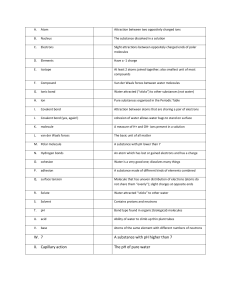
Topic 1: Atomic structure Element A substance made of only one atom Atomic proton Total number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom mass of nucleon number number equal total number of protons and neutrons inside of the nucleus of an atom Nucleon number The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes An atom of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons st 1 ionization The energy needed to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of atoms of an energy element in the gaseous state to form 1 mole of gaseous ions nd 2 ionization As the energy needed to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of positively energy charged +1 cations of an element in the gaseous state to form 1 mole of positively charge +2 cations of and element Topic 2: atoms, molecules and stoichiometry Unified atomic One twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom mass Relative atomic The average mass of atoms of an element, taking into account the proportions of mass naturally occurring isotopes, compared to 1/12 of atom of carbon-12 isotope 12 C Relative formula mass Relative isotopic mass Relative molecular mass Avogadro constant The ratio of the average mass of the atoms of an element to the unified atomic mass Mass of 1 formula unit of a compound compared to 1/12 of an atom of carbon 12 isotope, 12C Mass of one particular isotope of an element compared to 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12 isotope, 12C The mass of a particular isotope of an element which has the Avogadro number of atoms (6.02 x 1023 ) Mass of a molecule compared to 1/12 of an atom of carbon isotope, 12C the ratio of the weighted average mass of a molecule of a molecular compound to the unified mass unit The no of particles (atoms, molecules, ion, electrons) in one mole of any substance (6.02 x 1023) Topic 3: chemical bonding Electronegativity A measure of the tendency of an atom in a covalent bond to attract a bonding pair electron Bond energy The energy required to break 1 mole of covalent bond between two atoms in the gaseous state Bond length The distance between the nuclei of the two atoms joined by a covalent bond Dative bond/ (covalent) bond with both electrons are provided from the same / one species\ coordinate bond OR shared pair (of electrons) are provided from the same species / one atom owtt Topic 4: States of matter Ionic solids It consists of positive and negative ions arranged alternatively in a crystal lattice and are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. Metallic solids It consists of a lattice of a positive metal ions with the outer electrons forming ‘sea of delocalised electrons’ Malleable Easily rolled into sheets or hammered into shapes Ductile Easily drawn into wires Simple molecular It consists of a lattice of discrete molecules held together by weak intermolecular solids forces of attraction Giant molecular It consists of a lattice of atoms held together by strong covalent bonds solids Topic 5: chemical energetics Exothermic Release heat to the surrounding reaction Endothermic Absorbs heat from the surrounding reaction Enthalpy change The change in heat energy content measured at standard pressure Enthalpy change The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements of formation under standard conditions Enthalpy change As the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance completely burnt in of combustion excess oxygen under standard conditions Enthalpy change The enthalpy change when one mole of a water is formed in the neutralization of neutralization between an acid and an alkali, the reaction being carried out in aqueous solution under standard conditions Rate of reaction Change in amount of substance with time Topic 6: electrochemistry Redox reaction A reaction in which the reduction of one reactant and the oxidation of another reactant occurs Oxidizing agent Reactant that causes oxidation but itself reduced in the process Reducing agent Reactant that causes reduction but itself oxidise in the process Oxidation Loss of electrons Reduction Gain of electrons Disproportionation The simultaneous oxidation and reduction of same species in one chemical reactions reaction Topic 7: equilibria Reversible reaction Kp A chemical reaction which can proceed in both directions Mole fraction of a gas Strong acids The ratio of moles of a particular gas to the total number of moles of gas present Equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressures It completely dissociate in water to form H+ ions Weak acids Strong base Weak base Bronsted – lowry acid It partially dissociate in water to form H+ ions only few acid molecules will ionised in water to give H+ ions most of the acid molecules remain unionised in water It completely dissociate in water to give OH+ ions A substance that partially dissociate in water to give OH+ ions only few base molecules will ionized in water to give OH+ ions most of the base molecules remain unonised in water A species which donates H+ to a base Bronsted – lowry bases Conjugate base A species which accepts protons H+ from an acid Conjugate acid This is the article formed when the base has accepted the proton Ph scale A numerical scale that shows how acidic and alkali a solution is This is particle left when the acid has given away its proton Topic 8: reaction kinetics Rate of reaction Change in concentrations of reactants and product per unit time Effective collision When particles collide in the correct orientation and enough energy for a chemical reaction to take place Activation energy The minimum amount of energy that reactant particles must possess in order to react Catalyst A substance that which alters the rate of a reaction but is left chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction Homogeneous A catalyst and the reactants in a catalysed reaction are in the same phase catalyst Heterogeneous A catalyst that is in a different phase to the reactants catalyst Topic 9: the periodic table: chemical periodicity Atomic radius Half the distance between two covalently bonded atoms Van der waals’ Half the distance between two atoms which are not chemically bonded radius Melting point The temperature at which a pure solid is in equilibrium with its pure liquid at atmospheric pressure Topic 13 : Organic chemistry Hydrocarbons Compound that are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms only Functional group An atom or group of atoms, when present in an organic molecule decides the physical and chemical properties of that molecule Empirical formula The simplest ration of the number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of a compound General formula A formula that represent a homologous series of compounds using letter and numbers A group of organic compounds that have the same functional group, the same general formula the same general formula and the same chemical properties Molecular formula Gives the actual number of atoms of each element present in one molecule of a compound Structural formula Show how the constituent atoms of a molecule are joined together Displayed formula Shows both the relative placing of atoms and the number of bonds between them Skeletal formula Show the carbon skeleton only Three dimension Gives the best representation of the shape of a molecule formula Homolytic fission The breaking of a covalent bond such that one electron goes to each of the atom, forming free-radical Heterolytic fission The breaking of a covalent bond such that both the electrons go to the same atom, forming positive and negative ions Alkane Free radical initiation propagation Termination Nucleophiles Electrophiles Is an atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron formed from the homolytic fission of a covalent bond and are very reactive The first step and involves the breaking of covalent bond using the energy from ultraviolet light from the sun to form two free radicals The second step in which the formed radical can attack reactant molecules to form even more free radicals. These in turn can again attack other molecules to form more free radicals and so on Two free radicals react together to from a product molecule Are species which contain a lone pair of electrons and are attracted to regions of positive charge or electron-deficient sites in a molecule Are electron deficient species which can accept electrons and are attracted to regions of negative charge or electron rich Types of reaction Addition reaction Substitution reaction Elimination reaction Hydrolysis Condensation reaction Oxidation reaction Reduction reaction Mechanism Free-radical substitution reaction Electrophilic addition reaction Nucleophilic substitution reaction Nucleophilic addition reaction Involve two molecules joining together to form a single new molecule Involves replacing an atom by another atom Reaction in which a small molecule (such as H2O and HCl) has been lost A chemical reaction in which water reacts with a compound to produce other compounds. It involve the splitting of a bond and the addition of the hydrogen cation and the hydroxide anion from water. A reaction in which two organic molecules join together and involves eliminating small molecules such as H2O or HCL Is a reaction in which oxygen is added, electrons are removed or the oxidation number of a substance is increased A reaction in which oxygen is removed, electrons are added or the oxidation number of a substance is decreased A reaction in which halogen atoms substitute for hydrogen atoms in alkanes A reaction in which an electron rich region in a molecule is attacked by an electrophile followed by addition of a small molecule to give one product only a reaction in which an electron-rich nucleophile displaces a halogen A reaction in which a nucleophile attacks an electron deficient region in a molecule followed by the addition of a small molecule to give one product only