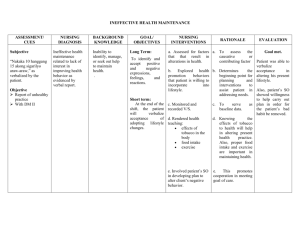
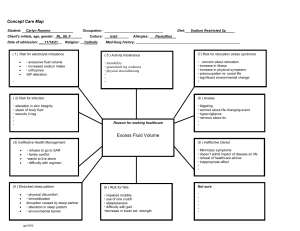
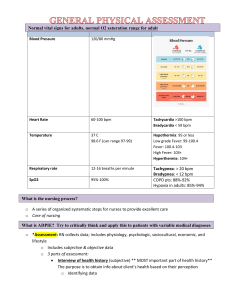
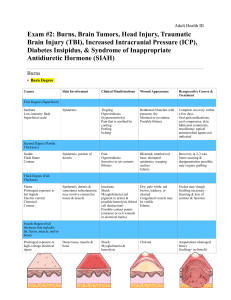
South Puget Sound Community College Nursing Program Care Plan Form NURS 241 Problem: Fluid volume excess due to congestive heart failure. General Goal: Demonstrate stabilized fluid volume with balanced I&Os, absence of edema and stable weight. Behavioral Outcome: Resident/Patient will: The patient will demonstrate loss of excess fluid by weight. Nursing Interventions 1. Administer Furosemide (Lasix) as ordered 2. Maintain fluid and sodium restrictions as indicated 3. Weigh patient daily and compare to previous weight. 4. Monitor and calculate 24 hour I&Os Evidence-Based Rationale Client Response to Interventions 1. Promotes diuresis 1. Patient lost 14lbs in 24 hours 2. Reduces total body water and prevents fluid reaccumulation 2. Patient’s sodium intake does not exceed 1500 mg. 3. Body weight is a good indicator of fluid balance and an increase indicates fluid volume excess. 4. Diuretic therapy may result in sudden increase in fluid loss (circulating hypovolemia), even though edema or ascites remains. 3. The patient does not demonstrate any weight gain from previous recorded weight. 4. The patient’s shows no signs of circulating hypovolemia. Urine output is 500 ml in 24 hours. Evaluate the resident’s/patient’s progress toward the behavioral outcomes: The patient’s edema has improved from a 4 to a 2 with a weight loss of 20lbs from diuresing at the hospital. Patient states she can breathe easier and understands her atrial fibrillation is a chronic condition and acknowledges the need for a low-sodium diet. Schuster, P.M. (2002). Concept mapping; A critical thinking approach to care planning. Philadelphia: F.A.Davis. JAH 9/2015, 10/20 South Puget Sound Community College Nursing Program Care Plan Form NURS 241 JAH 9/2015, 10/20