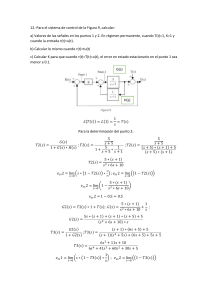
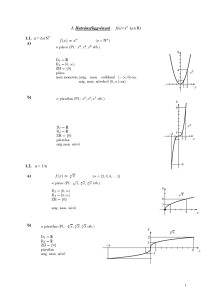
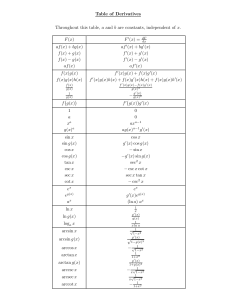
x a 8. Continuity at a if lim f x f a lim f x x a x a TYPES OF DISCONTINUITY 9 y 10 7 y 11 y 7 6 5 3 2 1 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 x 5 -1 1 Point or removable 2 3 4 2 5 Jump y 1 x 1 -1 -2 2 x 3 -2 -1 1 2 -1 -3 -4 -5 1 x -1 12 4 6 -2 Infinite Oscillating Basic Rules constant d d d 1. c 0 Constant 2. c f ( x) c f ( x) dx dx dx multiple d n d d d Sum & 3. x nx n 1 power 4. u v u v dx dx dx dx Difference d d v uu v d d d d u dx dx Quotient 5. (uv ) v uu v Product 6. 2 dx dx dx dx v v 1 7. f 1 x Inver se f f 1 x d d d 8. f g x f u g x where u g x Chain R ule dx dx dx WWW.MATHGOTSERVED.COM Exponential and Logarithm ic Functions d 1 du d 1 du 20. ln u 21. log a u dx u dx dx u ln a dx d u du d u du 22. e eu 23. a a u ln a dx dx dx dx d 1 du d u du 24. u 25. u dx dx u dx 2 u dx WHERE THE DERIVATIVE DOES NOT EXIST 26 27 y 28 y 7 x 4 1 2 x 1 -1 1 3 -1 -1 x -1 1 2 3 4 2 -2 5 Discontinuity Corner 1 1 -1 x 1 2 y 1 2 5 -2 29 y 6 2 Cusp Vertical tangent Linearization: L x f a f a x a ARITHM ETIC OF INFINITY 2. n 1. 2. n 3. 0 4.0 3. 0 Ind. 1. / Ind. 1. Ind. 2. n / 0 2. n 3. / n 3. n 4. n / 0 5. n / 0 4. n n 0 1 6. n / 0 1 5. n n 0 7. 0 / 0 = Ind. 1. 1 sin 1 1. 2. n Trig 3. 0 Ind 4. 0 0 2. 1 cos 1 power 5. n 6. 1 Ind 7. 0 0 Ind. 1. LIMITS(1) sin x sin x sin 2 x 1. lim 1 2. lim 0 3. lim 0 x0 x x0 x x x sin ax sin ax bx a cos x 1 4. lim 0 5. lim lim lim x0 x 0 x 0 x 0 x sin bx sin ax b bx 6.lim f x L exists If and only if lim f x lim f x L x a xa xa 7. f x is cont a if lim f x f a Trigonom etric F unctions d du d du 8. sin u cos u 9. cos u sin u dx dx dx dx d du d du 2 2 10. tan u sec u 11. cot u csc u dx dx dx dx d du d du 12. sec u sec u tan u 13. csc u csc u cot u dx dx dx dx Inverse Trigonom etric F unctions d 1 du d 1 du 14. sin 1 u 15. cos 1 u 2 dx dx dx 1 u 1 u 2 dx d 1 du d 1 du 1 1 16. tan u 17. cot u dx 1 u 2 dx dx 1 u 2 dx d 1 du d 1 du 18. sec 1 u 19. csc 1 u 2 2 dx dx u u 1 dx u u 1 dx DERITAVITIVES(2) LIMIT LAWS 30.Mean Value Theorem: If f is cont on a, b on and diff on a, b f b f a exist a c a, b s.t. f c ba f b f a 31.Rolle's Theorem : MVT where f c 0 ba 32. IntermediateValueTheorem. : If f is cont on a, b and d f a , f b then there is a c a, b st f c d Definition of Derivative f x h f x 33. f x lim h 0 h f x f a 34. f a lim x a xa APPROXIMATING AREA 35. f x Average rate of change = Slope of Secant line f b f a ba ANTIDIFFERENTION (INTEGRATION) RULES xright 20. Area = f x top xleft 21. Vol of rev = xright xleft f x down dx or Area = 2 ytop ydown f y f y dy left right 2 b f x a f x a dx Vol Cross sect.= A x dx top down a ii x g x d d f t dt f x iii ) f t dt f g x g x h g x h x dx a dx hx 18.Integration by parts: vdu uv vdu 19.Integration by substitution: use LIPET to select u f g x g x f u du INTEGRALS (3) 11. LRAMn = w f x1 f x2 .. f xn1 or w1 f x1 w2 f x2 .. wn1 f xn1 1. xn dx xn1 C 2. 1 dx ln x C 3. 