of the above
92.
Which type of the following pigment is giving leaf effect?
a) Opaque pigment
b) Extender Pigment
c) Laminar pigment
d) All of the above
93.
Specular Hematite is commonly called
a) Mill scale
b) Rust
c) MIO
d) Iron Sulphate
94.
Theory of overleap when the coating dries
a) Opaque pigment
b) Extender Pigment
c) Laminar pigment
d) All of the above
64 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
95.
2013
Which of the following considered being a laminar pigment?
a) Micaceous iron oxide
b) Red Lead
c) Coal tar
d) Zinc phosphate
96.
Which laminar pigment is best for UV protection?
a)Aluminum Flake
b)MIO
c)Glass Flake
d)Graphite
97.
Which of the following is not a laminar pigment?
a) Graphite
b) Glass Flake
c) Magnesium Silicate
d) Mica
98.
Expansion of CPVC
a) Central pigment volume concentration
b) Critical pigment volume concentration
c) Control pigment volume concentration
d) Critical paint volume concentration
99.
Too much binder to solid ratio gives
a) Good Opacity
b) Good Gloss
c) Cohesive Strength
d) Porous Film
100.
Greater cohesive strength
a) Below CPVC
b) Near CPVC
c) Above CPVC
d) All the above
65 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
101.
2013
Poor covering power
a) Below CPVC
b) Near CPVC
c) Above CPVC
d) All the above
102.
What would be the main problem of a low CPVC?
a) High opacity
b) Permeability
c) Low gloss
d) Low opacity
103.
Solvent are added to paint to reduce
a) Viscosity
b) Toxic
c) Velocity
d) Good gloss
104.
Properties of solvent
e) Strength
f) Flash Point
g) Evaporation rate
h) All the above
105.
The minimum temperature of the solvent at which the vapours given off are flammable if a
source of ignition is introduced as
a) Evaporation rate
b) Flash Point
c) Toxicity
d) Solvent strength
106.
Which property of a solvent is not best?
a) Low evaporation rate
b) Low toxicity
c) Low flashpoint
d) High evaporation rate
66 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
107.
2013
Toxicity measured in
a)Mph
b)Psi
c) Ppm
d)Cfm
108.
Which of the following is an additive?
a) Opaque pigments
b) Rust inhibitive pigments
c) Thickening agents
d) Thinners
109.
Which of the following are commonly used as anti-settling agents?
a) Heavy metal salts
b) Bentones & Waxes
c) Saturated Oils
d) Extender pigments
110.
Thixotrops are of _____________ type
a) Liquid
b) Solid
c) Gel
d) Solvent
111.
Anti-settling agents are
a) Bentones
b) Zirconium
c) Castor Oil
d) Cobalt
112.
Anti-settling agents are allow
a) low film thickness
b) higher film thickness
c) average film thickness
d) All the above
67 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
113.
2013
Which additive used in paints to stop settlements
a) Drying oils
b) Non Drying oils
c) Wax
d) Anti-skinning agents
114.
Basically plasticiser gives
a) flexibility
b) Thickness
c) oxidation
d) stop settlement
115.
Which additive in the paint helps to prevent film cracking in use?
a) A thyrotrophic
b) A plasticizer
c) A drier
d) A Stabilizer
116.
Example for drier additive?
a) Bentones and waxes
b) Castrol Oil
c) Methyl ethyl Ketoxime
d) Cobalt naphthantes
117.
Octoates and Cobalt naphthantes are
a) Plasticisers
b) Anti-selling agents
c) Driers
d) Anti-skinning agents
118.
Anti-oxidants are
a) Plasticisers
b) Anti-settling agents
c) Driers
d) Anti-skinningagents
68 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
119.
2013
Which one is used to retard the formation of skin in paint solution?
a) Palm Oil
b) Octoic Acid
c) Methyl Ethyl Ketoxime
d) Bentones
120.
If more pigments added in a paint, then the surface should be ___________
a) Gloss
b) Matt
c) Grinning
d) Fast Drying
121.
Which one is not a property of binder?
a) Adhesion
b) Cohesion
c) Evaporation
d) Dielectric strength
122.
When use Compound of Calcium pigment which type of colour produced?
a) Red
b) Black
c) White
d) Blue
123.
The most widely used materials for pipeline coating are which of the following?
a) Alkyd enamels
b) Fusion-bonded epoxies
c) Thermoset plastics
d) High density latexes
124.
Which term cannot be used for solid particles in binder?
a) Aggregates
b) Emulsion
c) Degree of dispersion
d) Fineness of grind
69 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
125.
2013
Which paint constituent can be found in powder form?
a) The Binders
b) The Solvents
c) The Driers
d) The Anti-skinning agent
126.
A paint said to have a good opacity will
a) Have low permeability
b) Have good hiding power
c) Have a low CPVC
d) Have a low minimum gloss value
127.
Which is not property of binder?
a) Cohesive Strength
b) Leafing Effect
c) Resist Water
d) Hold Pigments in suspension
128.
Which additive in the paint helps to prevent film cracking in use?
a) A thixotropic
b) A plasticizer
c) A drier
d) A Extender
129.
Magnesium silicate is
a) Clays
b) Chalk
c) Talcum
d) Slate flour
130.
Aluminium silicate is
a) Clays
b) Chalk
c) Talcum
d) Slate flour
70 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
131.
2013
Calcium carbonate is
a) Clays
b) Chalk
c) Talcum
d) Slate flour
132.
Magnesium silicate is
a) Rust Inhibitive pigment
b) Opaque pigment
c) Extender pigment
d) Laminar Pigment
71 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SOLUTIONS AND DISPERSIONS # 5
1.
A solution is
a) The resultant liquid of a polymerization event
b) The resultant liquid after dispersing a liquid another liquid
c) The resultant liquid of a solid suspension
d) The resultant liquid after dissolving a material in a solvent
2.
Paint is a _________________
a)Solution
b)Solute
c)Solvent
d) Dispersion
3.
Example for suspension
a) Water Based Emulsion
b) Oil Mixed With Water
c) Salt Water
d) Pigmented paint
4.
Example for Emulsion
a) Water with water
b) Oil Mixed With Water
c) Salt Water
d) Pigmented paint
72 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DRYING AND CURING OF PAINT FILMS #6
1. Solvent Evaporation
linear polymer
reversible or non-convertible
Chlorinated rubber, vinyl’s, acrylics, cellulosic materials
Thermoplastic
2.Oxidation
Branched polymer
convertible or non-reversible
Alkyds, Phenolics, natural oils and resins
3.Chemical Curing
2. Coalescence
Thermosetting(Coatings which do not melt after the application of heat are known as thermo
set coatings)
application of heat
convertible or non-reversible
materials like epoxy and urethane
Thermoplastic(Paints which melt when heat is applied are known as thermoplastic coatings)
application of heat
linear polymer
reversible or non-convertible
using material Polyethylene and Polypropylene
Name the Paints & give their drying and curing methods
Emulsion
coalescence
Alkyd
Solvent evaporation followed by oxidation
Chlorinated rubber
Solvent evaporation
Two pack epoxy
Solvent evaporation followed by chemical
curing
Fusion bonded epoxy
Heat cured
73 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1
2013
Which is not a drying method?
a) Coalescence
b) Air Drying
c) Stoving
d) Force Drying
2.
Ambient temperatures refers to
a) Coalescence
b) Air Drying
c) Stoving
d) Force Drying
3.
Which term is used when heat applied over 65 oC for Drying of Paint?
a) Metal Spray
b) Air Drying
c) Stoving
d) Forced Drying
4.
Which of the following is not a drying mechanism?
a) Coalescence
b) Oxidation
c) Stove drying
d) Chemical curing
5.
Chlorinated Rubber will dry
a) Oxidation
b) Chemical curing
c) Solvent Evaporation
d) None of the above
6.
Example for Solvent evaporation drying
a) Epoxy
b) Alkyd
c) Acrylic
d) Urethane
74 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Solvent evaporation dryingis
a) Branched polymer
b) Linear polymer
c) Crossed link polymer
d) None of the above
8.
Paint drying is solvent evaporation in
a) Convertible
b) Reversible
c) Non-reversible
d) Cross linked
9.
A single pack epoxy paint dry by
a) Coalescence
b) Chemical curing
c) Oxidation
d) Solvent evaporation
10.
A Multi component paint dried by
a) Solvent evaporation
b) Oxidation
c) Chemical reaction
d) Coalescence
11.
A typical pot life of paint used in BGas specification would be.
a) 20-30 minutes
b) 12-24 hours
c) 6-8 hours
d) 3-7 days
12.
A typical induction period of paint used in BGas specification would be.
a) 20-30 minutes
b) 12-24 hours
c) 6-8 hours
d) 3-7 days
75 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
Pot life mentioned in
a) Material data sheet
b) Job sheet
c) Paint inspection sheet
d) None of the above
14.
Stand time or lead time are called
a) Pot life
b) Induction time
c) Drying time
d) None of the above
15.
Two pack material curing agents
a) Alkyds and Acrylics
b) Tulane and Xylene
c) Amides and Amines
d) All of the above
13.
Pot life is
a)The period of the length of time after mixing which the paint should be before use
b) The period of time after mixing which the paint must be used
c) Physically join together
d) None of the above
14.
Chemically curing materials are
a) Convertible
b) Non-convertible
c) Reversible
d) All of the above
15.
Endothermic reactions are
a) Container will warm up and giving heat
b) Container will cooling and taking in heat
c) Container removes
d) All of the above
76 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT SYSTEMS #7
Functions of Primers, Midcoat, & Finish Coats.
Primer- To provide Maximum lasting adhesion to a substrate for the next paint layer and
corrosion.
retard
Midcoat- Barrier to prevent the passage of Water.
Finish Coat – Gives Final appearance, degree of gloss & colour. Resistance to abrasion, UV rays,
Weather .To aids the flow from the surface of the metal.
Mordent solution, t wash, wash primer = etch primer
Aluminium etch primer – poly vinyl butyl
77 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
The BGas specification for site application of paint system is
a) BGC/PS/PA10
b) BGC/PS/CW5
c) BGC/PS/PA8
d) BS 7079
2.
Which painting system contain with rust inhibitive pigment and anti-corrosive pigment
a) Mid coat
b) Top coat
c) Second coat
d) Primer coat
3.
PVB Primers mainly used for
a) All ferrous substrates
b) Aluminium
c) Galvanising
d) Steel Substrates
4.
Second Coat also known as
a) Primer
b) Mid coat
c) Top coat
d) Itching primers
5.
The function of a finish coat is mainly to provide.
a) Impermeability and adhesion
b) Aesthetic properties and water shedding
c) Cathodic protection and passivation
d) Increased thickness at low cost
6.
Which product should be used to damp or moist surfaces?
a) Water borne acrylic
b) Thermally Sprayed Aluminium
c) Moisture Curing Polyurethane
d) Micaceous Iron oxide
78 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Which one is thermoplastic?
a) Poly ethylene
b) Poly urethane
c) Epoxy
d) Natural Resin
8.
In powder coating, to complete the curegenerally takes
a) Three seconds
b) Less than three minutes
c) More than an hour
d) Eight hours
9.
Thick steel sections like powder are sprayed onto a
a) Preheated substrate
b) Post heated substrate
c) Low temperature
d) None of the above
10.
Thin steel sections like powder are sprayed onto a
a) Preheated substrate
b) Post heated substrate
c) Low temperature
d) None of the above
11.
Powder coating types may include which of the following?
a) Alkyds
b) Epoxies
c) Organic Zinc
d) Latexes
12.
Paint system: Properties and performance requirement, a detailed in PA9, paint testing is
mostly carried out according to which BS?
a) BS 729
b) BS 5493
c) BS 3900
d) BS 6072
79 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
AGI gas pipeline temperature is
a) Much cooler than ambient temperature
b) Hot than ambient temperature
c) Cooler than ambient temperature
d) None of the above
14.
A zinc phosphate pigmented primer would be a
a) Passivation system
b) Galvanic protection
c) Bimetallic principle
d) All the above
15. Organic Zinc rich epoxy would be provide a
a) Passivation system
b) Barrier system
c) Galvanic protection
d) All the above
80 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
WATER BORNE COATINGS# 8
1.
Which paint is not suitable for EPA?
a) Water borne
b) High volume solid
c) Solvent Based
d) Solvent free
2.
Which paint is not suitable for EPA?
a) Water borne
b) High volume solid
c) Low volume solid
d) Solvent free
3.
60% of Volume Solids paint using a hydrocarbon solvent will release
a) 400 cc
b) 450 cc
c) 200 cc
d) 350 cc
4.
Hydrocarbon known as
a) not harmful to environment, the ozone layer or to mankind
b) to be harmful to the environment, the ozone layer, and human life
c) In periods of high humidity drying will be retarded
d) None of the above
81 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT MANUFACTURE# 9
Direct charge mill: which take and mix all the raw ingredients together.
Example: Ball mill, Attritor mill, High speed dispersers.
2. Pre-mix mills; Take the ingredients which have been pre mixed to a rough consistency
and refine this mixture to high quality paint.
E.g. Bead mill (pear or sand mill), Colloid mill, Tipple roll mill, single roll mill
82 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
What are stages of paint manufacturing system?
a) Premixing
b) Dispersing mill
c) Letdown process
2.
d) All the above
Which one is not a direct charge mill?
a)Ball mill
b)Attritor Mill
c)Bead mill
d) Sand mill
3.
Which one is a direct charge mill?
a) Sand Mill
b) Single roll mill
c) Triple roll mill
d) Attritor Mill
4.
What type of machinery is used to produce large production runs of popularpaints?
a) Triple Roll mill
b) Colloid Mill
c) Ball Mill
d) Sand Mill
5.
Which paint mill produce expensive materials?
a) Triple roll mill
b) Single roll mill
c) Sand mill
d) Ball mill
6.
High speed dissolver mill is another name for
a) High speed disperser
b) Pearl mill
c) Colloid mill
d) Attritor Mill
83 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
High speed stone mill is another name for
e) High speed disperser
f) Pearl mill
g) Colloid mill
h) Attritor Mill
8.
Which mill widely used for producing thick paint?
a) Ball Mill
b) Pearl Mill
c) Triple Roll Mill
d) Single Roll Mill
9.
What type of equipment is used to produce mastics, putties and fillers?
a) Sand mill
b) Triple roll mill
c) Colloid mill
d) Attritor mill
10.
Bead mill or Pearl mill known as
a) Ball Mill
b) Sand mill
c) Triple Roll Mill
d) Single Roll Mill
11.
What type of equipment is used to produce silver and glitters?
a) Sand mill
b) Triple roll mill
c) Single roll mill
d) Attritor mill
84 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
TESTING OF PAINTS FOR PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE # 10
Paint density
weight per unit of volume
formula: Density =
Weight
volume
units for density are grams per cc
.
Density cup capacity 100 cc
Other names referring to the same cup are: 1 Relative density cup
2 Specific gravity cup
3 Weight per litre cup
4 Weight per gallon cup
5 Pyknometer
Density cup are using to 2 pack material has been mixed in the correct proportions.
Hegman grind gauge
also called a fineness of grind gauge
is used to measure the degree of dispersion of paint.
Its use only manufacture area.
Viscosity
Viscosity is defined as being a fluid resistance to flow.
Types of viscosity
1. Rotational Viscometers
2. Flow Viscometers (For measuring viscosity)
85 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
1. Rotational viscometers
Dynamic viscosity
Kinematic viscosity is measured using a Krebs Stormer Viscometer
2. Flow viscometers (Flow cups)
Different types of flow cups
Zahn and Frikmar, used for hot fluids,
Ford, ISO and DIN used for ambient temperature materials.
Thixotropic paints cannot be measured using a flow cup
Viscosity is low add paint
Viscosity is high add thinner ( solvent )
The thixotropic paints the viscosity can be measured by a rotation viscometer or another type of
viscometer paints.
Factors which cause poor adhesion of Paint system;
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
Surface preparation is poor.
Surface containing detrimental contaminants
Overpowered Burnished areas,
Surface Profile very less
Over thinning of Paints
Paint applied over rust or unprepared areas
Not proportionately mixing of Two Pack Paints.
Preparation of Two pack Paints for Use.
a. Plastic paper to be used underneath of paint tins,
b. All dust to be removed.
c. Lid to be opened without damaging of the rim.
d. All sediments at the bottom of the tin are to be mixed by stirring.
e. Solvents or Catalysts to be added slowly and gradually and mixed thoroughly in paint.
f. Up to 5 Liters Paint may be mixed by Manual, above 5 liters by Mechanical mixing to get
homogeneity.
g. Tin should be covered without Opening.
86 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
Transco Specification PA9 Specifies
a) New and Maintenance painting at work and site for AGI
b) Paint Properties and Performance
c) Internal coating of steel small bore pipe
d) Preparation of steel substrate before application of paint
2.
The temperature at which a vapour from a solvent will ignite in the presence of a source of
ignition is
a) Upper explosive limit
b) Dew point
c) Flash point
d) Relative humidity
3.
