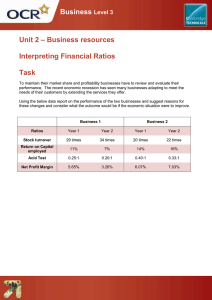
CHAPTER 2 : FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS INTRODUCTION Financial statements can be used to measure the company financial performances. Financial performance is not limited to company profit, but it also cover to asset and liability performance, cash liquidity and more. Financial statements consist of: 1. Statements of Comprehensive Income (SOCI) 2. Statements of Financial Position (SFP) 3. Cash Flow Statement OBJECTIVES Technique for analyzing the financial statements. A process of expressing financial data into standardized terms. Objectives of financial ratios analysis : i. Better understanding of business activities and performance. ii. Simplify accounting information. iii. Assess the operating efficiency of the business. iv. Help in comparative analysis such as inter-firm and intra-firm comparisons. IMPORTANCE OF RATIO Helpful in assessing operating efficiency of the business a. o Helpful in measuring financial solvency. b. o c. Rod of efficiency. The evaluation of changes during different period can be performed. Suitable tools for evaluating the liquidity and solvency position of a concern. Helpful in decision making o The information provided by ratio analysis is very useful for making decision on any financial activity. IMPORTANCE OF RATIO Helpful in communication d. Different financial ratios communicate the strength and financial standing of the firm to the internal and external parties. o Helpful in future forecasting. e. o Calculation of past years works guide line for the future. Helpful in comparing inter firm performance. f. Ratio analysis also serves as a stepping stone to remedial measures. It helps management evolving future 'market strategies‘. o APPROACH IN RATIO ANALYSIS a. Trend Analysis / Time Series Analysis b. Comparison of financial performance of the company based on ratios of the current year with the previous years. Comparative Analysis / Cross Sectional Analysis Firm can evaluate their financial performance by comparing ratios with other companies in the same industry using industry average ratios. Ratios can be classified into five areas : TYPES OF RATIO ANALYSIS a. Profitability – This ratio indicate business success in generating profit. b. Activity – measures the efficiency company managed short term assets and liabilities. c. Liquidity – measures company’s ability to meet its financial obligations when it due. d. Leverage – measures how a company is financed with respect debt and equity as well to evaluate financial risk. e. Investor – Common use to valuing target company in takeover, analyzing dividend policy and investor return. Gross profit margin Gross Profit X 100 Sales PROFITABILITY RATIO Operating profit margin Operating Profit Sales X 100 Net Profit Margin Profit after tax Sales X 100 PROFITABILITY RATIO Return on Capital Employed Profit before tax and interest X 100 Capital employed Return On Asset (ROA) Profit after tax Total Assets X 100 Return on Equity Net Profit – preferred shares dividends Common Equity X 100 Trade Receivables days = Debtor X 365 COGS ACTIVITIY RATIO Trade Payables Days = Creditor COGS Inventory Turnover = Inventory COGS X 365 X 365 Cash Conversion Cycle = Trade receivable days + Inventory turnover – Trade payables days Sales Sales/net working capital = Current Assets ACTIVITIY RATIO Fixed Asset Turnover = Sales Fixed Assets Current ratio Current Asset Current Liabilities LIQUIDITY RATIO Quick or acid test ratio Current Assets - Inventories Current Liabilities Debt-to-equity ratio Total Liabilities Total Equity LEVERAGE RATIO Debt-to-capital ratio Total Liabilities Total Debt + Equity Times interest earned (TIE) Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) Interest Expenses Earning per share (EPS) Net Profit for common shareholders Number of common shares outstanding VALUATION RATIO Price per earnings ratio (P/E ratio) Price per share Common Equity LIMITATION OF RATIO ANALYSIS 1. Ratio only concern on number that appears in financial statement (quantitative data). It omits other factors such as policies, competition, natural disaster and so on. 2. Ratio only use financial data. Price and value might be changes due to factors of economic situation, demand and supply etc. 3. Complexity in accounting, thus, proper presentation are needed so easy to explain