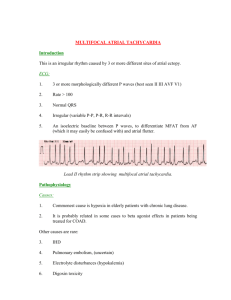
Class Class I antia rrhyt hmic drugs Class IA antiar rhyth mics Dru Main mechanism of Exa g action mple gro s up Fast sodi um cha nnel bloc kers Class IB antiar rhyth mics Inhibit conducti on velocity (negativ e dromo tropy), particul arly in depolari zed tissue (e.g., during t achycar dia): Statedepende nt: the faster the heart rate, the greater the effect →↓ the slop e of phase 0 depola rization Membra ne stabilize rs Separate d into 3 subgrou ps based Use Adverse Effects Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia(PSVT): AVNRTand AVRT(r eentry Especially antidrom ic AVRT and WPW (procainamide) Atrial fibrillation(AFib) and atrial flutter Ventricular tachycardia (VT) QT prolongation→ tors ade de pointes Thrombocytopenia Quinidine Quinism(cinchonis m): loss of visual acuity, hearing loss, tinnitus, headac he, psychosis Procainamide Drug fever Drug-induced lupus erythematosus(reve rsible) Disopyramide: antic holinergiceffects Moderate blockade of Na+ channels (intermedi ate association /dissociati on) Prolong a ction potential ( AP) durati on(right shift) → prolong effective refractory period (ER P) Minimal blocking of the K+ channel Quin idine Proc aina mide Diso pyra mide Ajm aline Weak blockade of Na+ channels (fast association /dissociati on) Shorten AP duratio n(left shift) → slow ERP Lido VT (especially post CNS: dizziness, caine MI) nausea, seizures Mexi AV block III, VES letin e Class Class IC antiar rhyth mics Dru Main mechanism of Exa g action mple gro s up upon their effects on the Na+ cha nnel and the AP duration Use Adverse Effects Strongest effect on ischemi c myocard ium Strong blockade of Na+ channels (slow association /dissociati on) → QRS prolongati on No to minimal effect on AP duratio n (no shift) → ERP un affected Inhibit β-adrenergic Class II Beta antiarrhyth bloc activation of mic drugs ker adenylate cyclase → ↓ cAMP → ↓ Ca2+ Decrease slope of phase 4 in pacemaker cells, leading to a slower conduction velocity Flec ainid e Prop afen one PSVT Proarrhythmia: cont AFib(cardioversion): raindicated postStructural heartdiseas MI! e must be ruled out prior to use! Atrial flutter Meto prolo l Esm olol Prop ranol ol Aten olol Tim olol AFib (frequency control) Atrial flutter PSVT Premature ventricular contractions VT Atrial premature beats [1] AV block, bradycardia Sedation, CNSdepre ssion Erectile dysfunction Exacerbation of asthma, COPD, and psoriasis If given with cocaine toxicity and pheochromocyto ma→ exacerbation due to unopposed α1 agonis Class Dru Main mechanism of Exa g action mple gro s up Inhibit potassium Class III Pota antiarrhyth ssiu delayed rectifier currents mic drugs m cha Prolongs AP nnel duration (Reverse bloc use-dependence) ker and effective refractory period (ERP) No effect on conduction velocity Use Adverse Effects Carv edilo l Sotal ol Ami odar one Dron edar one Sotal ol Bret yliu m Ibuti lide Dofe tilide m (except labetalol a nd carvedilol ) AFib(cardioversion and long-termrhythm control) Atrial flutter VT (not bretylium); see also advanced cardiac life support Sotalol: supraventric ular arrhythmias and vent ricular arrhythmias Inhibit slow calcium Class IV Calc antiarrhyth ium channels mic drugs cha Decrease slope nnel of phase 0 and 4 → bloc slower conduction ker velocity Prolong repolarizat ion of AV node Decreasing conduction velocity leads to increased refractor Vera pami l Dilti azem Nife dipin e AFib (frequency control) Atrial flutter PSVT Multifocal atrial tachycardia QT prolongation → tors ades de pointes Amiodarone Lowest risk of ventricular arrhythmiacompared to other drugs in its class Reversible corneade posits Photosensitivityof the skin Pulmonary fibrosis Liver dysfunction Peripheral neuropathy Thyroiddysfunction Sotalol: beta blocker adverse effects Verapamil AV block, bradycardia Obstipation Nifedipine Headache, flush, pitt ing edema Reflex tachycardia Diltiazem Both verapamiland n ifedipineadverse Class Dru Main mechanism of Exa g action mple gro s up Use Adverse Effects effects, but less prominent y period and PR interval See section on Class V Vari antiarrhyth able “Other mic drugs mec antiarrhythmic hani drugs” below for sms details. Ade nosi ne Digo xin Mag nesiu m sulfa te See section on “Other antiarrhythmic drugs” below for details. All antiarrhythmic drugs are also potentially proarrhythmic! Intravenous administration should be done with ECG monitoring! References: [2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9] Other antiarrhythmic drugs Adenosine (drug) Mechanism of action: transient AV node block Potassium channel activation → ↑ potassium efflux → hyperpolarization → ↓ calcium influx → decrease in intracellular cAMP → acute termination of supraventricular tachycardia Indications: Drug of choice for narrow QRS tachycardias, such as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias: AVNRT and orthodromic AVRT (except pre-excited tachycardias) Diagnostic value: exposing underlying AFib in supraventricular tachyarrhythmias Adverse Effects: Chest pain, flushing, hypotension, bronchospasm Sense of impending doom Asystole (rare) Contraindications Pre-excitation syndrome: antidromic AVRT including Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome AV block Asthma Digoxin Mechanism of action: Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPases → higher intracellular Na+ concentration → reduced efficacy of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers →higher intracellular Ca2+ concentration → increased contractility, decreased heart rate Indications: tachyarrhythmias (e.g., AFib) See cardiac glycosides for details. Magnesium sulfate Mechanism of action: decreases calcium influx → prevents early afterdepolarizations Indications: Torsades de pointes Eclampsia Constipation Tocolysis Adverse effects: Drowsiness Flush Loss of reflexes Respiratory depression I -channel blocker f Ivabradine Mechanism of action: Lowers heart rate by blocking the If channel in the pacemaker cells of the SA node Indications: Drug of last resort for symptomatic relief of stable coronary heart disease and congestive heart failure (NYHA II-IV) in sinus rhythm Adverse effects: Visual changes Bradycardia