Closed Abel cup used to:
a) Flash point Determination
b) Viscosity determination
c) Density determination
d) All the above
4.
How to heat the Abel cup
a) Direct
b) Indirect
c) Induction
d) None of the above
5.
How to identify the flash point temperature?
a) Blue flame flashes
b) Orange flame flashes
c) Red flame flashes
d) Yellow flame flashes
6.
Which flame signifies that the flash point temperature has been exceeded?
a) Blue flame flashes
b) Orange flame flashes
c) Red flame flashes
d) Yellow flame flashes
87 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Density defined
a) Weight per unit of volume
b) Metric per unit of volume
c) Volume divided by weight
d) All the above
8.
Density unit are
a) Weight per unit of volume
b) Metric per unit of volume
c) Gram per cc
d) All the above
9.
Capacity of Density cup
a) 200 cc
b) 300 cc
c) 1000 cc
d) 100 cc
10.
Density cup made by
a) Aluminium alloy
b) Stainless steel
c) Nickel
d) Iron
11.
What is pyknometer?
a) Opacity testing equipment
b) Whirling Hygrometer
c) Density Cup
d) Wind speed measuring equipment
12.
Which of the following is not another name for Density Cub?
a) Pyknometer
b) Psychrometer
c) Weight per gallon cup
d) Weight per litre cup
88 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
Which of the following is another name for Density Cub?
a) Relative density cup
b) Specific gravity cup
c) Pyknometer
d) All the above
14.
Mixing of two packs can be calculated by
a) Pyknometer
b)Closed Abel Cup
c)Pyro meter
d)Crypto meter
15.
What is the name of the equipment used to determine particle aggregate size?
a) Beck koller
b) Hegman gauge
c) Wolfe – wilborne
d) Kerbe Stormer
16.
What is another name of the Hegman grind gauge?
a) Kerbe Stormer
b) Fineness of grind gauge
c) Eccentric wheel
d) PIG
17.
How to determine grinding level on paint using Hegman grind gauge?
a) 5-10 aggregative protect from the surface in 3 mm gap
b) 5-10 aggregative protect from the surface in 2 mm gap
c) 50-100 aggregative protect from the surface in 3 mm gap
d) 50-100 aggregative protect from the surface in 2 mm gap
18.
Viscosity is defined as
a) A fluid’s resistance to flow
b) A liquid thickness
c) The temperature at which a liquid will flow
d) The point at which a liquid becomes solid
89 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
In which temperature Density, Viscosity etc. tests of Paints done
a) 20 ºC ± 0.5 ºC
b) 37 ºC ± 0.5 ºC
c) 100 ºC ± 0.5 ºC
d) Temperature not affected
20.
When temperature increases,__________
a) Viscosity increases
b) Viscosity decreases
c) Viscosity Stable
d) Drying time increases
21.
A Rotational Viscometer measures:
a) Direct Viscosity
b) Centrifugal Viscosity
c) Kinematic Viscosity
d) Dynamic Viscosity
22.
The viscosity of water is said to be approximately:
a) 1 g/cc
b) 1 poise
c) 1 stoke
d) 1 centi-poise
23.
What will be the unit of viscosity of a thixotropic paint?
a)Second
b)Centipoises
c) Ns/m2
d) Stoke
25.
__________ is not a unit of viscosity
a) Stoke
b) Poise
c) Littre
d) Second
90 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
26.
2013
Stroboscope checks
a) Rotation
b) Polarity
c) Potential
d) Aggregate count
27.
Ford flow cup nozzle is made of
a)Aluminum alloy
b) Stainless steel
c)Aircraft alloy
d)Tungsten carbide
28.
_____________ flow cup can be used to check viscosity of hot paint
a) Ford
b) Zahn
c) ISO
d) DIN
29.
Ford Flow cup made of ___________
a) Stainless Steel
b) Aircraft alloy
c) Aluminium
d) Glass Reinforced Plastic
30.
What is the name of vessel used to determine the viscosity of hot fluids, as per BGas
specifications?
a) Ford Flow cup No.4
b) Zahn Cup
c) Abel cup
d) Pyknometer
31.
What is size of hole in Ford Flow Cup?
a) 2 mm
b) 3 mm
c) 4 mm
d) 5 mm
91 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
32.
2013
A Rotothinner measured by:
a) Direct Viscosity
b) Centrifugal Viscosity
c) Kinematic Viscosity
d) Dynamic Viscosity
33.
Capacity of Ford Flow cup
a) 100 cc
b) 50 cc
c) 200 cc
d) 500 cc
34.
Viscosity for a paint is determine to
a) Flow of paint
b) Thinners added to paint over and above recommended
c) Measure the degree of dispersion of paint
d) Measuring density of paint
35.
Density calculated to
a) Flow of paint
b) Thinners added to paint over and above recommended
c) Measure the degree of dispersion of paint
d) Two pack material has been mixed in the correct proportions
36.
Which information is not available in MDS?
a) Flash point
b) Dew point
c) VS%
d) Recommended Thinner
37.
When two pack material used, calculated density valve 1.29 gm/cc, but achieved test result
in 1.35 gm/cc which is more dense?
a) Base
b) Activator
c) Thinner
d) Ratio to be changed
92 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
38.
2013
If 7.5 Liters Paint weighs 9.75 Kg, Relative Density is ______
a) 13.0 gm/cc
b) 13.0gm
c) 1.30 gm/cc
d) 1.3
39.
If Paint in a density cup weighs 135gm, Relative Density is ______
a) 135
b) 13.5gm/cc
c) 1.35
d) 1.35 gm/cc
40.
MDS shows a two pack paint density is 1.35 gm/cc, when the density check completed it
shows the density as 1.25.Which one is true
a) Base Part is High
b) Activator Part is High
c) Mix ratio on MDS is incorrect
d) Activator Part is Low
41.
If 11 Litres Paint Weighs 18 Kg then density =
a) 1.8 gm/cm
b) 1.6 gm/cm
c) 1.1 gm/cc
d) 1.6 gm/cc
42. Fineness of grind is a term used for
a) Premixing
b) Aggregate size
c) Profile roughness
d) PVC
43.
What is the specified temperature at which a Flash Point Determination test must be carried
out?
a) 20ºC
b) Upto 450ºc
c) There is no specific temperature
d) 25ºC seawater
93 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
44.
2013
Which of the following can be used to measure viscosity?
a) A Pyknometer
b) An aspirated psychrometer
c) An Abel closed cup
d) A Zahn cup
45.
Relative density units are
a) gm/cc
b) gm
c) kg/cc
d) None
46.
Density of water
a) 1 gm/cc
b) 2 gm/cc
c) gm
d) None of the above
47.
Dynamic viscosity
a) Centi
b) Centi-poise
c) Poise
d) Stoke
48.
Kinematic viscosity
a) Centi
b) Centi-poise
c) Poise
d) Stoke
49.
Looking at the stated angle is the paint where the surface will change from gloss to matt
a) 5-10 aggregates break through the surface of the paint
b) Measure the degree of dispersion of paint
c) Aggregative are present in all pigmented paints
d) None of the above
94 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
50.
2013
High viscosity is
a) High resistance to flow
b) Not run easily
c) Conversely
d) All the above
51.
Viscosity is a very important property for paint: it affects
a) Manufacturing process
b) Application process
c) Levelingproperties
d) All the above
52.
A device used to measure the degree of dispersion of paint is called
a) A gloss meter
b) A crypto meter
c) A paint inspector gauge
d) A Hegman grind gauge
53.
Approx. viscosity of paint is
a) 1 Centi-poise
b) 1 stoke
c) 2.4 Ns/m2
d) 1.2gm/cc
Density value is 1.29gm/cc calculate value is 1.35 gm/cc So that, Base is high
Density value is 1.35gm/cc calculate value is 1.29 gm/cc So that, Activator is high
95 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
FILM THICKNESSES # 11
WFTs Measurement Types
Eccentric wheel or comb gauges.
Disposable plastic gauges
supplied in small boxes containing several hundred
Stainless Steel gauges
supplied in sets of four in a leather wallet
Destructive test gauges for DFT
1. Paint inspectors gauge (PIG)
2. Ericson Test Drill and Saberg Thickness Drill
Nondestructive test gauges for DFT
Electronic and Magnetic.
1. Magnetic Horseshoe gauge
2. Banana gauge
3. Tinsley pencil or pull of gauge
Abrasion resistance
Equipment for testing paint films → Ericson, Taber and Gardner
Tested for film hardness
Buchholz Indentor & the Sward Hardness Rocker
for hard coatings is the Koenig Albert.
Types of cabinets test
Humidity cabinets
Salt spray cabinets
Water soak tests
Temperature cycling
Prohesion testing
Drying and curing tests
Ballotini test
Beck Koller Stylus test (BK trying time recorder)
96 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Other tests for drying
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Mechanical thumb test
Pencil scratch test (Wolff-Wilborn)
Mechanical scratch test
Gold leaf test
Thumbnail test
Opacity
Adhesion
V cut, Cross hatch Test, Dolly Test
Hydraulic adhesion test equipment ( HATE )
Paint FILM TESTING
a. Salt Spray Box- Marine Condition
b. Water Soak Test- Film Permeability
c. Tropical Box - High Humid Environment.
d. Temperature Cycling- Film Flexibility.
e. Cold Check Testing- Low temperature contraction cracking
97 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
Advantage of eccentric wheel for WFT measurement is
a) Correct DFT can be calculated from result
b) Permanent record
c) No other method for curved surface
d) Can be used for metal spray method
2.
How to use Eccentric wheel on a pipe
a)Perpendicularly
b)Circumferentially
c)Longitudinally
d)Not possible
3.
Which type of Comb gauge is not available?
a) Square
b) Circle
c) Triangular
d) Rectangular
4.
Biscuit Gauge is another name for
a) Hegman’s grind gauge
b) Surface Comparator
c) Banana Gauge
d) Comb Gauge
5.
How to use comb gauge on a pipe
a)Perpendicularly
b)Circumferentially
c)Longitudinally
d)Not possible
6.
If a comb gauge show 120-140 µm, then the actual Dft is
a) 120 µm
b) 130µm
c) 140 µm
d) 120 / 140 µm
98 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Graticule scale is a part of
a) PIG
b) Hegman Grind Gauge
c) Eccentric Wheel
d) Tough type Pfund Crypto meter
8.
Why an inspector use PIG Gauge
a) When substrate is non-ferromagnetic and coating is non-Ferro magnetic
b) When substrate is non-ferromagnetic and coating is Ferro magnetic
c) When substrate is Ferro magnetic and coating is Ferro magnetic
d) When substrate is ferromagnetic and coating is non-Ferro magnetic
9.
A Non Destructive test can be done
a) When substrate contain MIO
b) When substrate is non-ferromagnetic and coating is Ferro magnetic
c) When substrate is Ferro magnetic and coating is Ferro magnetic
d) When substrate is ferromagnetic and coating is non-Ferro magnetic
10.
A Destructive test can be done
a) Ericson test drill
b) PIG
c) Saberg thickness drill
d) All the above
11.
A Destructive test can be done
a) Ericson test drill
b) Pencil scratch test
c) Ballotini teat
d) Dolly test
12.
Sometime Tinsley pencil gauge is called
a) Paint Inspector Gauge
b) Foreman’s gauge
c) Banana gauge
d) Horseshoe gauge
99 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
A Banana gauge works on which principle
a) Magnetic resistance
b) Conductive resistance
c) Tension reluctance
d) Viscosity relativity
14.
Using the correct calibration shim, a banana gauge can be calibrated one
a) Blasted surface material
b) Painted surfaces
c) Steel with a covering of mill scale
d) All of the above
15.
Test for adhesion resistance on paint film
a) Ericson
b) Taber
c) Gardner
d) All of the above
16.
Test for hard coatings
a) dolly test
b) Banana gauge
c) Koenig Albert
d) All of the above
17.
What diameter is the conical mandrel, which is used in the flexibility test?
a) 8 mm to 25 mm
b) 12 mm to 18 mm
c) 5 mm to 50 mm
d) 3 mm to 37 mm
18.
Accelerated test are
a) Water soak test
b) Prohesion test
c) Salt spry cabinets
d) All of the above
100 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
Humidity cabinets conditions are
a) Humidity is very high at 95% and elevated temperatures up to 55oC
b) Humidity is very high at 90% and elevated temperatures up to 55oC
c) Humidity is very low at 95% and elevated temperatures up to 55oC
d) All of the above
20.
In paint testing, why is temperature cycling carried out?
a) To check for water absorption.
b) To check flexibility
c) To check contradiction cracking
d) To prove the service life of the coating system
21. What result will get by Temperature Cycling test?
a) Cracking
b) Blistering
c) Chalking
d) Discoloration
22.
Which of the following do not a drying test?
a) Ballotini test
b) Beck – Koller stylus test
c) Wolff wilborn test
d) Cross hatch test
23.
Which of the following is not a drying test?
a) Koening Albert
b) Beck Koller
c) Mechanical Thumb
d) Ballotni
24.
Which drying test involves the use of smell glass beads?
a) Wolf wilborne
b) Ballotini
c) Koenig Albert
d) Beck Koller
101 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
25.
2013
What is the name given to the drying test involving the use of glass beads?
a) Wolf Wilbrone
b) Taber
c) Ballotini
d) Erichsson
26.
Gold leaf test is used for _________
a) Adhesion
b) Drying
c) Residual tack
d) Dust detection
27.
Degree of Hardness of paint
a) Mechanical thump test
b) Wolff Wilborn Test
c) Gold Leaf test
d) Prohesion
28.
The Pencil Hardness Tests is used to determine which of the following?
a) Scratch hardness of a coating
b) Adhesion of a coating
c) Abrasion resistance of a coating
d) Indentation hardness of a coating
29.
Wet film opacity determined by
a) Cryptometer
b) Wolff Wilborn Test
c) Psychrometer
d) Prohesion
30.
Cryptometer known as
a) Hycrometer
b) PfundCryptometer
c) Psychrometer
d) Prohesion
102 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
31.
2013
What factors can affect Gloss?
a) Resin type, Solvent type, paint application technique
b) Refractive index, pigment colour, DFT
c) Particle size, CPVC, resin type, angle of light incidence
d) Pigment size, resin type, paint colour
32.
Which factor does not affect gloss of a paint film?
a) CPVC
b) Flash Point
c) Particle Size
d) Solvent type
33.
What is area for adhesion failure within a paint system?
a) Primer to substrate failure
b) Inter coat adhesion
c) Cohesive failure
d) All of the above
34.
Which type of test used craft knife?
a) Pencil scratch test
b) V cut Test or cross hatch test
c) Dolly test
d) None of the above
35.
Which of the following tests would be performed to determine the adhesion of a coating?
a) Pendulum rocker
b) Pull off Tape
c) Falling sand
d) Taber abraser
36.
HATE is an abbreviation of what?
a) Heat Affected Tension Expansivity
b) Hydrogen Arc Treatment Effect
c) Hydraulic Adhesion Test Equipment
d) Humidity Affected Temperature Evaluation
103 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
37.
2013
Which of the following is not an adhesion test?
a) Cross Hatch
b) Gold Leaf
c) HATE
d) Dolly test
38.
Which of the following is not an adhesion test?
a) Dolly test
b) Cross hatch
c) Kerbsstormer
d) HATE
39.
Dolly test used to check _____________
a)Hardness
b)Flexibility
c)DFT
d)Adhesion
40.
Pull of Adhesion is a term associated with
a) Tinsley pencil
b) Banana Gauge
c) HATE
d) Dolly Test
41.
If the required DFT is 50µm, then the particle size in the paint should be _____
a)50µm
b)Above 50µm
c)Below 50µm
d)All the above
42.
VS.%relate to
a)Volatile
b)Non volatile
c)Total Paint volume
d)Activator
104 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
43.
2013
What is the volume of paint required to cover a circular area of 15 meters radius, if the
material has WFT of 176µm
a) 76.38 L
b) 124.34 L
c) 214.34 L
d) 31.08 L
44.
What WFT should be measured, if a coating of 88 µm DFT is required with a 66% VS paint?
a) 158 m
b) 75 m
c) 58 m
d) 133 m
45.
What is the actual DFT, if banana gauge shows 335µm when checked on galvanising?
a) 335µm
b) 265µm
c) 235µm
d) 435µm
46.
Reflectometer measures _________
a) Aggregate Size
b) Agglomerates Percentage
c) Gloss
d) Colour
47.
Which of the following would not affect the degree of Gloss?
a) Surface profile
b) Critical Pigment Volume Concentration
c) Solvent type
d) Degree of dispersion
48
Dry film thickness assessment of a point film containing MIO can be carried out
a) Using a Tinsley film thickness gauge
b) By using Calibrated eccentric wheel
c) By reading taken using the paint inspections gauge
d) By using a banana Gauge
105 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
49.
2013
Prior to use, the gauge used to determine DFT must be calibrated,
a) Using sample plate, with a paint coating of known thickness
b) On the prepared surface, before paint application
c) Monthly, by authorized validation Centre
d) In the presence of the site engineer
50.
