Communication Models: Linear, Interactive, Transactional
advertisement

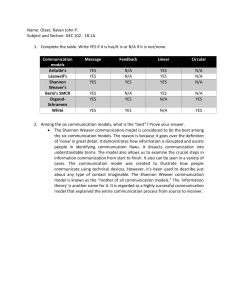
COMMUNICATION MODELS ( LINEAR, INTERACTIVE, TRANSACTIONAL ) Prepared by: Ana Mae F. dela Torre LINEAR MODEL OF COMMUNICATION ARISTOTLE MODEL SPEAKER SPEECH AUDIENCE EFFECT SHANNON AND WEAVER MODEL OF COMMUNICATION Claude Shannon and Warren Weaver Information Source Transmitter (Encoder) Channel Noise Source Receiver (Decoder) Destination THE SENDER-MESSAGE-CHANNEL-RECEIVER MODEL David Berlo (Berlo’s SMCR Model) Source Message Channel Receiver Communication Skills Content Hearing Communication Skills Attitudes Elements Seeing Attitudes Knowledge Treatment Touching Knowledge Social System Structure Smelling Social System Culture code Tasting Culture TRANSACTIONAL MODEL OF COMMUNICATION BARNLUND’S MODEL INTERACTIVE MODEL OF COMMUNICATION WHITE’S MODEL SCHRAMM’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION – OSGOOD-SCHRAMM COMMUNICATION MODEL Wilbur Schramm (1954) Message Encoder Decoder Interpreter Interpreter Decoder Encoder Message KEY TAKEAWAYS Three models for how communication functions have been proposed: linear, interactional, and transactional. **The linear model holds that a message travels in a straight line from its source, through a channel, and to its receiver. **The interactional model holds that communication travels in a circle as a sender transmits a message and then the receiver responds with feedback; thus both parties become sender/receivers. **The transactional model holds that sending and receiving occur simultaneously.