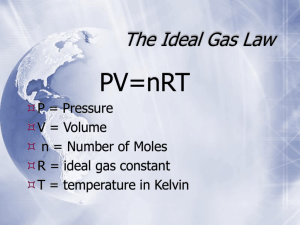
The Ideal Gas Law Is it really Ideal? Ideal Gases •When a gas temporarily conforms to all of the assumptions of the kinetic theory it can behave ideally •An ideal gas is also considered to conform to all gas laws. •Does not behave ideally at high pressures and/or low temperatures •Doesn’t really exist! Ideal Gases •Up until now we have only changed variables such as pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. •In each of these cases the amount of gas was assumed constant. •The combined gas law can be modified to include the amount of gas by including the variable, n. Ideal Gas Law This gas law relates the amount of gas (in moles) to the volume it would occupy at a particular temperature and pressure. We’ve already learned the combined gas law: P1 V1 n1 T1 = P2 V2 n2 T2 If we want to find conditions for an ideal gas, look what we can do! P1 V1 n1 T1 = (1 atm) (22.4 L) = (1 mol) (273 K) conditions @STP 0.0821 atm·L mol·K We call this R Ideal Gas Law STOP! It is PV=nRT Where, called P= pressure often (atm) V= volume (L) the “picky” law! n= moles (mol) The units must be R= 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K T= temperature (K) you see here! what R is called the Ideal Gas Constant (it has multiple values, but for our purposes we will only use this one). Ideal Gas Law Example At what pressure would 0.212 mol of a gas occupy 6.84L at 89°C? P= ? V= 6.84L n= 0.212mol R= 0.0821L·atm/mol·K T= 89°C + 273= 362K P= 𝑛𝑅𝑇 𝑉 PV=nRT P =(0.212mol)(0.0821)(362K) (6.84L) P = 0.92atm Ideal Gas Law Example At what temperature would 52.3g of methane (CH4) gas occupy 65.7L at 1.82 atm? PV=nRT 1.82 atm P= Or 65.7L V= PV = T 1 mol CH4 n= 52.3gCH4 x 16.05gCH = 3.26 mol CH nR 4 4 R= 0.0821L·atm/mol·K T= ? (1.82atm)(65.7L) = T (3.26mol) (0.0821) T = 447K Sample Problem Using Ideal Gas Law A child’s lungs can hold 2.20 L. How many grams of air do her lungs hold at a pressure of 1.01 atm and a body temperature of 37ºC? Use a molar mass of 29 g for air. P = 1.01 atm V = 2.20 L T = 310 K PV = nRT or PV / RT = n n = (1.01) (2.20) (0.0821) (310) n = 0.087 mol air 0.087 mol air x 29g air / mol air = 2.5 g air 10