What DFT should be achievable if the paint with the volµme solid of 54% is ….to WFT
of 135µm?
a) 65 µm
b) 72.9 µm
c) 75 µm
d) 82.9 µm
51.
A paint said to have good opacity will;
a) Have low permeability
b) Have good hiding power
c) Have a low CPVC
d) Have a low minimum gloss value
52.
Minimum WFT and DFT recommendations for paint applications, and advice on the addition
Of thinners etc., can be found:
a) On the label of the paint containers
b)In the project specification
c) On the manufacturer product data sheet
d) In BS 7079 part A
53.
DFT measured using Banana gauge can be carried out on the following:
a) Zinc galvanised surface which have been painted
b)Painted Aluminium substrate
c) Any paint containing MIO pigments
d) In BS 7079 part A
54.
For the WFT measured of a non-ferrous coating on a carbon steel pipe, which of the
following methods would be acceptable?
a) Banana gauge
b)Eccentric wheel used longitudinally
c) Comb gauge used circumferentially
d) Eccentric wheel used circumferentially
106 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
55.
2013
A paint said to have possess low opacity will;
a) Have low permeability
b) Have low hiding power
c) Have a low CPVC
d) Have a low minimum gloss value
56.
The equipment used to measure the hiding ability of paint is called:
a) A Reflectometer
b)A grind gauge
c) A psychrometer
d) A crypto meter
57.
DFT value can be determined by
a) Calculations
b) Destructive test gauges
c) Nondestructive test gauges
d) All the above
58.
Why using plastic shim on DFT measured?
a) Magnetically insulated
b) Correct film thickness
c) Nondestructive test gauges
d) All the above
59.
What type of test using for paint elasticity?
a) Impact test
b) Cupper test
c) Accelerated Test
d) Conical mandrel
60.
What type of test using for assessed for paint damage?
a) Impact test
b) Cupper test
c) Accelerated Test
d) Conical mandrel
107 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
61.
2013
Which test will be done only for paint evaporation?
a) Impact test
b) Flashpoint Test
c) Volatile / Non volatile
d) Conical mandrel
62.
Which paints cannot be measured by flow cup?
a) Thixotropic paints
b) Two pack material
c)Single pack material
d) All the above
63.
WFTs can be measured by using
a) Eccentric wheel
b) Comb gauges
c) PIG
d) A and B
64.
The Electro Magnetic Induction is suitable for
a) Ferro-magnetic substrates
b)Non ferro-magnetic substrates
c) A and B
d) None of the above
65.
The EddyCurrent is suitable for
a) Ferro-magnetic substrates
b) Non-ferro-magnetic substrates
c) A and B
d) None of the above
66.
The Magnetic Coating Thickness gauge
a) Horseshoe gauge
b) Tinsley pencil
c) PIG
d) Banana gauge
108 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
67.
2013
Solvent Evaporation Time, The SolGelTransition,Surface Drying Time and Final Dry Time
are given
a) Ballotini Test
b) Mechanical thumb test
c) BK drying recorders
d) Gold leaf test
109 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SPECIFIED COATING CONDITIONS # 12
Whirling Hygro meter is called
Aspirated Hygrometer or Psychrometer
Steel Temperature – Limpet gauge, pyrometer
Air Temperature – Dry Bulb thermometer
1.
Dew point is defined as
a) The temperature at which water vapour in the air condense
b) The temperature at which paint can be applied
c) The temperature of the steel
d) The temperature at which cross linking will commence
2.
Relative Humidity is defined as
a) The amount of water which is in the air at 25°C, in seawater,
b) The amount of water present in the air, expressed as a percentage of water that could
be in the air that temperature.
c) The temperature at which water vapour will condense
d) Dry bulb temperature measures against Wet Bulb temperature.
3.
A Whirling Hydrometer is also known as
a) A PfundCryptometer
b) A psychrometer
c) A spinning thermometer
d) A rotational viscometer
4.
What is the recommended speed at which a Whirling Hygrometer must travel through the
air?
a) 4 meters per sec
b) 2 mm per second
c) 5 km / hr
d) 100 meters per minute
110 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
5.
2013
When using a Whirling Hygrometer, the wet bulb temperature
a) Should always be read last
b) Will always be above the steel temperature
c) Should always be read first
d) Should not be connected to the wick
6.
The BGas specified conditions for site painting system is
a) Maximum wind sped 4 m/ sec, Relative humidity not less than 95%
b) Maximum 90% relative humidity, dew points less than 3ºC of steel temp.
c) As per BGC/PS/PA8
d) Minimum 27ºC Maximum 95%
7.
The BGas specified conditions for site painting system is
a) Maximum wind sped 4 m/ sec, Relative humidity not less than 95%
b) Maximum 90% relative humidity, dew points above 3ºC of steel temp.
c) Not more than 90% relative humidity
d) Minimum 27ºC Maximum 95%
8.
Steel and Air temperature is always
a) more than 5oC
b) less than 5oC
c) Within 3oC
d) More than 3oC
9.
Air temperature can be calculated by
a) Hygro meter
b) Thermo stat
c) Limpet gauge
d) Strobo scope
10.
The following is not information of Daily report sheet
a) Dew point
b) Relative Humidity
c) Relative Density
d) Air Temperature
111 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
11.
2013
Steel temperature can be measured by
a) Psychro meter
b) Limpet Gauge
c) Thermo meter
d) Horseshoe gauge
12.
Pyro meter is an instrument to check
a) Adhesion
b) Hardness
c) Steel Temp
d) Density
13.
How many seconds frame should be rotated at site?
a) 12-15 seconds
b) 20-25 seconds
c) 30-40 seconds
d) 10-20 seconds
14.
How many times frame should be rotated at site?
a) Only one time
b) 2 times
c) 10 times
d) Many times as is necessary
15.
Two consecutive spins the reading should be
a) Above 0.2oC
b) Within 0.2oC
c) below 0.2oC
d) Above 0.3oC
112 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
16.
2013
During rain, snow, or high winds”. When these conditions do not prevail” or similar, to allow
coating to continue using special products as a
a) Modern sensible paints
b) A Tentative paints
c) A thixotropic paints
d) None of the above
17.
Solvent evaporates very slowly at low temperatures, when
a) the air or metal temperature is down to within 3oC above the dew point temperature
b) the air or metal temperature is below 5oC
c) the relative humidity is more than 90%
d) None of the above
18.
When the relative humidity is more than 90%, using paints
a) Epoxy high build
b) Thermally spray Aluminium
c) Moisture curing polyurethane
d) None of the above
19.
The air temperature and dew point temperature, and wet bulb temperature on the whirling
hygrometer, When are all the same value
a) RH 100 %
b) RH 90%
c) RH 85%
d) RH 35%
113 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
CATHODIC PROTECTION 13
1.
External surface of tank cannot have
a) Electrolytic
b) Cathodic protection
c) Copper/Copper Sulphatehalf-cell electrode
d) Bimetallic
2.
Internal surface of tank canhave
a) Electrolytic
b) Cathodic protection
c) Copper/Copper Sulphatehalf-cell electrode
d) Bimetallic
3. When Cathodic protection is used to protect a pipeline, coatings are applied to
a) Improve the effectiveness of protection.
b) Improve the passage of current flow.
c) Make the pipe easier to inspect.
d) Increase the voltage needed for the CP system.
4.
___________ used to detect the voltage in impressed current system
a) National Grid
b) Transformer Rectifier
c) Copper/Copper Sulphate half-cell electrode
d) Sodium Chloride
5.
Impressed current system used to
a) Protect long length of pipelines a distance of 10 miles
b) Protect short length of pipelines a distance of 1 miles
c) Protect long length of pipelines a distance of 100 miles
d) Protect short length of pipelines a distance of 10 miles
114 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
6.
2013
National Grid connected through
a) pipeline
b) Transformer Rectifier
c) Copper wire
d) Galvanic system
7.
Positive side of the Transformer rectifier connectedto
a) pipeline
b) cathode system
c) ground bed
d) copper wire
8.
Pipe lines are making
a) anode system
b) cathode system
c) A and B
d) None of the above
9.
The voltage required operating the ICCP system?
a) 230V to 240 V
b) 10KV to 50 KV
c) 10V to 50V
d) 10mV 50mV
10.
Copper/Copper sulphates half-cell electrode is used to
a) Monitor CP Voltage
b) Supply current for CP
c) Detect Mill scale
d) Rectify AC to DC
11.
Electrical circuit of the corrosion reaction is the evolvement of hydrogen gas from
a) The Anode
b) The Cathode
c) Electrolyte
d) All the above
115 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
12.
2013
Which solution is used for Cathodic disbondment test?
a) Slightly acidic liquid
b) Salt water
c) Alkaline liquid
d) Distilled water
13.
Galvanic Anode System are called
a) Sacrificial Anodes Systems
b) Impressed Current Systems
c) Cathodic disbondment
d) None of the above
14.
A voltmeter is connected to the stud and to
a) The copper/copper sulphate half-cell
b) Transformer Rectifier
c) Copper wire
d) Galvanic system
116 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
HOLIDAY/PINHOLE DETECTION # 14
1.
When carrying out holiday detection using the sponge tester, what can we add to the water?
a) Salt
b) Detergent
c) Xylene
d) Inhibitor
2.
In FBE coatings greater than 20 thou thickness, holidays are detected using which of the
following?
a) Wet sponge holiday detector
b) Low voltage holiday detector
c) High voltage holiday detector
d) Low voltage DC holiday detector
3.
In FBE coatings less than 500µm thickness, holidays are detected using which of the
following?
a) Wet sponge pinhole detector
b) Low voltage holiday detector
c) High voltage holiday detector
d) Low voltage DC holiday detector
4.
What voltage settings are commonly used for sponge test holiday detection?
a) 5 Kv to 15 KV
b) 15 KvMaximum
c) 9v to 90 v
d) 110v to 240v
5.
What voltage settings are DFT of less than or equal to 300µm?
a) 5 Kv to 15 KV
b) 671/2to 90 v
c) 9v
d) 9v to 90 v
6.
What voltage settings are DFTs of 300-500µm?
a) 5 Kv to 15 KV
b) 671/2 to90 v
c) 9v to 90 v
d) 110v to 240v
117 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT APPLICATION # 15
1.
Basic paint application methods are
a) spray
b) Brushing
c) Roller
d) All the above
2.
What type of application used to welds, internal corners, bolts, rivets?
a) spray
b) Brushing
c) Roller
d) All the above
3.
Which correct equipment used for applying a Stripe Coat?
a) Gravity Cup
b) Roller
c) Paint Brush
4.
d) Spray application
Which paint application cannot use in industry as per PA10?
a) Brush
b) Roller
c) Airless spray
5.
d) Electro-static spray
What are the spray applications?
a) Conventional Spray
b) Airless Spray
c) Electric-static Spray
d) All the above
6.
What are the Conventional spray systems?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Suction Spray
Gravity Spray
Remote pressure spot Spray
All the above
118 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
Most tips are used in airless spray system RAC?
a) Tip life is to be increased
b) Costs can be kept down
c) Blockages can be cleaned
d) All of the above
8.
Paint spray tip sizes, pressure recommendation are generally found
a) On the point container
b) In the project specification
c) On the product data sheet
d) In the British Standards
10.
Which application greatly reduce pinholes?
a) Brush
b) Spray
c) Aerosol
d) Roller
11.
Spray tip with adjustable aperture size known as
a) Carbide
b) Venturi
c) Titan
d) Taber
12.
If an airless spray pump ratio 35;1 delivery pressure 2800.howmuch the inlet pressure
a) 100psi
b) 90psi
c) 80psi
d) 70psi
13.
The main difference between Airless and conventional spray is
a) Conventional spray gives better deposition rate
b) Conventional spray gives less waste
c) Airless spray gives better quality finish
d) Conventional spray gives better atomisation
119 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
14.
2013
How atomisation is achieved in conventional spray
a) Two air channels outside the nozzle
b) Air pressure applied before nozzle
c) Paint forced at high pressure
d) Hydraulic pressure
15.
If metal spray applied on a thin steel plate,
a) Plate should not be heated
b) Plate should be preheated
c) Plate should be post heated
d) Cannot be applied
16.
In the electrostatic spray painting process, the component must be
a) Positively charged
b) Negatively charged
c) 9 Volts DC
d) 15 Kv DC
17.
Which application method provides uniform film thickness?
a) Stripe coat
b) Airless Spray
c) Conventional spray
d) Electrostatic spray
18.
In Electrostatic spray, the thickness of paint film is controlled by
a) Time used to spray
b) Delivery Pressure
c) Orifice Size
d) Voltage
19.
Which of the following is often applied by electrostatic spray?
a) Zinc-rich epoxy
b) Powdered epoxy
c) Coal tar enamel
d) Epoxy grout
120 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
20.
2013
Which of the following is a disadvantage of electrostatic spray?
a) Poor coverage
b) Excessive overspray
c) Generally only one coat can be applied
d) Non-uniform film thickness
21.
Which paint application have “Insulation” effect
a) Airless Spray
b) Remote Pressure pot
c) Dip coating
d) Electrostatic spray
22.
Padding refers to what?
a) Protection for pipes during transport & storage
b) Protective clothing for TSA application
c) A paint application method
d) Material used to soak spillages
23.
Shearing Action produced by application of
a) Roller
b) Brush
c) Spray
d) Padding
24.
The relevant pain application information for any particular paint, product, such as paint
spray, tip sizes, pressure recommendation, etc are generally found
a) On the paint containers
b) In the project specification
c) On the Product data sheet
d) In the British Standards
25.
A common system for applying Hot metal spray coating is:
a) Conventional spray gravity cup
b) A gun containing fuel gas, oxygen and compressed air
c) High pressure airless spray system
d) Plural component pumps and gun
121 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
26.
2013
Round headed brushes called
a) Flat brush
b) Round brush
c) Tar brush
d) All the above
122 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
METAL COATINGS # 16
1.
Nuts and Bolts can be coated by
a) Calorising
b) Galvanising
c) Sheradising
d) Anodising
2.
At which temperature Aluminium melts
a) 100 oC
b) 240 oC
c) 425 oC
d) 625 oC
3.
At which temperature zinc melts
a) 100 oC
b) 240 oC
c) 425 oC
d) 625 oC
4.
Mostly offshore and onshore using metal coats
a) Sheradising
b) Calorising
c) Anodising
d) Galvanising
5.
To be done by immersing a component in a mix of fine sand and Aluminium powder and
heating
a) Sheradising
b) Calorising
c) Anodising
d) Galvanising
123 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
6.
2013
An electrolytic method of coating which results in the formation of a dense oxide
a) Sheradising
b) Calorising
c) Anodising
d) Galvanising
7.
Hot metal spraying are using temperature at
a) 625oC
b) 540oC
c) 425oC
d) 450oC
8.
The use of sealer to improve the performance and prolong the coating life with which of
the following coating systems
a) Polysiloxane
b) Polyurethane
c) Thermal metal spraying
d) Electrostatic spraying
9.
Thermally Sprayed Aluminium is not normally applied by which system?
a) Electric arc Spray
b) Sheradising
c) Wire & Pistol
d) Electro – plating
124 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
COATING FAULTS #17
1.
Addition of thixotropic helps to avoid _________
a) Blistering
b) Sagging
c) Cracking
d) Flaking
2.
Which coating fault occurs when over thinning paint?
a)Pinholes
b)Run
c)Spot rusting
d)Hair cracking
3.
Which fault relate to Peeling?
a)Orange peel
b)Flaking
c)Wrinkling
d)Cracking
4.
Which fault can be avoided when bitumen removed from paint system?
a)Bittiness
b)Blistering
c)Cracking
d)Bleeding
5.
Chalking occurs due to
a)Coating age
b)Weathering
c)Shelf life problem
d)Hygroscopic salts
6.
Which fault happens when over apply zinc silicate
a)Sagging
b)Run
c)Mud cracking
d)Holidays
125 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
A coating fault which resembles holidays
a) Checking
b) Cratering
c) Crazing
d) Cissing
8.
Over thickness of Zinc silicate cause
a) Sagging
b) Mud Cracking
c) Curtaining
d) Cohesive failure
9.
Ropiness is fault look like
a) Roller Stiple
b) Rivelling
c) Brush Marks
d) Blisters
10.
Which one is not a Paint Fault?
a) Grinning through
b) Efflorescence
c) Cracking
d) Bittiness
11.
Paint defect which their appearance is like a citrus of fruits skin.
a) Wrinkle
b) Shagging
c) Fish Eye
d) Orange peel
12.
Which coating fault will look like discoloration?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Chalking
Bleeding
Cissing
Curtaining
126 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
13.
2013
Efflorescence is
a) a weak surface layer of water-rich cement.
b) An oil reaction with alkalinity to make a soap.
c) Moisture passing through the concrete and carrying soluble concrete salts
d) Ice crystals on the surface
14.
