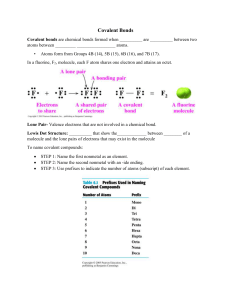
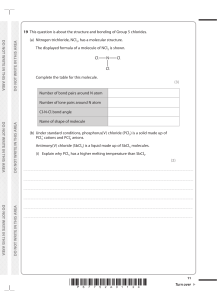
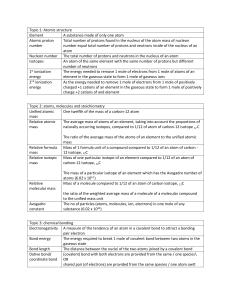
A. Atom Attraction between two oppositely charged ions B. Nucleus The substance dissolved in a solution C. Electrons Slight attractions between oppositely charged ends of polar molecules D. Elements Have a -1 charge E. Isotope At least 2 atoms joined together; also smallest unit of most compounds F. Compound Van der Waals forces between water molecules G. Ionic bond Water attracted (“sticks”) to other substances (not water) H. Ion Pure substances organized in the Periodic Table I. Covalent bond Attraction between atoms that are sharing a pair of electrons J. Covalent bond (yes, again!) cohesion of water allows water bugs to stand on surface K. molecule A measure of H+ and OH- ions present in a solution L. van der Waals forces The basic unit of all matter M. Polar molecule A substance with pH lower than 7 N. Hydrogen bonds An atom which has lost or gained electrons and has a charge O. cohesion Water is a very good one; dissolves many things P. adhesion A substance made of different kinds of elements combined Q. surface tension Molecule that has uneven distribution of electrons (atoms do not share them “evenly”); slight charges at opposite ends R. Solute Water attracted “sticks” to other water S. Solvent Contains protons and neutrons T. pH Bond type found in organic (biological) molecules U. acid Ability of water to climb up thin plant tubes V. base Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons W. 7 A substance with pH higher than 7 X. Capillary action The pH of pure water