1 dx ln ax b C 4. ekx dx ekx C x ax b n 1 a k 12. RRAMn = w f x2 f x3 f xn or w1 f x2 w2 f x2 .. wn1 f xn au cos kx sin kx x 5. a dx C 6. sin kx dx C 7. cos kx dx C x x x x x x ln a k k 13. MRAMn = w f 1 2 f 2 3 f n1 n or 2 8. sec x tan x dx sec x C 9. sec x dx tan x C 10. csc x cot x dx csc x C 2 2 2 x2 x3 xn1 xn x1 x2 w1 f w2 f 2 wn1 f 2 1 b 2 15. Average Value of f av f fave f x dx a b a b a Note: w and applies only for equal sub intervals n b x w 1 16. FTC I: f x dx f b f a 17 FTC II i f t dt F x 14. T= y1 2y2 2yn1 yn or w1 y1 y2 w2 y2 y3 ... n a a 2 2 Verbal Description Term Symbolic Graphical y 1. Derivative of f at a: The instantaneous rate of change of the function at a or the slope of the tangent line at a f a lim df dx x a h h 0 c a, b where A number c in an open (a, b) interval where the derivative is zero or does not exist 2. Critical Number c xa f a h f a f c 0 f c DNE y y f c 0 or f c DNE y 7 6 2 2 5 4 1 1 3 2 x x -2 -1 1 -2 2 -1 1 1 2 x -1 Corner 1 2 3 4 5 Discontinuity y y 1 2 x -1 1 1 -1 x -1 1 2 -2 Cusp Vertical tangent 3. First Derivative Test a) If f c ' s from to a) f ' c is a min f c b) If f c ' s from +to f ' c is a max y b) f c f c min f’: Is a point where f’ changes from increasing to decreasing or decreasing to increasing x y f x 0 f x is CU f x is CU on I Concave Down Motion definitions and Equations s t x b x a 8. Velocity: A Vector quantity that represents the rate of change of position v t s t b) If f c 0 on I f x 0 f x is CU f x is CD on I y f ' s from to or to f x ' s from + to or to Point of Inflection f c ' s from + to - b v t 7. Distance: A scalar quantity that represents total movement regardless of sign b d t x b x a v t dt a Speed v t 9. Speed: A scalar quantity that represents the rate of covering distance 11. Given initial position s a C the final position is a t v t s t represents the rate of change of velocity x c f c is a POI a 10. Acceleration: A vector quantity that x x Concave Up f’’: Is a point where f’’ changes from positive to negative or negative to positive 6. Displacement: A Vector quantity that represents the net change in position c f ' s from CU to CD or CD to CU f: Is a point where the concavity of f changes f c y 5. Point of Inflection at c x c a) If f c 0 on I a) If the second derivative is positive on an interval I then the function is Concave Up on I b) If the second derivative is negative on an interval I the function is Councave down on I 4. Concavity Test max VOCABULARY (4) y a) If the first derivative changes from negative to positive at c then the function has a relative minimum at c b) If the first derivative changes from positive to negative at c then the function has a relative maximum at c b given by s b s a s t dt a Reciprocal 1 csc x 1 cos x sec x 1 tan x cot x 1 sin x 1 sec x cos x 1 cot x tan x sin x csc x Quotient Pythogorean sin x sin 2 x cos 2 x 1 tan x cos x tan 2 x 1 sec 2 x cos x cot x cot 2 x 1 csc2 x sin x is given by Sine Curve sin x cos x 0 1 0 csc x Und. 1 x x -2π -3π/2 -π -π/2 π/2 π 3π/2 2π -2π -3π/2 -π -π/2 π/2 π 3π/2 2π -1 -1 y y y 30 45 60 90 6 4 1 2 3 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 3 1 2 1 1 3 2 2 sec x 1 2 cot x Und. 2 1 x x 2 3 3 3 2 x x 0 Linear y x quadratic y x 2 y tan x y 1 y 0 Cosine Curve y 2 3 Cubic y x 3 Radical y y y y x Und. 1 x x 2 2 1 2 1 Und. 3 0 x x Logarithmic y ln x Exponential y e x Absolute value y x AP Calculus Survival Kit circular y 9 x 2