Where bleeding is evident on a pipe which was previously coated with coal tar, the staining
would be which colour?
a) Black
b) Brown
c) Yellow
d) Red
15.
Lifting of coating material from surface is ______
a)Wrinkling
b)Lifting
c) Flaking
d)Mud cracking
16.
Paint defect which name is Fish Eye always causes by
a) Over Thickness
b) Substrate contains with oil
c) To much thinner
d) Using wrong mixing solvent
17.
Where paint particles fall outside the spray pattern, resulting in a dry, flat, pebbled
appearance, this is known as
a) Orange peel – flocculation
b) Dry spray-over spray
c) Floatation – flocculation
d) overspray-floatation
18. Inclusion, either airborne or from the paint itself?
a) Grinning through
b) Efflorescence
c) Cracking
d) Bittiness
127 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
Degradation of a binder due to disruptive factors in the environment is ______
a)Wrinkling
b)Lifting
c) Chalking
d)Mud cracking
20.
Gas, liquid or crystals are filled with ______
a)Wrinkling
b) Blisters
c) Flaking
d)Bittiness
21.
Where bleeding is evident on a pipe which was previously coated with bitµmen’s, the
staining would be which colour?
a) Black
b) Brown
c) Yellow
d) Red
22.
The presence of particles of gel, flocculated material or foreign matter in a coating material,
or projecting from the surface of a film.
a) Grinning through
b) Efflorescence
c) Cracking
d) Bittiness
23.
Sometimes forms on the floss film of a coating causing loss of gloss and dulling of colour
a) Efflorescence
b) Cracking
c) Bittiness
d) Bloom
128 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
24.
2013
Cracking that comprises of fine cracks, which may not penetrate the top coat, they occur
erratically and at random
a) Efflorescence
b) Cracking
c) Bittiness
d) Hair cracking
25.
cracking that comprises of fine cracks, which do not penetrate the top coat and are distributed
over the surface giving the semblance of a small pattern.
a) Cracking
b) Hair cracking
c) Checking
d) Mud cracking
26.
Cracking that resembles checking but the cracks are deeper and broader.
a) Crazing
b) Hair cracking
c) Checking
d) Mud cracking
27.
A drastic type of crazing producing a pattern resembling the hide of a
a) Crazing
b) Hair cracking
c) Crocodile
d) Mud cracking
28.
Where there is a complete absence of coating materials on random areas of the substrate
a) Ropiness
b) Holidays
c) Lifting
d) Mud cracking
129 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
COLOUR # 18
Hue
basic colour red, yellow, green and blue
Clockwise, red→ yellow →blue
Brightness
amount of lightness or darkness of the colour
degree of reflectivity
Saturation
How vivid colour appears
difference of a colours
Lower saturation, greyer the colour
Black and white and the greys in between are called “achromatic” colours
Other colours called “chromatic”
Colours clock also called three dimensional model of a helix.
The Munsell colour system
Having five basic colours→ Red, Yellow, Green, Blue and Purple
The BS 4800 colour system
Lightness is identified by capital letters A to E
A is Maximum lightness
E is minimum lightness
BS 5252, framework for colour co-ordination for building purposes
1.
What is BS 4800 specifies
a) Colour co-ordination
b) Specification of abrasive size sieves
c) Methods of test for paints
d) Glossary of paint and related terms
2.
What is 3 attributes which make up the colour of a paint?
a) White, black and colour
b) Hue, Brightness and saturation
c) Red, Yellow and Blue
d) Contrast, Density, and Definition
130 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
3.
2013
Which of the following are primary colours?
a) Blue Yellow and Green
b) Red Green and white
c) Red White and blue
d) Red Yellow and Blue
4.
In colour attributes, Brightness also referred by the term
a) Chroma
b) Intensity
c) Value
d) Weight
5.
Chroma, Intensity, Weight are used
a) Hue
b) Brightness
c) Saturation
d) All the above
6.
Hue refers to what?
a) Amount of lightness or darkness
b) Basic colour
c) How vivid colour appears
d) All the above
7.
Saturation refers to what?
a) Amount of lightness or darkness
b) Basic colour
c) How vivid colour appears
d) All the above
8.
Black White Grey is
a) Vivid Colour
b) Achromatic
c) Chroma
d) Basic colour
131 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
9.
2013
Which of the following is not a system for paint color classification?
a) BS 4800
b) BS 5252
c) Munsell
d) BGC/PS/CW5
10.
Which of the following is pipe colour coding?
a) BS 4800
b) BS 5252
c) BS 1710
d) BGC/PS/CW5
11.
How is the brightness of colour identified in BS 4800?
a) By Numbers 0-24
b) By Numbers 01-56
c) By letter A-E
d) By letter E-M
12.
RAL Number represents
a) Batch Number
b) Thinner Code
c) Colour Code
d) Solvent Code
13.
How is the Hue of colour identified in BS 4800?
a) By Numbers 0-24
b) By Numbers 01-56
c) By letter A-E
d) By letter E-M
14.
How is the saturation of colour identified in BS 4800?
a) By Numbers 0-24
b) By Numbers 01-56
c) By letter A-E
d) By letter E-M
132 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
HEALTH AND SAFETY # 19
OEL examples of some solvents
Solvent
Name
Aromatics
Aliphatic
Chlorinated
hydrocarbons
Alcohols
Ketones
Esters
1.
Xylene
Toluene
White Sprit
Hexane
Trichloroethane
Trichloroethylene
Methanol
Ethanol
Acetone
Methyl ethyl
ketone
Methyl acetate
Ethyl acetate
OEL in
ppm
100
50
100
500
350ab
100ac
200
1000
750
200
200
400
COSHH abbreviation
a) Control of Substance Hazardous to Health
b) Central of Substance Hazardous to Health
c) Control of Substance Hazardous to Help
d) Control of Substance Health to Help
2.
Which warning symbol represents Toxic
a)
Answer: B
3.
b.
c.
d.
This is the hazard warning symbol for
a) Toxic or Very Toxic
b) Harmful or irritant
c) Corrosive
d) Explosive
133 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
4.
2013
This is the hazard warning symbol for
a) Toxic or Very Toxic
b) Harmful or irritant
c) Corrosive
d) Explosive
5.
Who is having duty of Safety on a Working site (or) which person on site is responsible for
site safety?
e) HSE (Health & safety executive)
f) Contractor
g) Engineer
h) Employees
6.
The document issued by the HSE listing all known harmful substances, is
a) COSHH
b) SI 1657
c) EH40
d) IGE SR 21
7.
RAQ is an abbreviation of what?
a) Required Adherence Quota
b) Repair Area qualification
c) Required Air Quantity
d) Required Acceptance Quality
8.
Every depression is RAQ
a) 100 ppm
b) 500 rpm
c) 100 cc
d) 500 cc
134 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
9.
2013
In dragger tube Number specified is n=5, what is RAQ
e) 500 ppm
f) 5 rpm
g) 500 cfm
h) 500 cc
10.
After depressions the colour change is from white to
a) red
b) brown
c) reddish brown
d) black
11.
Which would be considered to be the most toxic?
a) Acetone
b) Xylene
c) Ethanol
d) Toluene
12.
When testing for Xylene using a Dragger Bellows, the crystals will charge colour.
a) Orange to Black
b) White to Red/Brown
c) White to Green
d) White to Black
13.
Expansion for PPM
a) Parts per million
b) Pounds per million
c) Parts per mill
d) None of the above
135 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DUTIES OF AN INSPECTOR # 20
As inspector what do you consider as your main responsibilities?
a) To asses the condition of substrate prior to treatment
b) To inspect surface preparation in accordance with BS 7099: measure and record
amplitude once in daily.
c) To ensure material used on site are to client’s specification.
d) Relative humidity, dew point, air temperature, metal temperature to be checked and
recorded at least four times daily.
e) Wet and dry film thickness to be checked and recorded frequent intervals.
f) To witness and and inspect application of each coat and inspect completed paint system in
accordance with the clients specification and good paint inspection practice.
g) To submit daily and weekly reports recoding all the relevant information as required by
the client. Copies to be retained by inspector.
1.
Which of the following is regarded as the duty of a panting Inspector?
a) Record Dew point, Relative Humidity & Monitor addition of Thinners
b) Check surface profile, cleanliness and make choice of paint color
c) Control of Abrasive type, blasting pressure and selection of personnel
d) Control of paint storage, appearance of finish, and painter’s timesheets
136 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
LIST OF SPECIFICATION AND BS NumberS 21
1.
Internal coating of pipeline comes under
a) PA7
b) PA8
c) PA9
d) PA10
2.
Methods of test for paints.
a) BS410
b) BS3900
c) BS7079
d) PA10
3.
Schedule of paint colours for building purposes.
a) BS4800
b) BS3900
c) BS7079
d) PA10
4.
Preparation of steel substrates before application of paints and related products
a) BS4800
b) BS3900
c) BS7079
d) PA10
5.
Visual assessment of surface cleanliness
a) BS4800
b) BS3900
c) BS7079
d) BS 7079 Group A
137 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
6.
2013
Methods of assessment of surface cleanliness
a) BS4800
b) BS 7079 Group B
c) BS7079
d) BS 7079 Group A
7.
Surface roughness characteristics of blast cleaned steel substrates
a) BS4800
b) BS 7079 Group B
c) BS7079 Group C
d) BS 7079 Group A
8.
Method of Surface Preparations
a) BS 7079 Group D
b) BS 7079 Group B
c) BS7079 Group C
d) BS 7079 Group A
9.
Paint properties and performance requirement
a) PA7
b) PA8
c) PA9
d) PA10
10.
The British standard for painting inspection?
a) BS 3900
b) IGE SR 21
c) BS 7079
d) ISO 8501
11.
Indentor test can be used to check?
a)
b)
c)
d)
EPA ( Environment Protect Act)
IGE / TD / 05
BS 7079
IGE SR 21
138 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
QUALITY #22
Manufacturer’s data sheet;
Product description, Recommended use, Technical information, Application data, Condition during
application, Drying and curing time, Recommended painting system, Storage and packing, Health
and safety
Product Data Sheet --- Information’s
Service temperature
Colour Code
Volume Solid
Spreading Rate
Flash Point
Specific gravity
VOC
Mixing Rating
Paint Application method
Thinner
Pot life
Nozzle orifice
Nozzle pressure
DFT, WFT
Issued Date
139 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT APPLICATION (PA 10) # 23
The Condition for final surface preparation:When conditions in the working area are such that metal surfaces are moist, damp or wet, final
preparation shall not be carried out.
-
Any surface preparation procedure or method of cleaning shall not be allowed to
contaminate wet paint film.
-
Equipment used shall be of non-sparking type.
-
Electrically operated tools are not permitted.
-
Power tools operated by compressed air shall have oil trap vapour trap fitted to the
compressed air lines.
-
All contaminants shall be removed by means of an approved solvent.
-
Allage and mould growth when in evidence shall be treated with biocide agent and left
for at least 24 hours in order that the biocide can kill the spores. It shall then remove by
scrubbing with stiff bristles brushes and clean water or by use of high pressure water
wash.
-
All surfaces shall normally be dry before painting commences.
Condition for application of paint as per PA 10 :Paint shall normally applied when
a) the RH % is less than 90%
b) the air and metal temperature is at least 3 deg C above the DP
c) Ambient and substrate temperature should not be below the set out by the paint
manufacturer for particular paint.
d) Paint shall not normally apply when conditions in the working zone are such that the
working surface becomes moist or damp during the painting operations.
e) Painting equipment’s shall be used in accordance with the paint manufacturer’s
recommendations.
f) All paint shall be applied in order to produce a firmly adhering continuous film, free from
misses, runs tears, sag etc.
g) Stripe coating shall be carried out to welds edges etc in order to achieve a full paint film
thickness as specified.
140 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
h) All painted areas must be thoroughly dry before being over coated and any contamination
of the paint film should be removed before further coats are applied.
i) Final coating shall be free from significant visible imperfection.
Health and safety
1) What document state health and safety at work?
H.A.S.W.A. : - hazardous and safety at work act1974.
2) What year was the health and safety act passed?
The control of substances hazardous to health regulations 1988 come in to force 1 st October
1989(COSHH regulations).
4) How long would be records of examinations monitoring test for five years and 30 years for
identifiable employees.
5) EPA – environmental protection act waste material disposal
What additional information you should need when maintenance painting a pipeline without
removing the existing coating
The following additional information to be recorded is.
-
Nature of the existing system must be established to decide the type of
preparation to be commenced.
-
Amount of surface contamination.
-
Extent of corrosion.
-
Extent of paint breaks down.
-
Compatibility of the existing system with the new system. if not compatible
select the appropriate tie coat.
-
In service environmental condition.
141 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION FOR
NEW AND MAINTENANCE PAINTING AT WORKSAND SITEFORABOVEGROUND
PIPELINEANDPLANT INSTALLATIONS
This Specification specifies procedures for painting the surfaces of all types of ferrous and non-ferrous
metal engineering components.
PA -10use in the following areas not suitable
a) below ground (buried)
b) offshore installations
c) internal coatings of pipes
d) stove enamel coatings
surface preparations and methods of application to be used in the particular applications. Only the
relevant SPAs need to be taken into account for a particular painting system.
Site safety requirements
All work carried out on the site shall comply with good safe working practice and the specific conditions of a
Permit to Work where issued on an operational site
Safe working areas - proper use and erection of scaffolding, ladders, etc
Safety requirements associated with abrasive blast cleaning
Identification of coating materials - with reference to any associated hazards such as toxicity,flammability,
etc.
Compliance with fire regulations - storing of combustible materials
Safe handling of coating materials and safety precautions on site
Environmental requirements
storage and disposal of paint
waste materials shall be in accordance with the current environmental requirements.
Contractor shall be alerted of the possible toxic nature of the deposits
paint debris
the appropriate action and Certification required for their disposal.
Purposes of this specification
compliant coating: a coating which complies with the requirements of the Environmental Protection Act1990.
Contractor: the Contractor's personal representatives, successors and permitted assigns.
damp surfaces: surfaces on which water is not readily detectable but of which the temperature is below the dew
point.
dew point: the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the water vapour in the air is equal to the saturation
vapour pressure over water.
142 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
fully weathered galvanizing: a galvanized steel surface on which a cohesive oxide layer has formed by natural
weathering. The surface will normally be dull and lacking in metallic sheen.
hot duty surfaces: metal surfaces on the assembly that will attain a temperature of 100 0 C or above during use.
short term protection: typically two years to three years life.
medium term protection: protection typically lasting five years.
long term protection: protection typically lasting ten years.
moist surfaces: surfaces from which standing water and droplets have been removed but on which there is a
noticeable film of water.
pot-life: the Maximum time during which a coating material supplied as separate components should be used after
they have been mixed together.
Transco: Transco - a part of BG plc.
T-wash: a non-proprietary material used as a primer or pretreatment for zinc metal surfaces.
Earliest stages of painting or re-painting
cost effective method(s) of surface preparation.
cost effective paint system(s) to give the required service life
Maintenance/re-painting
a) The existing paint system.
b) The extent of breakdown and corrosion.
c) The in-service environmental conditions.
d) The nature and extent of any surface contamination.
General conditions for Contractor
Clear information about contract, specification of job
Specified for SPAs
Method of Surface preparations
Painting system to be applied
Programme of work must be prepared and will get permission from Engineer
Listed of Paints in separate items on the contract document
Inspection
All painting shall be subject to inspection and no deviation from the requirements of this specification will be
permitted, unless previously agreed with the Engineer.
Independent inspection shall not in any way relieve the Contractor of his responsibilities under the terms or
conditions of the contract.
Detailed records of the surface preparation and paint system applied to any given structure shall be kept together
with the results of the inspection and testing carried out.
143 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Test areas
Contractor may be required to prepare and paint test areas to
correct quality of surface preparation
satisfactory film thickness
finish to the paint film is obtained.
equipment and techniques used for the accepted surface preparation
application of paint to the test areas shall be representative of those to be used for the main painting work.
Access equipment
particular importance that reference is made to Appendix B
Until approval has been given by the Engineer, fixed access equipment shall be left in position
Any movable equipment required (ladders, towers, etc.) shall remain on site and be readily available for
use.
Equipment to be protected and masked before preparation and painting
Masked are
fire protection equipment
weld end preparations
atmosphere sensing heads
spray heads
vents on control equipment
flame traps
lubrication points and nameplates
Contractor shall be responsible for removing all masking materials
Paints containing metallic zinc
Special care shall be taken to ensure that paints containing metallic zinc
zinc-rich paints are not allowed to contaminate stainless steel for reason is cause embrittlement
not be applied within 75 mm of weld end preparation
to avoid vapourisation of zinc during welding
Preparation of surfaces
Conditions for final surface preparation
metal surfaces are moist or damp, final surfacepreparation shall not normally be carried out.
surface preparation or cleaning method shall not be allowed to contaminate wetpaint films.
Equipment used on sitein sparks less.
Electrically operated tools shall not normally be permitted on site.
Power tools operated by compressed air shall have oil and vapour traps fitted to the compressed air lines.
