The Balance Sheet
advertisement

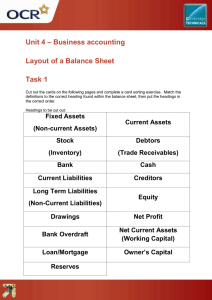
BBI1O1 The Balance Sheet The formal way of presenting the financial position for a company is the balance sheet A balance sheet is a statement showing the financial position of a person, business, or other organization Balance Sheet Example Features of the Balance Sheet The Balance Sheet looks like the Fundamental Accounting Equation A = L + OE Assets are on the left side and the liabilities and owner’s equity are on the right side Features of the Balance Sheet A Three Line Heading is Used WHO? – The name of the individual, business or other organization WHAT? – The name of the financial statement (in this case the balance sheet) WHEN? – The date on which the financial position is determined Features of the Balance Sheet The assets are listed in order of their liquidity Liquidity means the order in which the assets are converted into cash Cash on hand, bank balances are first, whereas equipment & building are listed later (they are normally not converted to cash, but used in business operations) Look at the Order of Liquidity Features of the Balance Sheet The liabilities are generally listed in the order in which they are normally paid The two final totals are listed on the same line on the balance sheet and are underlined with a double line Accounts Receivable Customers of the business will often buy goods or services with the understanding that they will be paid for in the future These debts owed represent a dollar value to the business, so the business has a right to include them among the assets on the balance sheet Each of these customers that owes money to the business is one of its debtors Accounts Payable A business often purchases goods and services from its suppliers with the understanding that payment will be made later These debts to suppliers represent an obligation of the business, so the business must include them among its liabilities Each of the suppliers owed money by the business is one of its creditors