南台生技碩專二 黃國清 指導教授 林宏榮 鄭伯智 The journal of clinical Investigation
advertisement

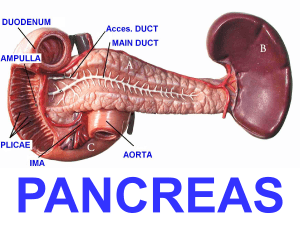
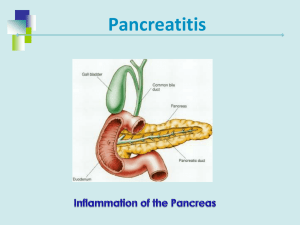
The journal of clinical Investigation Volume 124 Number 1 January 2014 南台生技碩專二 黃國清 指導教授 林宏榮 鄭伯智 Introduction 胰臟 • 外、內分泌功能的腺體 • 胰的內分泌部分叫做胰島(蘭氏小島) – β-細胞分泌胰島素,降低血糖,促進肝糖原的合成等作 用。 – α-細胞分泌升糖素,可以促進肝糖原分解,使血糖升高 • 胰的外分泌腺泡每天製造約1200~1500c.c.的胰液, 經由胰管送至十二指腸。胰液包括可分解蛋白質、 醣類、脂質、核酸的酵素如胰蛋白酶、胰澱粉酶、 脂酶、胰凝乳蛋白酶、胰核酸酶,以及可中和胃 酸的碳酸氫鈉。 Acute Pancreatitis (AP急性胰臟炎) Acute Pancreatitis Etiology and Pathophysiology Pancreatic Ducts become obstructed Hypersecretion of the exocrine enzymes of pancreas These enzymes enter the bile duct, where they are activated and with bile back up into the pancreatic duct Pancreatitis • 過早將胰酵素活化而引起胰臟自體消化, 輕者引起胰臟輕微水腫。重者造成壞死、 出血致死可能性。 Acute Pancreatitis Etiology and Pathophysiology • Trypsinogen胰蛋白酶原- (a proteolytic enzyme) – Normally released into the small intestine, where it is activated to trypsin – In AP, activated to trypsin in the pancreas causing autodigestion of pancreas 內科學誌 2013:24:162-180 臨床症狀 • 上腹痛、腹脹、發燒、嘔吐、吸收不 良、腹瀉、血糖不穩、黃疸、腹水、 呼吸窘迫或休克等。 合併症 •呼吸衰竭、腎衰竭、腸胃道出血、廣泛性 血管內凝血、出血性胰臟炎、肋膜積水、 廔管形成、假性囊腫、腹膜炎,或甚至死 亡。 Acute Pancreatitis Complications Pulmonary Pleural Effusion (enzyme induced Inflammation of Diaphragm) Atelectasis Abdominal distention & diaphragmatic movement Cardiovascular 3rd spacing BP, HR Vasoconstriction d/t SNS activation Coagulation Renall Immunological Trypsin activates both clotting & lysing factors DIC & PE Hypovolemia GFR Renal perfusion Clots in renal circulation ATN ARF GI motility bacteria outside GI Pancreatic abscess Necrosis infection 11 診斷 急性胰臟炎的診斷需要下列三點中的任何兩點 ( 一) 腹痛:急性發作而且持續以及劇烈的上 腹部痛,往往會擴散到背部 ( 二) 血清脂肪酶或澱粉酶上升超過正常值的 三倍 ( 三) 獨特的影像學檢查 急性胰臟炎的診斷與治療之最新進展:內科學誌 24:162-180 2013: • Intraacinar activation of proteolytic enzymes • Microcirculatory injury • Leukocyte chemoattraction, release of cytokines, and oxidative stress • One of the most feared complications of acute pancreatitis (AP) is infection and bacterial colonization of the necrotic pancreas • TLR4 activation is one of the mechanisms by which bacterial translocation may account for the development of severe experimental AP Carbon monoxide (CO) • Carbon monoxide (CO) is increasingly recognized as a cytoprotective and homeostatic molecule • The antiinflammatory and protective properties of CO are supported by accumulating evidence in animal models of cardiovascular disease, inflammatory disorders, and organ transplantation Cardiovascular Research: Volume 41, Issue 2, 1 February 1999 • Transition metal carbonyls, termed COreleasing molecules (CO-RMs), have been used in biological systems to deliver CO Goal of this study • Treatment effect of CO in AP • Molecular biology study of CO in AP Results CORM-2 ameliorates established experimental AP • choline-deficient diet supplemented with DL- ethionine (CDE) feeding – severe hemorrhagic AP associated with significant mortality Lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) a measure of pulmonary leukostasis CORM-2 suppresses systemic proinflammatory cytokines and TNF-α production by spleen and pancreatic macrophages Nature Reviews Rheumatology 4, 319-327 (June 2008) Lineage-positive (Lin+) cells are a mix of all cells expressing mature cell lineage markers. For example for mouse bone marrow: Mac-1 for myeloid cells, CD4 and CD8 for Tcells, CD19 or B220 for Bcells, Ter-119 for erythrocytes, ect. The rest of the cells are lineagenegative (Lin-) – they are not stained by the lineage antibodies. All stem and progenitor cell activity was identified withing Linpopulation, but not in Lin+ cells. http://stemcellassays.com/2009/11/what-islineage-negative-cells/ CORM-2 inhibits TLR4-mediated TNFα production in mouse and human monocyte/macrophages • Use calcium binding protein A8 (S100A8) and HMGBl to activate TLR4 Scientific Reports 3, Article number: 2960 (2013) Nature Reviews Rheumatology 7, 416-426 (July 2011) http://www.invivogen.com/review-damp Kidney International (2014) 86, 525–537. Kidney International’s 2013 Impact Factor is 8.520 生技所碩專研一 黃國清 High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) • has been recognized as an essential damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) • previously was thought to function only as a nuclear factor that enhances transcription • recently discovered to be a crucial cytokine that mediates the response to infection, injury and inflammation NATURE REVIEWS | IMMUNOLOGY: 2005(5):331-342 CORM-2 reduces macrophage TLR4/MD2 receptor expression during AP Front. Immunol., 25 July 2014 CORM-2 decreases LPS binding to TLR4/MD2 receptor complex Ablation of TLR4 in hematopoietic cells confers protection against AP CORM-2-primed cells ameliorate experimental AP • caerulein hyperstimulation mild to moderate AP CORM-2-primed cells ameliorate experimental AP Carbon Monoxide (CO)一氧化碳 • Given the potential toxicity of systemically administered CO-RMs or CO, • the authors tested whether monocytes/macrophages primed via CORM-2 pretreatment • CORM-2-primed cell transfer. 1. BM cells were isolated from Balb/c mice 2. CD11b-enriched cells were treated with either VE or 100 μ M CORM-2 overnight. 3. PBS, 5 × 106 cells were transferred i.v. into mice undergoing caerulein-induced pancreatitis, 90 minutes after the first caerulein injection 謝謝聆聽 歡迎討論