Before surface preparation shall be removed by washing with an appropriate solvent.
Biocidal Agent
All algae and mould growth shall be treated with a biocidal agent and left for a minimum of 24 hours.
It shallthen be removed by scrubbing with stiff bristle brushes and clean water or by use of high pressure water
washing.
Abrasive blast cleaning methods
Safety requirements associated with abrasive blast cleaning shall comply with IGE/SR/21.
The type of abrasive used of not less than 30 μm and not greater than 75 μm
144 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
The profile shall be measured using Testex replica tape
Non-metallic abrasives shall be of a silica free type
Air for blasting shall be clean, dry and oil free
Abrasive used in an open blast system shall be of the expendable typeand re -use not permitted.
closed blasting system (e.g. vacuum blasting) may also be re-use of abrasives shall be permitted the size of
the abrasive.
Wet blast systems shall be used for the removal of lead-based paint.
wet blasting, dry blasting shall be carried out to remove any subsequent flash rusting.
The scrapers shall be of the type having a carbide tip
using a needle gun to ensure that the profile of the surface shall not exceed 100 μm
needle gun are rogue peaks shall be removed
weld fluxand spatter shall be removed prior to painting operations
large areas consideration shall be given to the use of low pressure water detergent washing prior to
painting.
Storage of paints
conditions recommended by the paint manufacturer
accordancewith the appropriate fire regulations
On operational sites approved by theEngineer.
Pot life of paint time referred after mixing paint used time.
APPLICATION OF PAINT
Relative Hµmidity in the work zone is less than 90% / air and metal temperatures are at least 3 o C above the dew
point.
Paint shall not normally be applied moist or damp during the painting operation.
Stripe coating shall be necessary to achieve the required dry film thickness (DFT) at edges and to ensure
coverage of weld profiles.
MEASUREMENT OF PAINT THICKNESS
paint thickness shall be accordance with procedures in BS 3900: Part C5
Quality control thickness measurements of paint films containing micaceous iron oxide (MIO) pigment
Over coating ( paint film) measured by wet film thickness gauge (e.g. comb gauge).
The wet film thickness needed to achieve the specified DFT differs from paint to paint.
145 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Treatment of contaminated paint film
Contaminations
Treatment
Loose paint particles, rust, debris and other atmospheric
contamination or salt deposition
Wash down using soft nylon brushes and clean water.
Drythoroughly
Oil or grease
Brush and wash with an appropriate solvent then scrub
with a 2%solution of detergent in clean water. Wash
with clean water and drythoroughly
Foreign materials (e.g. shot or grit) embedded in the
paint film
Re-prepare the affected areas and re-apply the complete
paintingsystem
SPECIFIC PAINTING APPLICATIONS (SPAs)
NEW AND MAINTENANCE PAINTING FOR LONG TERM PROTECTION OF
INSTALLATIONS AND COMPONENTS( SPA1)
SPA1 applies to the painting at works or site of new installations and components and to site
maintenance painting of carbon steel surfaces operating below 100 0 C.
SPA1 shall apply to:
a) Part painting of new components at works
b) Completion at works or site of components part painted at works
c) Site painting of uncoated and unsuitably coated surfaces
d) Site maintenance painting
Before preparation and painting commences, those surfaces not to be painted shall be masked
Each coat of paint shall be of a contrasting colour to the previous coat
PREPARATION FOR PAINTING OF ------ UNCOATED OR UNSUITABLY COATED
SURFACESAT WORKS OR SITE ----- TABLE SPA1a
All mill scale, corrosion products and, where applicable, unsuitable existing paint and coatings shall be
removed from the surface.
The surface finish at the time of painting shall be equivalent to BS 7079 Sa 2 ½ quality and have a profile within the
range of 30 μm and 75 μm . This shall normally be achieved by blast cleaning.
146 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
UNCOATED OR UNSUITABLY COATED SURFACES ------ TABLE SPA1a
Operation
Number
1
2
Subject of
operation
Mask areas
Blast clean
Comments
BS 7079 Sa 2½ quality; Maximum
profile 75 µm
Relevant clauses in PA10
Equipment protect
Abrasive blast cleaning
3
Clean all surfaces
Immediately prior to primer
application
Surface preparation of weld area
4
Apply primer
Dry film thickness dependent
upon system (see Table SPA1e)
Application paint & measurements
5
Apply Micaceous
iron oxide
Dry film thickness 75
µmminimum
Over coat
PREPARATION OF PAINTED SURFACES WITH LIMITED COATING DAMAGE
Procedure (see also Table SPA1b) shall be applied where slight damage to the factorycoating has occurred
duringtransport and/or storage.
Methodof cleaning shall be by mechanical wire brushing.
The edges of the existing remaining coating shall be feathered.
COATING DAMAGE ------- TABLE SPA1b
Operation
Number
1
2
3
Subject of
operation
Mask areas
Mechanically wire
brush and feather
edges
Clean all surfaces
4
5
Comments
BS 7079 St3 quality as minimum
Relevant clauses in PA10
Equipment protect
Manual mechanical methods
Immediately prior to primer
application
Surface preparation of weld area
Apply primer
Dry film thickness dependent
upon system (see Table SPA1e)
Application paint & measurements
Apply Micaceous
iron oxide
Dry film thickness 75
µmminimum
Over coat
147 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
FINAL COATING
On completion of painting must be the final coating.
One coat of finish shall be applied, by brushing or spraying to a DFT specified.
The final coating shall have an acceptable uniform appearance and shall be free from cosmetic defects
FINAL COAT -------TABLE
Operation
Number
1
Subject of
operation
Clean all surfaces
2
3
SPA 1c
Comments
Relevant clauses in PA10
Immediately prior to primer
application
Surface preparation of weld area and final
coat
Apply undercoat
Dry film thickness dependent
upon system (see Table SPA1e)
Application paint & measurements and under
coat
Apply finish
Dry film thickness dependant
upon system
Finish coat
MAINTENANCE PAINTING -------TABLE SPA 1d
APPLICATION OF PAINT TO PREPARED SURFACES
For paint applied at works the preferred system is a high solids solvent based epoxy primer and epoxy MIO
Coat
One coat of primer shall be applied, by brushing or spraying as appropriate, to all prepared exposed metal
within 4 h of metal preparation and before any rust blooming or contamination of the surface occurs
The paint shall overlap onto any existing coating by at least 100 mm.
Over coating is normally carried out within three months of the application of the MIO coat and in
Accordance
PREFERRED SYSTEMS ---- TABLESPA1e
Stage
1
2
3
4
Total
Compliant solvent-based
High build epoxy Aluminium primer
Epoxy Micaceous iron oxide
High build epoxy undercoat
Epoxy or polyester acrylic finish
Minimum dry film thickness
(µm)
75
75
75
40
265
148 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
Stage
1
2
3
4
Total
Water-borne acrylic
Primer
Micaceous
Undercoat
Finish coat
2013
Minimum dry film thickness
(µm)
50
75
50
50
225
NEW AND MAINTENANCE PAINTING FOR INDOOR USE OR SHORT TERM
PROTECTION(SPA2)
SPA2 applies to new and maintenance painting for indoor use or short term protection of carbon steel
surfaces operating below 100oC
Surfaces shall be prepared as requirementsof BS 7079 St 3 quality as a minimum
TABLE SPA2a - Operation chart for new painting for INDOOR USE & SHORT TERM
PROTECTION
TABLE SPA 2b - Operation chart for maintenance painting for INDOOR USE &
SHORT TERM PROTECTION
PAINTING OF METAL SURFACES FOR HOT DUTIES --- (SPA3)
SPA3 applies to the painting of surfaces which are likely to operate at 100 0 C or above.
Areas where the operating temperature of the metal surface is likely to reach, but not exceed, 149 0 C shall
be painted.
Areas where the operating temperature of the metal surface is likely to exceed 149 0 C and 340 0 C shall be
Protected
FOR DUTIES AT TEMPERATURES FROM 100 0 C TO 149 0 C (TABLE SPA3a)
All surfaces not to be painted shall be masked
all surface contaminants shall be removed by washing
Mechanical cleaning in accordance ( blast cleaning )
Applying Aluminium pigmented epoxy or urethane primer
Paint shall be applied within four hours of blast cleaning but before any rust blooming or contamination
occurs
over coating times, further coats of primer shall be applied to achieve a total minimum DFT of 100 μm for
urethane or 250 μm for the epoxy
Heat resistant paints are normally pigmented with Aluminium flake, therefore a finish to a designated
colour may not be possible
149 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
Operation
Number
1
2
3
Subject of
operation
Mask
Remove surface
contamination
Blast clean
4
Apply primer
5
Apply additional
coat of primer
Comments
2013
Relevant clauses in PA10
Equipment protect / masked
Surface preparation by washing
BS 7079 Sa2 ½ quality,
Maximum profile 75 µm
Dry film thickness depends on
primer used
Dry film thickness depends on
primer used
Preparation for painting
Aluminium pigmented epoxy or urethane
primer
Over coat minimum DFT of 100 μm for
urethane or 250 μm for the epoxy
FOR DUTIES AT TEMPERATURES FROM150 0 C TO340 0 C (TABLE SPA3b)
Thermally sprayed Aluminium (TSA) shall be applied to prepared surfaces in accordance with BS EN
22063 and/or BS 2569: Part 2.
TSA is deemed to be impractical due to operational restraints for this high temperature.
Use of paint systems based on inorganic zinc silicate or polysiloxane primers –manufacturer
recommendations
Withthe use of inorganic zinc silicate, mud cracking of the coating may result–manufacturer
recommendations
Operation
Number
1
2
3
Subject of
operation
Mask
Remove surface
contamination
Blast clean
4
Apply system
1
TSA
2
Inorganic Zinc
silicate
polysiloxane
Inorganic primers
3
Comments
Relevant clauses in PA10
Equipment protect / masked
Surface preparation by washing
BS 7079 Sa3quality, Maximum
profile 75 µm
System chosen from below lists
Abrasive blast cleaning / Preparation for
painting
inorganic zinc silicate or polysiloxane
primers
Optional systems
accordance with BS EN
22063 and/or BS 2569: Part 2.
Must be applied TSA
Manufacturers recommendations
inorganic zinc silicate
Manufacturers recommendations
polysiloxane primers
FOR DUTIES AT TEMPERATURES ABOVE 340 0 C (TABLE SPA3c)
Thermally sprayed Aluminium (TSA) shall be applied to prepared surfaces in accordance with BS EN
22063 and/or BS 2569: Part 2.
TSA is deemed to be impractical due to operational restraints for this high temperature.
use of paint systems based on inorganic zinc silicate or polysiloxane primers –manufacturer
recommendations
With the use of inorganic zinc silicate, mud cracking of the coating may result–manufacturer
recommendations
TSA and inorganic zinc silicate primers are used, they shall be sealed with a high temperaturesealer.
Sealers shall be applied and cured in accordance with the manufacturers' recommendations
150 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
Operation
Number
1
2
3
Subject of
operation
Mask
Remove surface
contamination
Blast clean
4
Apply system
4a
TSA
b
c
Apply sealer
Apply heat to cure
sealer
5a
Inorganic zinc
silicate
Apply sealer
Apply heat to cure
sealer
b
c
6a
Polysiloxane
inorganic primer
Comments
2013
Relevant clauses in PA10
Equipment protect / masked
Surface preparation by washing
BS 7079 Sa3quality, Maximum
profile 75 µm
System chosen from below lists
Abrasive blast cleaning / Preparation for
painting
inorganic zinc silicate or polysiloxane
inorganic primers
Optional – TSA system
accordance with BS EN
Must be applied TSA
22063 and/or BS 2569: Part 2.
Manufacturers recommendations Apply High temp. sealer
Manufacturers recommendations Apply High temp. sealer
/ check plant operating
instruction
Optional-Inorganic zinc silicate system
Manufacturers recommendations Paint system inorganic zinc silicate
Manufacturers recommendations inorganic zinc silicate
Manufacturers recommendations inorganic zinc silicate
/ check plant operating
instruction
Optional-polysiloxane system
Manufacturers recommendations Must be applied polysiloxane inorganic
primer
TSA system will provide longest service life.
PAINTING OF DAMP FERROUS SURFACES – SPA 4
This SPA4 applies to the painting of ferrous surfaces on which the presence of condensation during
painting cannot be operationally prevented
A Number of paint systems are available which are tolerant to damp surfacescannot be used on wet
surfaces.
They shall not be used when ice is present, or where the surface temperature is likely to be below 3 0 C.
Types of materials which are known to perform satisfactorily on damp metal surfaces are:
a) Moisture curing polyurethanes.
b) High solids multi-component epoxy paints.
Any oil or grease shall be removed by swabbing with grease removing solvents. The surface shall
subsequently be washed with a 2% detergent solution
All surfaces shall be blast cleaned to achieve BS 7079 Sa 2 ½ quality immediately
a degree of rust blooming is acceptable
the manufacturers' instructions shall be followed
Immediately prior to painting, all droplets and standing water shall be removed from the surfaces to be
painted by mopping or using a squeegee. Cloths or rags shall only be used if they are lint-free.
All grit and dust shall be removed from the blast-cleaned surface by washing with clean water
All paints shall be brush applied.
151 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINTING OF DAMP FERROUS SURFACES – SPA 4
Operation
Number
1
Subject of
operation
Remove all surface
contamination, etc.,
2
3
Blast clean
Wash
4
Remove droplets
and standing water
Apply system
5
Period before
next operation
Maximum 4 hrs
In accordance
with
manufacturer’s
instructions
Comments
BS 7079 Sa 2 ½ quality
To remove all grid &
dust
Surface shall not be wet
To be applied by
brushing
Relevant clauses in PA 10
Cleaning surface &
contaminations / remove oil &
grease
Abrasive blast cleaning
Grid & dust must be removed
Remove droplets and standing
water
Application of paint by brush
PAINTING OF NON-FERROUS SURFACES– SPA6
This SPA6 applies to the painting at site of the non-ferrous surfaces specified below:
a) New galvanized surfaces.
b) Weathered galvanized surfaces.
c) Previously painted galvanized surfaces.
d) Aluminium surfaces.
Above listed are painted primarily to provide corrosion protection
theminimum dry film thickness 120 μm with MIO build coat
e) Stainless steel.
f) Pre-painted cladding ('Plastisol' cladding or equivalent).
g) Glass reinforced plastics (GRP).
h) Fusion bonded epoxy (FBE).
i) Multi component liquids (MCL).
j) Concrete.
Above listed are painted for cosmetic purposes only
Donot require a MIO coat.
All these surfaces, especially Aluminium and stainless steel shall be thoroughly cleaned
and then lightly abraded to provide an adequate key for the new paint system (see Table SPA6a).
PREPARATION OF SURFACES FOR PAINTING
All forms of surface contamination and disbonded paint shall be removed, especially oil, grease, salts, dirt
and dust.
This should be achieved by the use of detergent cleaners or emulsifying agents followed by a clean water
rinse.
.
152 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
APPLICATION OF PAINT TO PREPARED SURFACES
Compliant materials of the type listed in Table SPA6b shall be specified by the Engineer and applied.
The choice of the generic paint system will determine the initial coat required and this is shown in Table
SPA6c.
Water borne acrylic paint systems do not require a separate primer as the MIO will fulfill this function.
Coating systems shall full gloss finish of the same generic type as thepreceding coats.
Anepoxy primer and intermediate coat have been applied,
Anepoxy acrylic or epoxypolyester topcoat shall be specified.
In some situations, it may be required to terminate the paint system at the MIO coat.
Non-ferrous surfaces - surface preparation --- TABLE SPA 6a
Surface preparation
Non-ferrous surfaces
Comments
Preferred option
a
First option
Sweep abrasive blast
Hand abrading
Stiff bristle
brushing
Sweep abrasive blast
Hand abrading
Sweep abrasive blast
Hand abrading
New galvanizing
b
Weathered galvanizing
c
d
Previously painted
galvanizing
Aluminium
e
Stainless steel
Sweep abrasive blast
f
Pre-painted cladding
(‘Plastisol’ cladding or
equivalent)
Glass reinforced plastics
Fusion bonded epoxy
Multi component liquids
Concrete
Sweep abrasive blast
Hand abrading
Sweep abrasive blast
Sweep abrasive blast
Sweep abrasive blast
In accordance
with the
Manufacturers’
recommendations
Hand abrading
Hand abrading
Hand abrading
g
h
i
j
The preferred and first options
eliminate the need for an ‘Etch’
primer. An ‘Etch’ primer (Twash)
shall be used where these
options are impractical
Weathered surface provides its
own key
Thin gauge Aluminium should
not be blast cleaned and should
be treated with an etch primer
prior to the application of
intermediate and finish coats.
