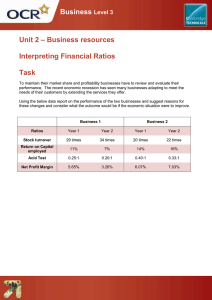
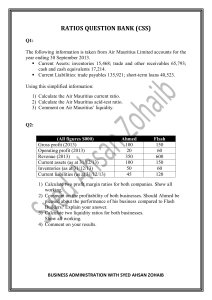
Profitability ratios assess a company's ability to earn profits from its sales or operations, balance sheet assets, or shareholders' equity. Profitability ratios indicate how efficiently a company generates profit and value for shareholders. Higher ratio results are often more favorable, but these ratios provide much more information when compared to results of similar companies, the company's own historical performance, or the industry average. The return on assets ratio formula is calculated by dividing net income by average total assets ROAs over 5% are generally considered good and over 20% excellent. However, ROAs should always be compared amongst firms in the same sector. ROE Ratio = Net Income/ Shareholder's Equity This ratio tells you how much money the company earns on an investor's dollar ROEs of 15–20% are generally considered good. ROE is also a factor in stock valuation, profit margin indicates how many cents of profit has been generated for each dollar of sale. Total Revenue - Total Expenses ) / Total Revenue.20% margin is considered high (or “good”) A liquidity ratio is a type of financial ratio used to determine a company's ability to pay its short-term debt obligations Current ratio is a comparison of current assets to current liabilities, calculated by dividing your current assets by your current liabilities.more than 1 is good. QR = (Cash + Cash Equivalents + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivable) / Current Liabilities The ideal quick ratio is considered to be 1:1, so that the firm is able to pay off all quick assets with no liquidity problem The cash ratio is a liquidity measure that shows a company's ability to cover its short-term obligations using only cash and cash equivalents. Cash ratio = (Cash + Marketable Securities) / Current Liabilities Although there is no ideal figure, a ratio of not lower than 0.5 to 1 is usually preferred.