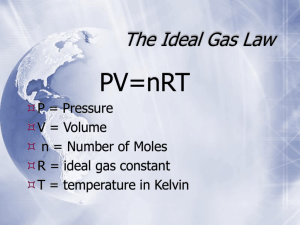
GASES Matter and the Environment Miss Gaby Montemayor GASES ● One of five states of matter. ● Particles have high kinetic energy and are loosely packed. ● No definite shape or volumen. Ideal GASES ● Gases whose particles do not repel or attract each other ● Gases whose particles have only elastic collisions Ideal GASES ● Ideal gases are a concept that helps us approximate the behavior of real gases. ● Certain gases are close to ideal, so this concept is useful. IDEAL GAS LAW Ideal GAS LAW ● Describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount (in moles) of an ideal gas. Ideal GAS LAW Expressed by the formula: PV= nRT Ideal GAS LAW Expressed by the formula: PV= nRT P= Pressure V= Volume n= moles R= Ideal Gas constant T= Temperature (in Kelvin) PRESSURE Pressure= Force/Area Pressure units include - atm (atmospheres) - Pascals (N/m2) - mmHg (mm of Mercury) volume Volume indicates the amount of space taken up by a gas. Volume units include: - Liters (L) - Cubic meters (m3) MOLES Describes the amount of gas molecules 1 mol= 6.022x1023 molecules WHY DOES 1 MOL EQUAL 6.022X 1023 MOLECULES? AVOGADRO’s NUMBER Amadeo Avogadro proposed that the number of atoms or molecules is proportional to its physical mass. AVOGADRO’s NUMBER Avogadro’s number is a proportion used to relate the number of atoms in an element or molecules in compound to its physical mass. 6.022x1023 MOLE International System of Units (SI) that measures the amount of ”chemical entity”. 1 mole= 6.022x1023 MOLE A mole is just a number! For example: 1 dozen= 12 of something 1 mole= 6.022x1023 of something TEMPERATURE ALWAYS expressed in Kelvin. How to convert from ºC to K: T= ºC+273.15 Hence: 0ºC= 273.15 K IDEAL GAS CONSTANT (R) Its is a number that describes the behavior of gases under ideal conditions. STP Stands for STANDARD TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE (STP). The conditions are: - Temperature= 273.15 K (0ºC) - Pressure= 1 atm IDEAL GAS CONSTANT (R) States that 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.414 L. R = PV nT IDEAL GAS CONSTANT (R) States that 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.414 L. R = PV = (1 atm)(22.414L) nT (1 mol) (273.15) IDEAL GAS CONSTANT (R) States that 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.414 L. = 0.082 atm*L mol*K IDEAL GAS CONSTANT (R) States that 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.414 L. R= 0.082 atm*L mol*K = 8.31 J mol*K HOW TO IDENTIFY IDEAL GAS LAW PROBLEMS? ü Problem gives data on pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles ü Problem specifies the value of R SAMPLE PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1- SOLVING FOR PRESSURE If a 3.0 L tank of oxygen (O2) contains 0.45 moles of O2 at 24ºC, what is the pressure (in atm) in the tank? R= 0.0821 L*atm/mol*K PROBLEM 1- SOLVING FOR PRESSURE P= ? V=3.0 L n= 0.45 moles R= 0.0821 L*atm/mol*K T= 24ºC +273.15= 297.15K PROBLEM 1- SOLVING FOR PRESSURE PV= nRT P= nRT V PROBLEM 1- SOLVING FOR PRESSURE P= (0.45 mol) (0.0821 L*atm/mol*K)(297.15 K) 3.0 L P= 3.6 atm PROBLEM 2- SOLVING FOR VOLUME A ball is filled with 2.1 moles of gas. The temperature is 25ºC and the pressure in the ball is 2.5 kPa. Find the volume of the ball. R= 8.31 L*kPa/mol*K PROBLEM 2- SOLVING FOR VOLUME P= 2.5 kPa V= ? n= 2.1 moles R= 8.31 L*kPa/mol*K T= 25ºC +273.15= 298.15K PROBLEM 2- SOLVING FOR VOLUME PV= nRT V= nRT P PROBLEM 2- SOLVING FOR VOLUME V= (2.1 mol) (8.31 L*kPa/mol*K)(298.15 K) 2.5 kPa V= 2,081.21 L PROBLEM 3- SOLVING FOR MOLES A gas tank has a volume of 130 L. How many moles of gas are required to fill the drum at 110kPa of pressure and 27ºC? R= 8.31 L*kPa/mol*K PROBLEM 3- SOLVING FOR MOLES P= 110 kPa V=130 L n= ? R= 8.31 L*kPa/mol*K T= 27ºC +273.15= 300.15K PROBLEM 3- SOLVING FOR MOLES PV= nRT n= PV RT PROBLEM 3- SOLVING FOR MOLES n= (110 kPa) (130 L) (8.31 L*kPa/ K*mol) ( 300.15 K) n= 5.73 moles PROBLEM 4- SOLVING FOR TEMPERATURE A 5.0 L tank of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas contains 7.0 mol of CO2 at 4.8 atm of pressure, what is the temperature (in K) in the tank? R= 0.0821 L*atm/mol*K PROBLEM 4- SOLVING FOR TEMPERATURE P= 4.8 atm V= 5.0 L n= 7.0 moles R= 0.0821 L*atm/mol*K T= ? PROBLEM 4- SOLVING FOR TEMPERATURE PV= nRT T= PV nR PROBLEM 4- SOLVING FOR TEMPERATURE T= (4.8 atm) (5.0 L) (0.0821 L*atm/ K*mol) (7.0 mol) T= 41.76 K