Chlorinated hydrocarbon solvent
shall not be used
Only Aluminium oxide should be
used as the blasting medium
Surface abrasion may not be
required for new concrete. Old
paint should be removed if
required using scrabblers
153 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Non-ferrous surfaces - Paint systems - TABLE SPA6b
Non-ferrous surfaces
a
New galvanizing
Groups of paint systems
Comments
G1
G2
G3
Water-borne
acrylic
Epoxy high
build
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
Alkyd or
modified
alkyd
b
Weathered galvanizing
Water-borne
acrylic
Epoxy high
build
c
Previously painted
galvanizing
Water-borne
acrylic
Epoxy high
build
d
Aluminium
Water-borne
acrylic
Epoxy high
build
e
Stainless steel
Water-borne
acrylic
Epoxy high
build
f
Pre-painted cladding
(‘Plastisol’ cladding or
equivalent)
Glass reinforced
plastics
Water-borne
acrylic
h
Fusion bonded epoxy
Water-borne
acrylic
i
Multi component
liquids
Water-borne
acrylic
j
Concrete
Water-borne
acrylic
Moisture
cured
urethane
Moisture
cured
urethane
Moisture
cured
urethane
Moisture
cured
urethane
Moisture
cured
urethane
g
Water-borne
acrylic
Any damaged galvanizing shall be
repaired with zinc rich epoxy
Any damaged areas where the steel
substrate is exposed, should be repaired
in accordance with SPA1
For new concrete a sealer coat may be
required
154 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Non-ferrous surfaces - Paint systems - Initial coat - TABLE SPA6c
Groups of paint systems
Non-ferrous surfaces
G1
a
New galvanizing
b
Weathered galvanizing
c
Previously painted
Galvanizing
d
Aluminium
e
Stainless steel
f
g
Pre-painted cladding
(‘Plastisol’ cladding or
equivalent)
Glass reinforced plastics
h
Fusion bonded epoxy
i
Multi component liquids
j
Concrete
G2
G3
Water-borneacrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 65µmminimum )
Pigmented highbuildEpoxy
( 65µmminimum )
Alkyd ormodifiedalkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 65µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 65µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 65µmminimum )
Water-borneacrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 45µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 45µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 45µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 45µmminimum )
Water-borne acrylic
Micaceous iron oxide
( 45µmminimum )
Single pack waterborneacrylic primer
(30µmminimum )
Pigmented high build Epoxy
( 65µmminimum )
Alkyd or modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Pigmented high build Epoxy
( 65µmminimum )
Alkyd or modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Pigmented high build Epoxy
( 65µmminimum )
Alkyd or modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Chloride free Epoxy high build
( 65µmminimum )
Compatible moisturecured
urethane (25µmminimum )
Compatible moisture cured
urethane (25µmminimum )
Compatible moisture cured
urethane (25µmminimum )
Compatible moisture cured
urethane (25µmminimum )
Moisturecuredurethane sealer
Compatible Alkyd or
Modifiedalkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Compatible Alkyd or
Modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Compatible Alkyd or
Modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Compatible Alkyd or
Modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Compatible Alkyd or
Modified alkyd
( 40µmminimum )
Institution of Gas Engineers (IGE) Recommendations
IGE/SR/21 - Blast cleaning operations
155 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Sequence of Events leading to Clients Inspection
a. Their reasons are mainly due to malpractices of contractor personals and also in the lapse of
the painting Inspector responsibility.
b. Surface preparation is very important, may not been carried out as per requirement. Could be
contaminants present like oil, grease, &dust.
c. Painting carried out in adverse weather conditions.
d. Application of subsequent coat without previous coat not fully cured.
e. Coating intervals not adhered.
f. Skipping or missing out a coat
g. Use of jelled paints. Paint shelf life expired.
h. Not following the coating system sequence.
i. Materials used are not the approved ones& doesn’t meet the specification.
Recording of information following Project Completion.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
To have record of work stoppage due to adverse weather conditions (down time)
To have record of Materials consumed.
Manpower deployed and Equipment used.
Record of wastage material.
Estimation of project cost for future tendering purpose.
Client/ Contractor Relationship
Good working relationship helps to resolve problems.
To arrive at an amicable Solution.
To express Concern, practical difficulties and work related problems to resolve.
To ensure safe working methods are adopted.
Co-ordial relationship will contribute to understand the job more precisely.
156 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
1.
2013
PA 10 specification is suitable for use in the following area:
a) Onshore installations
b) offshore installations
c) internal coatings of pipes
d) below ground (buried)
2.
PA 10 specification is not suitable for use in the following area:
a) Stove enamel coating
b) internal coatings of pipes
c) below ground (buried)
d) All of the above
3.
PA 10 does not deal with which of the following?
a) Maintenance Painting
b) Above ground plant installation
c) Buriedpipelines and fittings
d) Works plants installation
4.
What is mean by compliant coating?
a) Coating which applied on specified atmosphere condition
b) Coating which suitable with the requirements of the EPA
c) Coating which suitable for the steel substrate
d) Coating with non-compliance report
5
Which situation is expressed as damp surface?
a) Surface with detectable water
b) Surface temperature below dew point
c) Surface with a noticeable film of water
d) Surface temperature above dew point
6.
A Galvanized substrate with oxide layer has formed called
a) New Galvanising
b) Weathered Galvanising
c) Unsuitable galvanizing
d) Previously painted Galvanising
157 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
7.
2013
A Galvanized substrate with oxide layer has not formed called
a) New Galvanising
b) Weathered Galvanising
c) Unsuitable galvanizing
d) Previously painted Galvanising
8.
Which surfaces comes on hot duty surfaces
a) Metal surfaces attaining a temperature above 340o C
b) Metal surfaces attaining a temperature above 100o C
c) Metal surfaces attaining a temperature above 37o C
d) Metal surfaces attaining a temperature above 540o C
9.
Long term protection, coatings as required by PA10, are expected to last, typically
a) upto 4 years
b) upto 6 years
c) upto 10 years
d) upto 15 years
10.
Medium term protection, coatings as required by PA10, are expected to last, typically
a) upto 4 years
b) upto 6 years
c) upto5 years
d) upto10 years
11.
Short term protection, coatings as required by PA10, are expected to last, typically
a) 2 years to 4 years
b) 2 years to 3 years
c) 2 years to 5 years
d) 3 years to 5 years
12.
A Coating continues protection of 7 years, which falls in _____________
a) Long term protection
b) Medium term protection
c) Short term protection
d) Fixed term protection
158 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
13.According to Transco , an Engineer is
a) Appointed by a contractor and notified in writing to client
b) Appointed by Client and notified in writing to contractor
c) Responsible for coating and records
d) Higher authority
14.Which of the following is normally NOT considered to be a part of the role of a coating
inspector?
a) Observe the work
b) Write non-conformance reports
c) Supervise the labour work
d) Document the work
15.
A primer used for pretreatment for zinc metal surfaces.
a) Zinc rich epoxy
b) T.Wash
c) FBE
d) Zinc Phosphate
16.
Who is having permission to change a specified paint system?
a) Paint technologist
b) Painting inspector
c) Engineer
d) Contractor
17.
Specifications for a particular job must be decide by the
a) Paint technologist
b) Painting inspector
c) Engineer
d) Contractor
18.
Programme of work which must be prepared by the
a) Paint technologist
b) Painting inspector
c) Engineer
d) Contractor
159 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
19.
2013
Relevant local site regulations should be detailed in writing by the
a) Painting inspector
b) Engineer
c) Contractor
d) Paint technologist
20.
In accordance with PA 10, surface preparations by abrasive blast cleaning, shall provide a
peak-to-through height or profile measurement of
a) Not less than 350 µm and not greater than 100µm
b) Not less than 35 µm and not greater than 80µm
c) Not less than 35 µm and not greater than 100µm
d) Not less than 30 µm and not greater than 75µm
21.
Paints should be supplied by one
a) Manufacturer
b) Engineer
c) Contractor
d) Paint technologist
22.
All the paints must be stored under cover and in conditions recommended by the
a) Painting Manufacturer
b) Engineer
c) Contractor
d) Paint technologist
23.
All the paints are on operational sites, the storage method and area must be approved by the
a) Painting Manufacturer
b) Engineer
c) Contractor
d) Paint technologist
24.
Vaccume blasting is
a) Water blasting
b) Abrasive blasting
c) Closed blasting
d) Air blasting with water
160 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
25.
2013
Open blasting system is
a) Expendable
b) Re-use abrasive
c) Non-expendable
d) None
26.
Expendable abrasives can be reused for site blast cleaning?
a) IF it is more economical to do so
b) If the site engineer witness that they are cleaned in fresh water first.
c) Not under any circumstances
d) Provided they are mixed with fresh abrasive first
27.
Which of the following dry abrasives should not be re-cycled or reused
a) Steel shot
b) Chilled Iron grit
c) Copper slag
d) Shot and grit mix
28.
May reduce the expected life of paint system
a) Sa2
b) Sa3
c) Sa2 ½
d) St2
30.
Paints must not be used beyond manufacturers stated
a) Shelf life
b) Induction period
c) Dew point
d) St2
31.
Paint shall be normally applied when the RH in work zone is?
a) Less than 89%
b) Between 71 to 89%
c) Less than 90%
d) Greater than 90% or more
161 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
32.
2013
Overcoming times shall be determined by?
a) The contractor
b) Painting inspector
c) The manufactures data sheet
d) The painter
33.
Which information on a paint manufacture’s data sheet, is commonly notnormally stated?
a)Batch number
b) Orifice size
c) Spreading rate
d) Method of cleaning equipment and tools
34.
One method of ensuring the achievement of the required DFT to edges of weld profiles
during the paint application on site is
a) By adding of extra solvent thinners to the paint material
b) By increasing the duration of spray application at these areas
c) By stripe coating
d) By electrostatic spray application
35.
When a multi-component paint reaches the end of its recommended pot life
a) It can be used provided environmental condition are right
b) It can be remixed into fresh paint for use
c) It can be used for maintenance painting
d) It should not be used
36.
Wet abrasive blast cleaning of a surface should be followed by dry abrasive blast
cleaning?
a) Only as directed by the engineer
b) To remove the surface profile created by the wet process
c) Because the immediate oxidation of the substrate after wet blasting must be removed
d) Does not required
37.
All mechanical damage, such as surface lamination and sharp edges, observed on a
substrate should be
a) Immediately removed by carefully grinding
b) Carefully removed by means of spark free power brushes
c) Reported to site engineer, for his assessment
d) They will be normally being removed during blasting operations.
162 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
38.
2013
All waste material resulting from surface preparation and painting operations be disposed
of in accordance with
a) RIDDOR regulations
b) The health and safety at work act
c) The environmental protection act
d) IGE/SR/21
39.
After applying primer on steel surface, Paint got wetted by raining. As a painting
inspector what you do?
a) Wait for water to dry
b) Blast to remove existing primer, recoat
c) Continue next stage after rain
d) Recoat primer without removing existing coat
40.
Where defects removal has been carried out, the area concerning shall be
a) Sprayed
b) Re-blasted
c) Separately Primed
d) Brush painted
41.
What would be the correct course of action upon discovering that the contractor has applied
a coat of paint, out of sequence?
a) Blast and re-coat
b) Apply the correct coating over the top
c) Informed the Engineer
d) Add an extra protective coating
42.
Wa1, Wa2 are grades of
a) Abrasive blasting
b) Closed blasting
c) Water Blasting
d) Weathering Grades
163 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
43.
2013
Flash rusting of a substrate
a) May result in the substrate being discarded
b) Should be removed by hand abrasion
c) Should be removed by dry abrasive blast cleaning
d) Is acceptable for painting, when environmental conditions are satisfactory
44.
The maximum time for blasting or surface preparation before coating must applied in
a) 2 hrs after completion of surface preparation
b) 4 hrs after completion of surface preparation
c) one working day after completion of surface preparation
d) There is no maximum time limit
45.
The paint should be applied after blasting?
a) Within 3 hours after blasting
b) Within 5 hours after blasting
c) Within 4 hours after blasting
d) Within 8 hours after blasting
46.
The British standard for preparation of steel substrate before the application of paint and
related products is
a) BS 2451
b) BS 5252
c) BS 4800
d) BS 7079 Part A1
47.
The most common type of thermally sprayed material for hot duty application is
a) Zinc
b) Graphite
c) Silicon
d) Aluminium
48.
According to PA10 paint shall be normally be applied when air and substrate temps are
a) Within 3Cof dew point
b) Within 3C below dew point
c) Atleast 3Cof below dew point
d) greater than 5C
164 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
49.
2013
De-lamination is a fault occurs when using
a) Epoxy
b) CR
c) Micaceous Iron Oxide
d) Poly Urethane
50.
What is the solution, if damage occurs to a galvanizing?
a) T Wash
b) Zinc Rich Epoxy
c) CR
d) Water Borne Acrylic
51.
According to PA10, what is the correct course of action upon discovering foreign bodies
embedded in the paint film?
a) Apply an extra protective barrier coat
b) Re-blast, and re-coat
c) Lightly abrade with emery paper, apply stripe coat
d) Make a report to the engineer
52.
According to PA10, is the addition of Thinners allowed?
a) Yes, at the engineers discretion, up to 20% max.
b) Only if the paint is difficult to apply
c) Yes, in accordance with the product data sheets
d) No, under no circumstances.
53.
In accordance with PA10 section 32, paint application by roller is
a) Not allowed
b) Highly desirable for large areas
c) Only to be used primer coats on blast cleaned surfaces
d) Not recommended
54.
New and maintenance painting for indoor use or short term protection of carbon steel
surfaces operating at
a) above 100oC
b) below 100oC
c) below 50oC
165 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
d) below 75oC
55.
Which table followed to preparation for paintingof uncoated or unsuitably coated surfaces?
a) SPA 1e
b) SPA 1a
c) SPA 1b
d) SPA 1c
56.
Which type of paint applied at works in preferred system is high solids according to PA10?
a) Solvent based epoxy primer
b) Water borne acrylic
c) Zinc rich epoxy
d) Moisture cure polyurethanes
57.
What is the maximum allowable time lapse between blasting and coating?
a) 24 Hours
b) 7 days
c) 4 hours
d) 1 Hour
58.
What is the approximate overlap area in painting?
a) 100 mm
b) 100 cm
c) 10mm
d) 100 µm
59.
What is the minimum time for over coating?
a) 30 Minutes
b) 4 Hrs
c) 12 Hrs
d) Manufacturer recommend
60.
Over coating is carried out ?
a) Within one month
b) Within two month
c) Within three month
166 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
d) Within four month
61.
Alternative equivalent complaint system are available may be proposed to Transco?
a) Water borne paints
b) Thixotropic paints
c) Zinc rich epoxy
d) Metal spray paints
62.
Final coat must be?
a) Safety
b) Cosmetic defects
c) Finish coat
d) All the above
63.
Over coat of MIO should be applied to all primers to a Minimum DFT?
a) 100 µm
b) 120µm
c) 75 µm
d) 70µm
64.
Final coating will require to a Minimum DFT?
a) 100 µm
b) 120µm
c) 75 µm
d) Defendant upon system
65.
What is the total thickness of compliant epoxy based paint?
a) 325 µm
b) 225µm
c) 265µm
d) 365µm
167 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
66.
2013
What is the total thickness of water borne acrylic paint?
a) 325 µm
b) 225µm
c) 265µm
d) 365µm
67.
The specified preferred 4 coat paint system in British Gas PA10 is
a) Red Lead, Zinc based undercoat, polyurethane, Acrylic finish
b) Zinc Chromate primer, Micaceous Iron Oxide, Chlorinated Rubber,Moisture Tolerant
Polyurethane
c) High build Epoxy Aluminium primer, Epoxy Micaceous Iron oxide, Epoxy
undercoat, Epoxy Polyester or Acrylic finish.
d) Zinc galvanise, Micaceous Iron Oxide, Thermally sprayed aluminium, silicone sealer
68.
Compliant systems which meet the requirement of
a) T/SP/PA/9
b) T/SP/PA/8
c) T/SP/PA/10
d) T/SP/PA/7
69.
For long term protection, preferred system at site refers which table
a) SPA 1a
b) SPA 1b
c) SPA 1d
d) SPA 1e
70.
BGC/PS/PA10 contains which table, specifying the coating systems?
a) Spa 6a
b) Spa 1e
c) spa 4a
d) spa 3c
71.
What is the specified abrasive overlap requirement on repair areas?
a) 250 mm
b) twice pipe diameter
c) 100 mm
d) 1 meter
168 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
72.
2013
The specified 3 coat paint system in British Gas PA10 is
a) Primer coat
b) Mid Coat
c) Finish Coat
d) All the above
73.
Which grade of surface preparation required for hot duty surfaces from above 150 oC
a) Sa1
b) Sa2
c) Sa2½
d) Sa3
74.
Which type of operational chart required for hot duty surface from 100 oC149oC?
a) SPA 3a
b) SPA 3b
c) SPA 3c
d) All the above
75.
Which type of operational chart required for hot duty surface from 150 oC340oC?
a) SPA 3a
b) SPA 3b
c) SPA 3c
d) All the above
76.
Which type of operational chart required for hot duty surface above340oC?
a) SPA 3a
b) SPA 3b
c) SPA 3c
d) All the above
169 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
77.
