Pancreatitis
advertisement
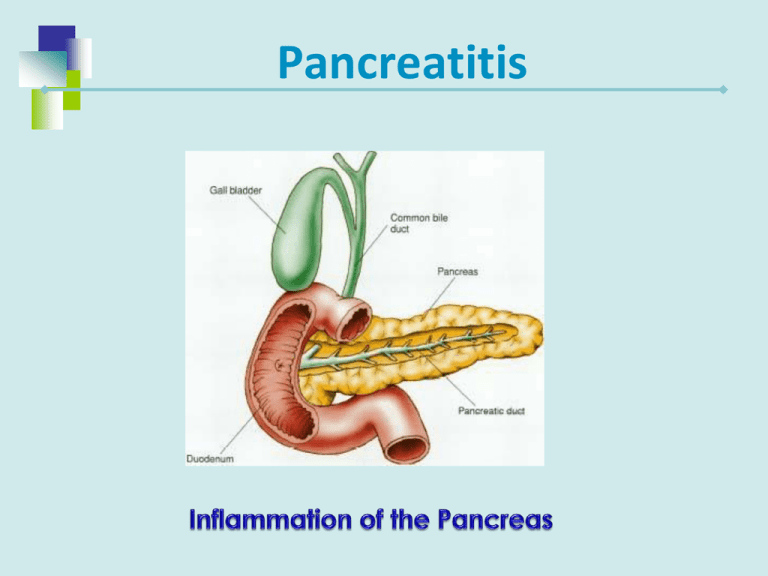
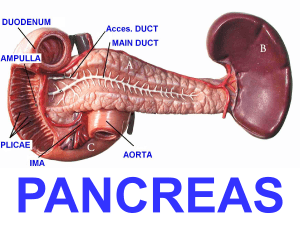
Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Function of the pancreas is to release proteolytic enzymes that assist in the breaking down food products so that nutrients can be absorbed. Acute Pancreatitis Etiology and Pathophysiology Pancreatic Ducts become obstructed Hypersecretion of the exocrine enzymes of pancreas These enzymes enter the bile duct, where they are activated and with bile back up into the pancreatic duct Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Etiology and Pathophysiology Trypsinogen- (a proteolytic enzyme) Normally released into the small intestine, where it is activated to trypsin In AP, activated to trypsin in the pancreas causing autodigestion of pancreas Progression of Disease Autodigestion Acute Inflammation of Pancreas Necrosis of Pancreas Digestion of vascular walls Thrombus and Hemorrhage Death Precipitating Factors Trauma Use of alcohol * Biliary tract disease Viral or Bacterial disease Cholelithiasis * Peptic Ulcer Disease *most common causes Acute Pancreatitis Clinical Manifestations Severe Abdominal pain is predominant symptom Pain located in LUQ and mid-epigastrium Commonly radiates to the back Sudden onset Severe, deep, piercing, steady Aggravated by fatty meal or lying recumbent position Not relieved by vomiting Acute Pancreatitis Clinical Manifestations Cyanosis, Dyspnea Bowel sounds decreased or absent Low-grade fever, Leukocytosis Hypotension, Tachycardia Jaundice Flushing Abnormal lung sounds - Crackles Discoloration of abdominal wall – Turner’s or Cullen’s sign SIGNS OF SHOCK Acute Pancreatitis Diagnostic Studies History and physical examination Laboratory tests Serum amylasehallmark test Serum lipase – also elevated Blood glucose Serum calcium Triglycerides Acute Pancreatitis Diagnostic Studies Flat plate of abdomen Abdominal/endoscopic ultrasound Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Chest x-ray CT of pancreas Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Acute Pancreatitis Can be a medical emergency associated with a risk for lifethreatening complications Acute Pancreatitis Complications Two significant local complications Pseudocyst Abscess Acute Pancreatitis Complications Pseudocyst Cavity surrounding outside of pancreas filled with necrotic products and liquid secretions Abdominal pain Palpable epigastric mass Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia Elevated serum amylase Acute Pancreatitis Complications Pancreatic abscess A large fluid-containing cavity within pancreas Results from extensive necrosis Upper abdominal pain Abdominal mass High fever Leukocytosis Acute Pancreatitis Complications Main systemic complications are? Pulmonary Cardiovascular Electrolyte imbalance – Hypocalcemia Acute Pancreatitis Goals of Care Relief of pain Prevention or alleviation of shock Decrease respiratory failure ↓ of pancreatic secretions Maintain Fluid/electrolyte balance Treatment and Nursing Care 1. Pain management IV morphine or Dilaudid Antispasmodic agent Bentyl Pro-Banthine Spasmolytics – Nitroglycerine Positioning – sitting up and leaning forward Why is it important to relieve pain? Treatment 2. Prevention of Shock – hemodynamic stability * Administer Blood, Plasma expanders, Albumin * LR solution What is the cause of shock? Treatment and Nursing Care 3. Suppress pancreatic enzymes * NPO * NG suction * Antacids, H2 receptor antagonists, antispasmotics 4. Decrease respiratory distress * Oxygen; check O2 saturation levels * Semi-fowlers position, knees flexed, position changes * C, DB; incentive spirometer 5. Antibiotics Treatment and Nursing Care 6. Correction of electrolyte imbalance/ hypocalcemia 7. Maintain Hydration / Nutrition Treatment and Nursing Care Surgical therapy – if related to gallstones ERCP Endoscopic sphincterotomy Laparoscopic cholecystectomy Treatment - Home Care Follow up care Dietary teaching High-carbohydrate, low-fat diet Abstinence from alcohol, Patient/family teaching * Signs of infection, high blood glucose, steatorrhea