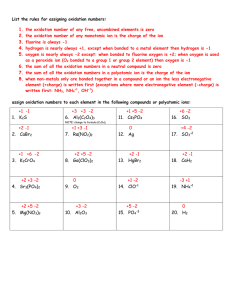
elements known elements in the periodic table naturally occurring are synthesize in laboratories Dalton’s Symbols Element’s name can be based on: Color Chlorine Greek “chloros” meaning greenish yellow Element’s name can be based on: Color Iodine Greek “iodes” meaning violet Element’s name can be based on: Color Cesium Latin “coesus” meaning skyblue Element’s name can be based on: Color Iridium Latin “iris” meaning rainbow Element’s name can be based on: Color Rubidium Latin “rubidos” meaning deepest red Element’s name can be based on: People einsteinium from Albert Einstein the proponent of relativity theory Element’s name can be based on: People curium from Pierre and Marie Curie the discoverers of radium Element’s name can be based on: People fermium from Enrico Fermi, pioneer in nuclear physics Element’s name can be based on: People nobelium from Alfred Nobel the inventor of the dynamite and the founder of Nobel Prize Element’s name can be based on: People mendelevium from Dmitry Mendeleev the chief architect of the periodic table Element’s name can be based on: Places americium from America Element’s name can be based on: Places californium from California Element’s name can be based on: Places germanium from Germany Element’s name can be based on: Places francium from France Element’s name can be based on: Places ytterbium from Ytterby, a town in Sweden Element’s name can be based on: Heavenly Bodies cerium from asteroid Ceres Element’s name can be based on: Heavenly Bodies helium from Greek “helios” the sun Element’s name can be based on: Heavenly Bodies neptunium from the planet Neptune Element’s name can be based on: Heavenly Bodies mercury from the planet Mercury Element’s name can be based on: Heavenly Bodies uranium from the planet Uranus Element’s name can be based on: Miscellaneous Aluminum from Latin “alumen” alum Element’s name can be based on: Miscellaneous Argon from Greek “argos” inactive Element’s name can be based on: Miscellaneous barium from Greek “barys” heavy Element’s name can be based on: Miscellaneous calcium from Latin “calx” lime Element’s name can be based on: Miscellaneous fluorine from Latin “fleure” to flow International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry The element’s symbol consist of one, two, or three letters with the first letter in uppercase and the remaining letter/s in lowercase. It is usually derive from the element’s chemical name. Element Latin Name Symbol Antimony Copper Gold Iron Potassium stibium cuprum aurum ferrum kalium Sb Cu Au Fe K Element Latin Name Symbol Lead Mercury Silver Sodium Tin plumbum hydragyrum argentum natrium stannum Pb Hg Ag Na Sn John Dalton (1766-1844) developed the atomic theory in the early part of 19th century Jons Jacob Berzelius (1779-1848) A Swiss chemist who proposes the use of letters as symbols for elements oxida + ion numbers oxidanumbers + ion is the positive or negative number associated with the ability of an atom to lose or gain electrons Group 1A 1+ 2A 2+ 3A 3+ 4A 2+ 4+ 4- 5A 5+ 3- 6A 6+ 2- 7A 7+ 1- oxidanumbers + ion + - The common positive oxidation numbers of all elements is the group number. Nonmetals starting from group 4A to 7A can have negative oxidation numbers equal to the group number minus 8. + oxidanumbers + ion The oxidation number of an uncombined element is ZERO. - oxidanumbers + ion In a compound, the less electronegative element is assigned a positive oxidation number and the more electronegative one is assigned a negative oxidation number. + oxidanumbers + ion the sum of the positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero 1+ _ H2O2 + 2( 1) + ( 2)=0 + oxidanumbers + ion the sum of the positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero 6+ 2 S2O3 + ( 6) + 3( 2)=0 + oxidanumbers + ion hydrogen in most compounds has an oxidation number of (+1), an exception to this convention is in hydrides where the oxidation number of hydrogen is ( 1) when attached to metals like magnesium hydride (MgH2) + oxidanumbers + ion The oxidation number of oxygen is (-2), except in peroxides where the oxidation number is (-1) and in OF2 where its oxidation number is (+2) + oxidanumbers + ion Electronegative elements in group 7A such as F, Br, Cl, and I generally exhibit the oxidation number of (-1) in most compounds CLASSIFICATION OF IONS Classification Examples 2+, Li+, Mg2+, N3-, O2-, FFe monoatomic by composition polyatomic kind of charge SO42- , ClO3- , CO32- cation Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ anion Cl-,O2-,I- magnitude of monovalent Li+, K+, OHcharge divalent Ca2+, SO42-, Cu2+ monoa+omic ion the oxidation number is properly written after the + or - sign polya+omic ion the sum of the oxidation numbers of an individual ion is known as charge, it is written first before the + or the - sign Quick Qui Group 1A 1+ 2A 2+ 3A 3+ 4A 2+ 4+ 4- 5A 5+ 3- 6A 6+ 2- 7A 7+ 1- Using the table, assign oxidation numbers to each component element in the following compounds: 1. NaBr 2. BaCl2 3. Al2O3 4. CaS 5. H2O2