2013
According to Transco PA10,which metal spray not required a sealer
a) TSA
b) Polysiloxane Inorganic Coating
c) Poly Vinyl Buterol
d) Inorganic Zinc Silicate
78.
For the painting of damp ferrous substrate, all paint should be?
a) Dried with the assistance of a warm air blast
b) Spray applied
c) Over coated as quickly as possible
d) Brush applied
79.
Which application method used to apply paints on damp surface
a) Brush
b) Roller
c) Airless Spray
d) Dip coating
80.
It is advisable to apply Moisture curing polyurethane by
a) Airless spray
b) Brushing
c) Roller
d) Padding
81.
Beryllium Bronze is a material useful in the manufacture of
a) Power wire brushes
b) Welding electrodes
c) Comb gauges
d) Nonmetallic reinforcement spacers
82.
What is the material used to carry out repairs in dµmp conditions?
a) Moisture Curing Polyurethane
b) Moisture Tolerant Resin
c) Chlorinated Rubber
d) Water Borne Acrylics
170 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
83.
2013
_________ can be applied when Relative humidity = 100%
a)Epoxy
b)CR
c)Poly urethane
d)Zinc Rich Epoxy
84.
Over application of inorganic zinc silicate (IZC) may result in
a) Grinning
b) Checking
c) Flocculation
d) Bittiness
85.
Where a silicone sealer is applied to an Inorganic Zinc Silicate coating system, how is the
sealer cured?
a) Propane torch
b) Electric induction pads
c) It cures when the system begins to operate
d) It does not require curing
86.
Which paint is more suitable for hot duty surface above 150ᵒ C
a) Zinc Silicate
b) High Solid Epoxy
c) Urethane
d) CR
87.
What is the approximate induction period of CR
a) 20 minutes
b) 30 minutes
c) 6-8 hrs
d) Not Applicable
88.
Which one is not included in non-ferrous substrate?
a) Stainless steel
b) Mild steel
c) New Galvanising
d) Weathered Galvanising
171 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
89.
2013
Which blasting is suitable for non-ferrous substrates
a) Thorough abrasive blasting
b) Sweep blasting
c) Sa2½
d) Not Applicable
90.
Which Abrasive is preferred to use on stainless steel
a)Copper slag
b)Steel Grit
c)Steel Shot
d)Aluminium oxide
91.
Which surface preparation is used for weathered galvanising
a) Sweep Blast
b) Stiff Bristle Brushing
c) Through Blast
d) Sa2½
92.
What surface preparation is specified in PA 10 for weathered galvanisedsteel?
a) Sa 2 ½, followed by T-wash mordant primer
b) Sa 3, followed by etch primer
c) Hand abrasion with a stiff bristled brush only
d) Sa 1 followed by water washing
93.The most widely used materials for pipeline coating are which of the following?
a) Alkyd enamels
b) Fusion-bonded epoxies
c) Thermoset plastics
d) High density latexes
94.
Thin gauge Aluminium should be treated
a) Alkyd enamels
b) Blast clean
c) Etch primer
d) Aluminium oxide
172 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
95.
2013
Which type of surfaces to the paint primarily to provide corrosion protection at non-ferrous?
a) New galvanised
b) Weather galvanised
c) Aluminium surface
d) All of the above
96.
Which type of surfaces to the paint to provide cosmetic protection at non-ferrous?
a) Glass reinforced plastics
b) Concrete
c) Multi component liquids
d) All of the above
97.
Which surface is requiring to MIO build coat at non-ferrous?
a) New galvanised
b) Weather galvanised
c) Aluminium surface
d) All of the above
98.
What type of pigment used to galvanising suffered damage of more than a scratch or gouge
repair?
a) Zinc rich epoxy
b) Polyethylene
c) Aluminium
d) Zinc
99.
What type of paint systems used for glass reinforced plastics at non-ferrous?
a) Water-borne-acrylic, Moisture cured urethane, Alkyd or modified alkyd
b) Water-borne-acrylic, Micaceous iron oxide, Alkyd or modified alkyd
c) Water-borne-acrylic, Epoxy high build, Alkyd or modified alkyd
d) Solvent-borne-acrylic, Micaceous iron oxide, Alkyd or modified alkyd
100.
What type of paint systems used for Aluminium surface at non-ferrous?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Water-borne-acrylic, Moisture cured urethane, Alkyd or modified alkyd
Water-borne-acrylic, Micaceous iron oxide, Alkyd or modified alkyd
Water-borne-acrylic, Epoxy high build, Alkyd or modified alkyd
Solvent-borne-acrylic, Micaceous iron oxide, Alkyd or modified alkyd
173 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
101.
2013
What type of paint systems of initial coat used for weathered galvanising at non-ferrous?
a) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, pigmented high build epoxy, Alkyd or
modified alkyd
b) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Compatible Moisture cured urethane,
Compatible Alkyd or modified alkyd
c) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Chloride free high build epoxy, Compatible
Alkyd or modified alkyd
d) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Moisture cured urethane, Alkyd or modified
alkyd
102.
What type of paint systems of initial coat used for Pre-painted cladding at non-ferrous?
a) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, pigmented high build epoxy, Alkyd or
modified alkyd
b) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Compatible Moisture cured urethane,
Compatible Alkyd or modified alkyd
c) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Chloride free high build epoxy, Compatible
Alkyd or modified alkyd
d) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Moisture cured urethane, Alkyd or modified
alkyd
103.
What type of paint systems of initial coat used for stainless steel at non-ferrous?
a) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, pigmented high build epoxy, Alkyd or
modified alkyd
b) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Compatible Moisture cured urethane,
Compatible Alkyd or modified alkyd
c) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Chloride free high build epoxy
d) Water-borne-acrylic Micaceous iron oxide, Moisture cured urethane, Alkyd or modified
alkyd
104.
Which of the following substrate are not dealt with in table SPA6 of PA10?
a) Concrete
b) Stainless steel
c) Galvanised surface
d) They are all dealt with under that system
174 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
105.
2013
All surface breaking laminations observed on a substrate shall be:
a) Reported to the welding inspector immediately
b) Removed by chipping hammer under the supervision of the blasting foreman
c) Removed by grinding with the agreement of the engineer
d) Removed by sharp edged scraper with the permission of the safety manager
106.
A newly galvanised substrate has a surface:
a) Where a cohesive oxide layer has not been formed and which exhibits a dull appearance
lacking in metallic sheen
b) On which a cohesive oxide layer has not been formed and which exhibits a dull
appearance lacking in metallic sheen
c) Whicha cohesive oxide layer has not been formed, showing a brightin metallic sheen
d) On which a cohesive oxide layer has been formed, showing a bright in metallic sheen
107.
In accordance with PA 10 table SPA 3c, where TSA or IZS have been as the preferred
coating for surface operating above 340oC:
a) They should be cured by a chemical reaction
b) They coating must be immediately heated to 340oC
c) They should be sealed with polysiloxane inorganic coating
d) They must be further protected by the application of silicone sealer
108.
The most widely used materials for pipeline coating are which of the following?
a)Alkyd enamels
b) Fusion-bonded epoxies
c)Thermoset plastics
d) High density latexes
109. Powder coating types may include which of the following?
a)Alkyds
b)Epoxies
c)Organic Zinc
d)Latexes
110.
Which of the following is normally NOT considered to be a part of the role of a
175 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
coating inspector?
a) Observe the work
b)Write non-conformance reports
c) Supervise the labours work
d) Document the work
Additional Questions:
1.
Thermal spray coatings method may expel a VOC of
a) 100%
b) Near 75%
c) Near 50%
d) 0%
2.
The use of an electrostatic handgun has a transfer efficiency of which of the following?
a) <25%
b) <50%
c) Between 50 - 75%
d) About 98%
3.Which information normally not given by the manufacturer’s data sheet?
a) Batch numbers
b) Orifice size
c) Spreading rate
d) Over Coat time
4.A paint viscosity test is carried out at a controlled temperature in order to?
a) Promote paint flow
b) Warm the paint up
c) Keep the weigh even
d) Promote uniformity of the test
5. Etch Primers as
a) Etch Primer is one kind of surface Preparation Material which is used instead of abrasive
blasting.
b) Etch primed surfaces will be slightly rough
c) And they will provide, key for the succeeding Painting application.
d) All of the above
6.
Solvents are
176 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
a) Solvents form the evaporative part of the drying process.
b) Thins the Paint so it can be easily applied.
c) Washes out brushes & Equipment.
d) All of the above
7.
Larger areas we go for open site abrasive blasting, depending on the type of system we go for
a) Sa1, Sa2, Sa2.5, Sa 3.
b) St2, St3.
c) Hand abrade with Emery paper Grit 80/120/200
d) All of the above
8.
Areas very small and for spot repairs we go for Mechanical Power tool cleaning
a) Sa1, Sa2, Sa2.5, Sa 3.
b) St2, St3.
c) Hand abrade with Emery paper Grit 80/120/200
d) All of the above
9.
Areas which are inaccessible for mechanical Buffers (Grinding machine) we go for
a) Sa1, Sa2, Sa2.5, Sa 3.
b) St2, St3.
c) Hand abrade with Emery paper Grit 80/120/200
d) All of the above
10.
Polyurethane coats have a finish which is of
a) High Gloss
b) They are abrasion resistant,
c) Polyurethane coats can be cleaned easily well resistant to UV
d) All of the above
11.
Epoxy coatings are one of the
a) Strongest Binders
b) They provide High Build coating suitable for Airless Spray Application.
c) They can be modified form for High Temperatures and Damp surfaces
d) All of the above
177 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
12.
2013
Disadvantage of Epoxy coatings
a) It will make a Poor finish coat because they will chalk easily
b) Strongest Binders
c) They provide High Build coating suitable for Airless Spray Application.
d) They can be modified form for High Temperatures and Damp surfaces
13.
Risk Assessments when Painting.
a) Fire Risk due to Inflammable nature of substances of paint.
b) Fumes &Inhalation of Toxic gases
c) To use appropriate P.P.E
d) All of the above
14.
Risk Assessments when Blast cleaning
a) Working in confined space
b) To obtain work permit for the job
c) To display boards
d) All of the above
15.
Problems are coming when Density & Viscosity of paint are not correct.
a) Poor opacity
b) poor Gloss & slow drying,
c)
Poor durability
d) All of the above
16.
Paint not be applied to the defined D.F.T. Drying problem may occur.
It may create the surface defects like
a) Runs
b) Sags
c) Thixotropic points
d) All of the above
178 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
17.
2013
Visually examine the surface
a) The Substrate prior to blasting for any inherent defects
b) Detrimental contaminants such as oil. Mud etc.
c) Observe the surface for unusual discoloration
d) All of the above
18.
Make scotch test to ensure that the surface is free from dust particles. On Dry Paint films
a) Uniform in appearance
b) Free from Paint Faults and low DFT areas
c) Missed & skipped areas
d) All of the above
19.
What are the important properties of paint?
a) Ability to preserve the surface from corrosion& other type of deterioration.
b) Show some sacrificing effect and Decorative purpose.
c) Opacity, tinting power, resistance to acid alcoholic and light.
d) All of the above
20.
Degree of gloss determined by
a) Degree of pigment dispersion.
b) Size of pigment particles
c) The pigment volume concentration and binder type
d) All of the above
21.
A coat of paint which can tie two normally incompatible systems together
a) Mid Coat
b) Final Coat
c) Tie Coat
d) None of the above
179 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Procedure for using replica tape is as follows:
Zero the dial micrometer. Clean the anvils (paper or fingers) an d allow the contacts to
come together, release the locking screws and adjust the bezel so that the zero isimmediately
behind the large needle.
Remove the backing paper from the replica tape, ensure that the small white disc with the
black ring is detached also. Stick the replica tape to the area to be measured.
Using a pen or pencil end, or the specially provided plastic stick, rub firmly and evenly all
over the area of the mylar. This causes the testex paste to pass into the troughs and the
peaks of the blast will butt up to the transparent mylar.
Remove the replica tape and check. The mylar area should no longer be white (now grey),
and pinpricks of light should be visible through the mylar when held up to the light.
Place the testex paste area between the anvils of the micrometer and allow them too gently
close together. From the final reading on the gauge deduct two thou if using an imperial
gauge or 50µm if using a metric gauge. The balance figure is the peak to trough height of
the profile.
Procedure for using density cup: Weigh the clean, empty cup and the lid on a metric scale, sensitivity ± 0.1gm.
Fill the density cup with the paint, to within approximately 2mm of the brim.
Allow any entrapped air bubbles to burst and replace the lid slowly and firmly until it seats
firmly on the shoulder of the brim.
The chamfer in the lid allows air to be expelled as, the lid is replaced, followed by paint
over the required 100cc volume. If no paint is expelled remove the lid and add more.
Wipe off any excess paint from the vent and weigh the filled cup.
Deduct the weight of the empty cup from the final weight and divide by 100.
The answer is the density in gram/cc.
Procedure for Using viscosity: Ensure that the equipment and paint temperatures are at 20oc ± 0.5oc.
Level off the equipment using the bubble level and adjustable screw legs.
Put the lid to one side when levelling is complete.
Place a suitably sized receptacle under the orifice (greater than 100cc).
Place a finger over the nozzle orifice and fill with the paint to be tested, up to the brim,
leaving a convex meniscus.
Using a straight edge (a ruler) quickly scrape excess material into the overflow rim on the
top of the cup.
Simultaneously start a stopwatch (or use sweep second hand) and remove finger from the
nozzle.
The paint will run from the orifice in a continual stream. At the first distinctive break in
the stream i.e. when it drips, stop the watch. The time in seconds is recorded as the
viscosity, at the measured temperature.
Procedure for this operation are using comb gauge: Select the appropriate gauge with the smallest increment rise tooth to tooth.
Apply the gauge firmly, perpendicular to the substrate into the paint film ensuring that the
two end lands are firmly on the substrate.
Withdraw the comb gauge and look at the teeth.
Two values should be recorded. The number above the last tooth wetted by the paint and
the value of the next highest not wetted.
180 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Procedure for whirling Hygro meter:a. Hold the Hygrometer Straight facing the Wind direction. In the Wind direction and start
rotating to 30 -40 rotations per second.
b. First read the wet bulb temperature immediately then the dry bulb temperature.
c. Repeat the operation to get two consecutive readings within 0.2 c
Calibration of Banana Gauge:
1. Choose a magnetically insulted shim of known thickness, close to the thickness of the paint
you expect to find.
2. Place the shim on the same substrate surface finish as the surface finish on which the paint film
to be measured is attached, e.g.-if the paint
Is on a blasted surface, calibrate the gauge on a uncoated Blasted surface.
3. Place the magnet onto the shim and press firmly on the instrument, Wind the scale wheel
forwards (away from you).Until the Magnet is Definitely attached to the shim substrate.
4. Gradually wind the wheel backwards slowly until the magnet detaches itself. T At this point,
move the cursor on the instrument to the thickness of the shim as shown on the Scale wheel.
With some instrument the scale itself must be moved to line up with a fixed cursor.
5.When using the later type of instrument .rotate the wheel to zero to locate the position of the
scale adjuster.
6. The instrument is now calibrated and may be used to measure the D.F.T of any nonmagnetic
paint films to a claimed accuracy
Procedure for Abel Cup:Fix the Abel cup containing the substance for the assessment into a water bath.
Activate the source of ignition every ½ deg C rise in temperature.
Apply a heat source to the water bath and monitor the air/vapour temperature in the Abel cup.
A flash point temperature is identified when a blue flame flashes over the substance being
assessed.
181 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Procedure for pull of adhesive test
a) Clean and degrease the surface to be tested.
b) Roughen the surface fine/medium grain emery sheet.
c) Mix regular araldite and stick dolly dolly to the surface and leave for 24 hours at 25 deg C
d) Cut paint around the dolly down to the substrate using a special cutter.
e) Attach pull off instrument and apply pulling the force.
f) Test results require careful interpretations. Some normal values obtained for acceptable Adhesion
are as follows.
1500 psi
- epoxy based systems
3000 psi
- alkyd based systems
12000 psi
- zinc etch primer.
182 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
CALCULATIONS AND FORMULA’S
WFT x VS % = DFT x 100
1) DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
2) WFT = DFT x 100 / VS %
3) VS.%= DFT x 100 / WFT
4) V= AREA x WFT / 1000
AREA = METER = CM
Area
square meter-
m2
convert to cm2
M2 = CM2 (100 x 100= 10000)
For example:
1) Given 10 Diameter in Area
Using 3.14 x 5 x 5
2) Tank is 5 Diameter
Using 3.14 x 2.5 x 2.5
Tank is 6 meter height
2xЛxrxh
Using 2 x 3.14 x 2.5 x 6
3) Given Area in 7 meter radius
Using 3.14 x 7 x 7
1. Density = Weight / volume
a) Weight = Density x Volume
Relative density or specific gravity is the density of any substance compared to the
density of water.
b) Specific gravity = Density of the substance/density of water
183 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
B. Gas 3.2 MathExercises
WFT calculations
1) What WFT would need to be applied to give a DFT of 45 µm using a paint of 56% vs.?
