Heart Failure Study Guide: Symptoms, Treatment, Nursing Care
advertisement

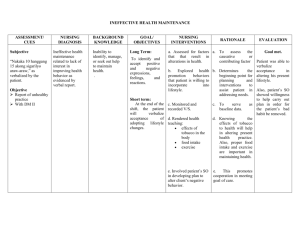
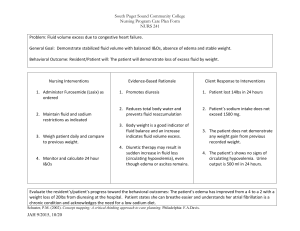
Chapter 34: Heart Failure 1. 2. Complete the following chart with the clinical manifestations of each. Highlight KEY differences that distinguish each type. Right-sided heart failure (HF) Left-sided heart failure (HF) Dependent edema Jugular venous distension Abdominal distension Splenomegaly Anorexia Nocturnal diuresis Hypertension/hypotension SOB Severe fatigue Pulmonary problems: Dyspnea Tachypnea Crackles Dry cough Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Pulmonary edema Mark the area where the nurse would monitor for edema that occurs from rightsided heart failure & congestion occurs from left-sided heart failure. CRITICAL THINKING Read the following case study and answer the questions. Mr. Stephan, age 70, is admitted to the cardiac unit for increasing dyspnea on exertion and fatigue. Subjective Data Objective Data • History of HF for 2 years • Unable to walk one block without increasing dyspnea • Increasing fatigue during the last 2 weeks • Sleeps at 60-degree angle in reclining chair • Blood pressure 140/78 mm Hg, pulse 108 beats per minute, respirations 24 breaths per minute, temperature 98.8°F (37.1°C) • Chest x-ray examination: left and right ventricular hypertrophy, bilateral fluid in lower lung lobes • Jugular vein distention at 45 degrees • Bilateral crackles in lung bases • Has frequent dry cough • Nonpitting edema 1. Explain the cause of Mr. Stephan’s fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath. Impaired gas exchange r/t fluid in lungs Fluid imbalance 2. Which of Mr. Stephan’s signs and symptoms are from left-sided HF and which are from right-sided HF? Left: left ventricular hypertrophy, bilateral fluid in lower lung lobes, bilateral crackles in lung bases, dry cough, activity intolerance Right: right ventricular hypertrophy, jugular vein distention, nonpitting edema 3. Explain the purpose of each of the following therapies. How would they be beneficial in treating Mr. Stephan’s heart failure? • Furosemide (Lasix) 40 mg by mouth twice daily: ▪ Diuretic that would remove excess fluid buildup • Lisinopril (Zestril) 5 mg by mouth daily: ▪ Antihypertensive (ACE inhibitor) that would lower risk of fatal cardiovascular event, reduces afterload and SVR, dilates venule and arterioles, improves renal blood flow, and inhibits ventricular hypertrophy • 2g sodium diet: ▪ Excess sodium may worsen HF symptoms and facilitate an exacerbation • Oxygen 4 L/min: ▪ Brings O2 saturation back up while patient’s heart recovers • High Fowler position: ▪ Reduces chances of aspiration due to fluid in the lungs, and provides comfort while breathing for the patient 4. Mr. Stephan suddenly becomes dyspneic and anxious. He has moist crackles throughout his lungs and pink frothy sputum. Explain what is happening. • His condition is worsening because excess fluid and blood is collecting in the lungs, which is a sign that both sides of the heart are failing 6. List two priority nursing diagnoses and goals for Mr. Stephan’s chronic HF. Impaired gas exchange o No crackles in lungs within next 24 hours Fluid Imbalance o Input matches output by day of discharge 7. What are Mr. Stephan’s health learning needs to manage his chronic condition? Restrict sodium and fluid intake Learn signs and symptoms of worsening condition (i.e. pink, frothy sputum or weight gain >3lbs in a day) What medications to take and indications for them Lecture Notes Systolic dysfunction o Inadequate contractility Diastolic dysfunction o Heart is unable to relax & fill with blood HF usually starts on left side the progresses to right side Look at BNP, edema in hands/feet or lungs, urine output Order of systolic HF to diastolic HF o Heart damage or dysfunction occurs Other form of cardiac issue precedes it o Neurohormonal compensatory mechanisms are involved Responsible for signs and symptoms of HF o Less blood is ejected from the ventricle o Sympathetic stimulation occurs to increase cardiac output Release of epinephrine and norepinephrine increases HR, decreases renal perfusion, and increase cardiac output o Heart muscle thickens Aka “hypertrophy” o Cardiac muscle becomes fibrotic Cardiac cells become dysfunctional and diastolic HF develops LEFT SIDED = LUNG o Symptoms Dyspnea S3, s4 (murmur) RIGHT SIDED o Symptoms JVD Weight gain Peripheral edema Diagnosing it o Measure EF Compensatory mechanisms o RAAS system to alleviate fluid o Hypertrophy Acute HF o Geriatric: confusion, loss of LOC o Anxious pale, cyanotic o Diaphragmatic breathing, nasal flaring o Left sided Cough Hemoptysis Orthopnea Pulmonary congestion o Right sided Hepatomegaly Edema (bipedal) Ascites Distended neck vein BNP levels (400 is normal) EF < 40 Drug therapy o Diuretics o Vasodilators Nitro IV o Morphine for dyspnea and anxiety (and resp depression) o Positive inotropes o Anticoagulants Avoid clot formation Monitor hemodynamic status Chap 37 notes Indicative of PAD o Lower peripheral pulse o Shiny leathery skin of legs with eczema o Compression stockings are recommended S&S of DVT o Pain on dorsiflexion DVT o Elevate extremities (prevents edema) o Rest o Anticoagulants o Compression stockings o Lovanox (subq) to help with the reduced ambulation Look up Virchow’s triad PAD venous disorders o Symptoms occur when arteries are 60-70% blocked o Clots will be from chest down in the arteries o S&S Intermittent claudication Paresthesia (pressure, sensation loss in lower extremities) Pain at rest Venous: spider veins Arterial: pale feet?? o o o o o o o o o o o o Hemoglobin levels Cholesterol level BMI level NSAIDs can cause bleeding in GI so educate not to take while on anticoagulants Atherectomy can be an intervention Ineffective tissue perfusion Acute care Monitor skin and temperature Capillary refill Presence of peripheral pulses distal to the operative site Sensation and movement of extremity At risk Immobility Chronic HF or atrial fibrillation Obese Pregnant Superficial vein thrombosis Vitamin K antagonists Warfarin (antidote protamin sulfate) Vitamin K levels Avoid foods with vitamin K while on warfarin Green leafy vegetables Don’t increase amount in diet Thrombin inhibitors Heparin Or lovanox Tutorial Notes Usually never do nothing, call doctor, or continue to monitor Continue to monitor = focused assessment S3 gallop = worsening HF Anime recs 1. Dorohedoro 2. Samurai champloo 3. Michiko to hatchin 4. Mob psycho 100 5. Space dandy 6. Cowboy bebop 7. Aggretsuko 8. Pop team epic 9. Super crooks 10. Demon slayer 11. Ajin demi human 12. Ghost in the shell