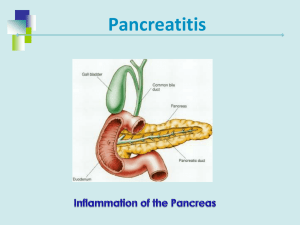
Acute pancreatitis. Dr. Maha Hafez. II year general surgery resident Istiklal hospital Amman- Jordan December, 2020 P A N C R E A S Acute Pancreatitis. Definition. • Acute relapsing pancreatitis. • Chronic pancreatitis. • Chronic relapsing pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis. Classification. Acute pancreatitis is divided into the following: ( Atlanta Criteria 2013) ▪ Mild acute pancreatitis, which is characterized by the absence of organ failure and local or systemic complications ▪ Moderately severe acute pancreatitis, which is characterized by transient organ failure (resolves within 48 hours) and/or local or systemic complications without persistent organ failure (>48 hours) ▪ Severe acute pancreatitis, which is characterized by persistent organ failure that may involve one or multiple organs Acute Pancreatitis. Classification. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Etiology. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Physiopathology. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Symptoms and signs. • Acute onset of persistent, severe abdominal pain: In patients with gallstone pancreatitis, the pain is well localized and the onset of pain is rapid, reaching maximum intensity in 10 to 20 minutes. In contrast, in patients with pancreatitis due to hereditary or metabolic causes or alcohol, the onset of pain may be less abrupt and the pain may be poorly localized. In approximately. 50% of patients, the pain radiates to the back . The pain persists for several hours to days and may be partially relieved by sitting up or bending forward. • 90% of patients have associated nausea and vomiting which may persist for several hours. • Severe acute pancreatitis: dyspnea due to diaphragmatic inflammation secondary to pancreatitis, pleural effusions, or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Symptoms and signs. • Good to bad general conditions. • Vital signs changes according to severity of pancreatitis. (fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxemia, and hypotension). • Dehydration. • General pallor/jaundice/cachexia. • Abdominal distention, tenderness and hypoactive bowel sounds. • 3% Cullen´s & Grey Turner signs. • Findings suggestive of the underlying etiology: hepatomegaly, xanthomas, parotid swelling, trauma, enter point … Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Serum amylase : rises within 6 to 12 hours of the onset of acute pancreatitis, return to normal within 3-5 days. Sensitivity 67 - 83 % specificity of 85-88%. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Serum lipase: rises within 4-8 hours of the onset of symptoms, peaks at 24 hours, and returns to normal within 8 to 14 days. Sensitivity 82 – 100%. Specificity up to 99% Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. • • • • • • • Leukocytosis. CRP Elevated Hcto. Elevated BUN. Metabolic acidosis. Hypocalcemia. ALT > 3x normal gallstone pancreatitis (96% specific, but only 48% sensitive. Markers of immune activation Acute pancreatitis • Alteration in serum glucose is associated with elevations in C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and PMN elastase Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Ranson’s Prognostic Signs that Correlate with the Risk of Major Complications or Death Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Acute Pancreatitis. Colon cut-off sign Sentinel loop Abdominal radiography Pancreatic calcifications Chronic pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis. Elevation of a hemidiaphragm, pleural effusions, basal atelectasis, pulmonary infiltrates, or acute respiratory distress syndrome Chest X ray Abdominal US The pancreas appears diffusely enlarged and hypoechoic on abdominal ultrasound. Gallstones may be visualized in the gallbladder Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020.) Acute Pancreatitis. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Baltazar severity index. Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. MRI is as effective as CT in demonstrating the presence and extent of pancreatic necrosis and fluid collections, and is probably superior for indicating the suitability of such collections for nonsurgical drainage . MRI can characterize the "pancreatic necrosis" seen on CT as necrotic pancreatic parenchyma, peripancreatic necrotic fluid collections, or hemorrhagic foci MRI showing acute edematous pancreatitis. pancreas showed swelling and there was homogeneous peripancreatic fluid collection on the axial T1WI (A, arrow) and the T2WI (B, arrow). The pancreas was homogeneous enhanced after contrast injection (C, asterisk). After 9 days of treatment, the peripancreatic collection was absorbed (D, arrow) Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Evaluation. Acute Pancreatitis. Management. Supportive care with the use of IV fluid hydration is a mainstay of treatment for AP in the first 12-24 hours Medge gastroenteroly:New concepts in the management of acute pancreatitis. Publish date: February 1, 2019. Amar Mandalia, MD Matthew J. Dimagno, MD, AGAF Acute Pancreatitis. Management. • Gastric decompresion with NG tube +-. • Nutritional support. • Antiemetics: metroclopramide/ondasetron. • PPI • Respiratory support. • DVT prophylaxis. • Blood gas analysis if o2 sat less than 90 % or if the clinical situation demands. • Urine output Medge gastroenteroly:New concepts in the management of acute pancreatitis. Publish date: February 1, 2019. Amar Mandalia, MD Matthew J. Dimagno, MD, AGAF Acute Pancreatitis. Management. Acute Pancreatitis. Course of disease. Disease course . Approximately 85% of patients with acute pancreatitis have acute interstitial edematous pancreatitis ; 15% of patients have necrotizing pancreatitis with necrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma, the peripancreatic tissue, or both. 4% Acute Pancreatitis. Local Complications. <4 weeks Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Local Complications. >4 weeks Santhi Swaroop Vege, MD. Management of acute pancreatitis.Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com (Accessed on December 25, 2020 .) Acute Pancreatitis. Systemic Complications. Thank you