Models of Communication: Aristotle, Lasswell, Shannon, Berlo
advertisement

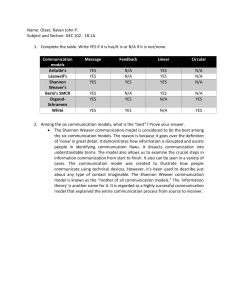
Models of Communication Models of Communication Aristotle’s Model of Communication Lasswell’s Model of Communication Shanon and Weaver’s Model of Communication Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication Aristotle’s Model of Communication Aristotle 384-322 B.C. HE IS A GREEK PHILOSOPHER AND WRITER HE WAS BORN IN STAGIRA,NORTHEN GREECE HE STUDIED PHYSICS, LOGIC, MATHEMATICS AND ETC. Aristotle’s Model of Communication Widely accepted and most common model of communication Sender sends message to receiver A response is expected Elements of Aristotle’s Model of Communication Example: A politician gives a speech during an election campaign. Speaker • Politician Speech • Speech to win the votes of the citizens Audience • Citizens at the time of the campaign Effect • Negative or Positive Effect Lasswell’s Model of Communication Harold Lasswell American political scientist Born in Donnellson, Illinois in 1992 Wrote dissertations about propaganda techniques during the World war Lasswell’s Model of Communication This Model answers the following questions: Who? Said what? In which channel? To whom? With what effect? Lasswell’s Model of Communication Shannon and Weaver’s Model of Communication Known as the “mother of all models” (Derived from helpfulprofessor.com /shannon-weaver-model/) Developed by Warren Weaver and Claude Shannon Was specially designed to develop the effective communication between sender and receiver Was initially developed to improve technical communication (Derived from https://www.communicationtheory.org/shannon-andweaver-model-of-communication/) Key Concepts of Shannon and Weaver’s Model of Communication Sender - source of the message Encoding - process by which a source selects symbols to represent an idea Message - the content of the communication Channel - the medium through which the message must pass (Derived from socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Argument_and_Debate/Arguing_Using_ Critical_Thinking_(Marteney)/02%3A_Communicating_An_Argument/2.03%3A_The_Communi cation_Model) Key Concepts of Shannon and Weaver’s Model of Communication Receiver - the target audience of the message Decoding - translate the message code to symbols that the receiver could understand Noise - anything that disrupts or distorts the communication process Feedback - information sent back to the source (Derived from socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Argument_and_Debate/Arguing_Using_ Critical_Thinking_(Marteney)/02%3A_Communicating_An_Argument/2.03%3A_The_Communi cation_Model) Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication Developed by David Berlo, American communication theorist, 1960 “communication occurs when the sender and receiver are on the same level” includes four components: the sender, message, channel, and the receiver End of Presentation Thanks for listening!