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
45x100 / 56 4500/56 = 80.36µm
2) What WFT would need to be applied to give a DFT of 60 µm using a paint of 40% vs.?
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
60x100 / 40 6000/40 = 150µm
3) A paint of 38% vs. was used to give a DFT of 45 µm what wad the WFT?
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
45x100 / 38 4500/38 = 118.42µm
4) A DFT of 55 µm was obtained from a paint of 55% vs. what was the WFT applied?
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
55x100 / 55 5500/55 = 100µm
5) What WFT would be applied to leave a DFT of 65 µm using a paint of 49% vs?
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
65x100 / 49 6500/49 = 132.65µm
184 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DFT calculations
1) What would be the DFT if 20 liters of paint, vs. 45% covered an area of 9m x 12m?
Area
m2 -
Step -1
Area 9 x12 = 108
V= AREA x WFT / 1000
Step -2
WFT = V/A x 1000
WFT = 20/ 108 x1000
WFT = 185.18µm
Step -3
DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
DFT = 185.18 x45 /100 8333.32/100 = 83.33µm
2) 25 liters of paint, vs. 65% was used to cover a circular area of 10m diameter. What would
be the resulting DFT?
Area
diameter -
Step-1
Area = Лr2
3.14 x5 x5= 78.5m2
Step -2
WFT = V/A x 1000
WFT = 25/ 78.5 x 1000
WFT = 317.47µm
Step -3
DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
DFT = 318.47x65 /100 20700.63/100 = 207µm
3) What DFT would be obtained if paint vs. content 42% was applied at a WFT of 84 µm?
DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
DFT = 84x42 /100 3528/100 = 35.28µm
185 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
4) What would be the resulting DFT if a paint containing 83% and WFT of 130 µm, what would be
the resulting DFT?
DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
DFT = 130x83 /100 10790/100 = 107.9µm
5) A paint, vs. 65% was applied at a WFT of 130 µm, what would be the resulting DFT?
DFT = WFT x VS % / 100
DFT = 130x65 /100 8450/100 = 84.50µm
VS calculations
1) A DFT of 53 µm was obtained from a WFT of 110 µm, what was the vs. % of the paint?
VS. %= DFT x 100 / WFT
53 x 100 /110 =5300/110 =48.18%
2) A paint was applied at 120 µm WFT. The resulting DFT was 65 µm, what was the vs. %?
VS. %= DFT x 100 / WFT
65 x 100 /120 =5300/110 = 54.17%
3) What would be the vs. % of a paint if it was applied with a WFT of 120 µm and a DFT of
68 µm was obtained?
VS. %= DFT x 100 / WFT
68x 100 /120 =6800/120 = 56.67%
4) What was the vs. % of a paint with a DFT of 36 µm, when the WFT was 108 µm?
VS. %= DFT x 100 / WFT
36 x 100 /108 =3600/108 = 33.33%
5) A DFT of 62 µm was measured, from a WFT application of 100 µm, what would be the
vs. % of the paint used?
VS. %= DFT x 100 / WFT
62 x 100 /100 =6200/100 = 62%
186 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Volume calculations
1) What volume of paint would be required to cover an area of 300 square meters, to a specified DFT
of 65 µm, using a paint of 45% vs.?
Step – 1
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
65x100 / 45 6500/45 = 144.44µm
Step -2
Area
Square meter -
Area = 3002
Convert Square is to CM2100 x 100 = 10000
Step – 3
V= AREA x WFT/1000
3002 x 144.44 /1000
300 x10000 x 144.44 /1000 x 10000
433.33/10 =43.33 liters.
2) How much paint would be required to coat a tank, roof and side sheets to a DFT of 100µm? The
tank is 5 meters diameter and 6 metersheight. The paint to be used is solvent free.
Step – 1
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
100x100 / 100 10000/100 = 100µm
Step -2
Area
Tank is 5 meters diameter and 6 meters height
Area = Лr2
3.14 x 2.5 x 2.5= 19.63m2
Height is 2Лrh
2 x 3.14 x 2.5 x 6= 94.20m2
Total diameter = 19.63 +94.20 = 113.83m2
Convert to CM is 100 x 100 = 10000
Step – 3
V= AREA x WFT/1000
113.83m2 x 100 /1000
113.83 x10000 x 100 /1000 x 10000
113.83/10 =11.38 liters
187 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
3) How much paint would be needed to cover a circular area of 10 meters diameter, using apaint 65%
vs. to a DFT of 60 µm?
Step – 1
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
60x100 / 656000/65 = 92.30µm
Step -2
Area
10 diameter
Area = Лr2
3.14 x 5x 5= 78.50m2
Step – 3
V= AREA x WFT/1000
78.5m2 x 92.3 /1000
78.5m2x10000 x 92.3 /1000 x 10000
7246.15/1000 =7.25 liters
4) A circular area of 7 meters radius is to be coated to a DFT of 45 µm. What volume ofpaint would
be required if the vs. content was 48%?
Step – 1
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
45x100 / 484500/48 = 93.75µm
Step -2
Area
7 meters radius
Area = Лr2
3.14 x 7x 7= 153.86m2
Step – 3
V= AREA x WFT/1000
153.86m2 x 93.75 /1000
153.86m2 x10000 x 93.75 /1000 x 10000
14424.37/1000 =14.42 liters
188 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
5) How much paint would be needed, at 55% vs., to coat an area of 250 square meters to aDFT
of 60 µm?
Step – 1
WFT = DFT x 100/ VS%
60x100 / 556000/55 = 109.09µm
Step -2
Area
250 square meters
Area = 2502
Convert Square is to CM2100 x 100 = 10000
Step – 3
V= AREA x WFT/1000
250m2 x 109.09 /1000
250m2x10000 x 109.09 /1000 x 10000
2727.25/100 =27.27 liters
Density and SG exercise
1) What would be the weight of 16.5 liters of paint with a SG of 1.45?
Density = Weight / volume
Density
Weight = Density x Volume
= 1.45 x 16.5
= 23.93 kgs
2) What is the density of paint if 7.5 liters weighs 9.75 kg?
Density = Weight / volume
= 9.75 / 7.5
= 1.3 gm/cc
189 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
3) What would be the relative density of paint in question two?
Relative Density = Density of the substance/density of water
= 1.3 /1
= 1.3
No units for RD
4) If the weight of 25 liters of paint is 37.5 kg, what would be the SG?
SG= Weight / volume
= 37.5 / 25
=1.5gm/cc
Density value is 1.29 gm/cc calculate value is 1.35 gm/cc So that, Base is high
Density value is 1.35 gm/cc calculate value is 1.29 gm/cc So that, Activator is high
5) A 2 pack epoxy should be mixed at one part base to one part activator; the base has adensity of
1.4gm/cc and the activator 0.9 gm/cc. What would be the density of the mixedcomponents?
Density= 1Base + 1Activator
= (1)1.4 +(1) 0.9
= 2.3/2
= 1.15 gm/cc
6) A 2 pack paint is mixed at a ratio of six parts pack A (density 1.3gm/cc) to one part pack B
(density 0.9gm/cc). What would be the density of the combined parts?
A = 6 part x 1.3
B = 1 part x 0.9
7.8gm/cc
0.9 gm/cc
Total = 7 part 8.7gm/cc
Density is = 8.7/7 = 1.24 gm/cc
190 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
7) A mixed 2 pack paint has a density of 1.35gm/cc. The density of the base was 1.5gm/cc
and the activator 0.9gm/cc. The mixing ratio was 3:1. Has the paint been mixedcorrectly?
A = 3 part x 1.54.5gm/cc
B = 1 part x 0.9 0.9 gm/cc
Total = 4 part
5.4gm/cc
Density is = 5.4/4 = 1.35gm/cc
Density value is 1.35gm/cc calculate value is 1.35gm/cc So that, correct paint mix
8) A mixed 2 pack paint has a density of 1.35gm/cc. Mixed at a ratio of 6:1, base density
1.45gm/cc, activator density 0.95gm/cc. Has the paint been mixed correctly?
A = 6 part x 1.458.70 gm/cc
B = 1 part x 0.950.95gm/cc
Total = 7 part
9.65gm/cc
Density is = 9.65/7 = 1.38gm/cc
Density value is 1.35gm/cc calculate value is 1.38gm/cc So that, Base is high
191 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PRACTICAL PURPOSE
RH AND DPCOMMONTABLE
WB
8
8
10
DB
10
8
8
DP
7
8
9
RH
89%
100%
90%
STEEL TEMP/AIR DEP
11
8
9
Y/N
Y
N/ NOT POSSIBLE
N/ NOT POSSIBLE
1. Steel / Air temperature is always above 5oC
2. Steel/ Air temperature at least @ 3oC above the Dew point
3. Relative Humidity not more than 90%
4. Ambient temperature: - It is the surrounding air temperature also referred as dry bulb temperature.
Practical Questions:
46. Use surface Needle gauge
a) Below 70 µm b) above 70 to 150µm c) above 150 to 200 µm d) above 200 to300µm
47. Use Dial micrometer with replica tape
a)Below 70 µm b) above 70 to 150µm c) above 150 to 200 µm d) above 200 to300µm
48. Find Dew point using dew point calculator?
WB = 10 DB = 12
a) DP is 8b) DP is 9c) DP is 7
d) DP is 10
RH is 77%
RH is 83% RH is 89% RH is 92%
49. FindRelative Humidity using dew point calculator?
WB = 10 Dew point is = 12
a) DP is 8
b) DP is 9
c) DP is 7 d) DP is 10
RH is 77% RH is 83% RH is 89% RH is 92%
50. Use digital Elcometer find coat thickness
a)Below 100µm b) above 200 to 350µm c) above 350 to 600µm d) above 600
192 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Practical Theory Questions:
Photographs
HYGROSCOPIC (OSMOTIC) BLISTERS
Copper Slag
193 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Abrasive CONTAMINATED
GARNET
194 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
METALLIC GRIT.
METALLIC SHOT
195 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
AGRICULTURAL BY-PRODUCT
SIEVES TO BS 410
196 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SURFACE NEEDLE GAUGE
DIAL MICROMETER AND SURFACE REPLICA TAPE
197 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DIAL MICROMETER AND SURFACE REPLICA TAPE
SURFACE COMPARATOR TO BS 7079 Pt C, ISO 8503
198 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
RUST GRADES
199 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
BLASTING GRADES A
BLASTING GRADES
B
2013
Sa 2.5 and Sa 3
Sa 1and Sa 2
200 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
BLASTING GRADES
B
2013
Sa 2.5 and Sa 3
BLASTING GRADES, COMPARISONS
201 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
BLASTING GRADES
C
Sa 1 and Sa 2
BLASTING GRADES
C
Sa 2.5 and Sa 3
2013
202 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
BLASTING GRADES
D
Sa 1 and Sa 2
BLASTING GRADES
D
Sa 2.5 and Sa 3
2013
203 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
HYPODERMIC NEEDLE GAUGE
SURFACE PREPARATION
HAND AND POWER TOOL CLEANING BSt
2 and St 3
204 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
HAND AND POWER TOOL CLEANING CSt
HAND AND POWER TOOL CLEANING D
2013
2 and St 3
St 2and St 3
205 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
SURFACE PREPARATION ---- FLAME CLEANING
206 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
pH INDICATOR PAPERS
2013
CHEMICAL CLEANING
SALTS DETECTION, BRESLE SAMPLE PATCH KIT
207 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
QUANTITITIVE TESTS FOR HYGROSCOPIC SALTS
MERKOQUANT TEST
BRESLE SAMPLE PATCH
208 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT TESTING --DENSITY CUP
THE DENSITY ( SG ) CUP
209 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
HEGMAN GRIND GAUGEFOR FINENESS OF GRIND
DEGREE OF DISPERSION
210 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
ROTATIONAL VISCOMETER WITH ROTOTHINNER MEASURES DYNAMIC
VISCOSITY. UNITS, POISES
KREBS STORMER VISCOMETERKINEMATIC VISCOSITY
211 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
A FORD FLOW CUP
FORD FLOW CUP IN ITS RETORT AND SHOWING THE 4mm DIA HOLE
212 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
FORD FLOW CUP
213 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
WET FILM MEASUREMENT
ECCENTRIC WHEEL
214 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
WET FILM THICKNESS MEASUREMENT
COMB GAUGES
DESTRUCTIVE TEST GAUGES
THE P.I.G
215 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DESTRUCTIVE TEST GAUGES. THE SABERG TEST DRILL
DFT MEASUREMENTS ELECTRONIC GAUGES
ELECTROPHYSIC MINI TEST
THE EXACTO
216 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
ELCOMETER 456
DRY FILM THICKNESS MEASUREMENT, MAGNETIC.
TINSLEY PENCIL
217 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
COLOUR CODED CALIBRATION SHIMS
PURPLE → 25µm
BLUE → 50µm BROWN→ 125µm
→ 250µm
YELLOW → 500µm
WEATHER CONDITIONS
WHITE
DEW POINT CALCULATOR
READ OFF RH FROM TIP OF BLACK ARROW,
218 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
DRY FILM THICKNESS MEASUREMENT, MAGNETIC,
HORSESHOE GAUGE
219 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
THE BANANA GAUGE MODEL 111
THE BANANA GAUGE MODEL 211
220 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
FLEXIBILITY TEST
2013
CONICAL MANDREL
DRYING AND CURING TESTS
BK DRYING TIME RECORDERS
221 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
MECHANICAL THµMB TEST, THROUGH DRYING
WOLFF- WILBORN PENCIL SCRATCH TEST
222 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
OPACITY, THE PFUND CRYPTOMETER
HIDING POWER CHARTS AND ADJUSTABLE APPLICATOR
223 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
ADHESION TESTS CROSS CUT ( CROSS HATCH ) TEST SPECIAL CUTTER
TOOL
224 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
ADHESION TESTS THE DOLLY TEST
ADHESION TESTS THE HYDRAULIC ADHESION TESTER
225 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
WEATHER CONDITIONS WHIRLING HYGROMETER
WEATHER CONDITIONS MAGNETIC CONTACT
226 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
STEEL TEMPERATURES TERMOCOUPLE
CATHODIC PROTECTION
MONITORING POTENTIALS
COPPER /COPPER SULPHATE HALF CELL REFERENCE ELECTRODE
227 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
CATHODIC DISBONDMENT TEST
228 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
HOLIDAY/PINHOLE DETECTION
229 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
PINHOLE/HOLIDAY DETECTION
2013
SPONGE DETECTOR
VOLTAGE RANGE 3 TO 90v.SOME HAVE ONLY 2 SETTINGS. INTERMEDIATE
67.5v.
230 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
PAINT FAULTSBITTINESS
INCLUSION, EITHER AIRBRONE OR FROM THE PAINT ITSELF
231 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
BLEEDING
DISCOLOURATION
SOLVENT FROM THE TOP OF COAT SOFTENS THE UNDER LYING MATERIAL
BROWN FOR BITUMEN, YELLOW FOR COAL TARS
232 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
BLISTERING
BLISTERS CAN BE FILLED WITH GAS,LIQUID OR CRYSTALS
233 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
CHALKING
DEGRADATION OF A BINDER DUE TO DISRUPTIVE FACTORS IN THE
ENVIRONMENT
234 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
CISSING
235 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
CRACKING
crocodile
236 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
CRATERING
BOWL SHAPED DEPRESSIONS
CURTAINS SAGS
237 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
RUNS
TEARS
238 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
COATING FAULTS
2013
FLAKING
MATERIAL PROGRESSIVELY GETS BRITTLE WITH AGE, CRACKS AND BEGINS TO
DETACH
HOLIDAYS
UNCOATED AREA
239 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
LIFTING
CAUSED BY SOLVENT STRENGTH AND
LACK OF OBSERVANCE OVERCOATING TIME
240 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
ROPINESS
BRUSHMARKS
WRINKLING
241 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
RIVELLING
COLOUR
MUNSELL AND BS 4800
YELLOW THROUGH GREEN ,BLUE
PURPLE, RED AND BACK TO YELLOW
242 | P a g e
BGAS GRADE 2/3 MODEL MULTILE CHOICE QUESTION &ANSWER
2013
Dräger tube and Dräger bellows
Hazard warning symbols
Black symbol of skull and crossbones on an orange square
Toxic or Very Toxic
Black diagonal cross on an orange square
Harmful or Irritant
test-tube dripping onto a hand with a chunk out
adjacent to a test tube dripping onto a stone flag with orange
Corrosive
243 | P a g e

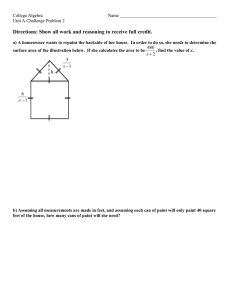

![[Agency] recognizes the hazards of lead](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007301017_1-adfa0391c2b089b3fd379ee34c4ce940-300x300.png)
