The Basics of Arrhythmia
advertisement

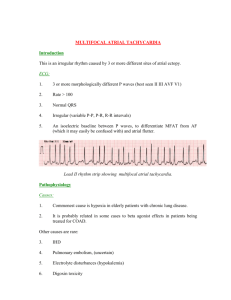
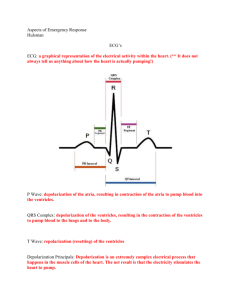
The Basics of Arrhythmia Arrhythmias - the bare bones Basic Physiology reminder Basic ECG reminder • • • • Rate Rhythm PR interval QRS complex – – – – Width Any Q waves? Axis Lateral lead R wave progression • ST and T waves Basic ECG reminder What is an arrhythmia? • Abnormalities of electrical rhythm • Supraventricular – SVT, AF, Atrial flutter – Re-entrant tachycardias • Ventricular – VT, VF, Torsdaes de pointes • Asystole and PEA Clinical manifestations • Palpitations • Syncope • If going fast enough, can precipitate cardiac ischaemia and chest pain • • • • Cardiac failure Decreased level of consciousness Hypoperfusion of all organs Cardiac arrest Common arrhythmias Ventricular Atrial • AF • VT • A Flutter • VF • Paroxs. SVT • Torsades – AVNRT – AVRT (WPW) – Multifocal atrial tachycardia Bradyarrhytmia • Medication • AV block • SSS Ventricular fibrillation What rhythm is it? • Is it sinus? • Is it going at a life-theratening rate? – 220 minus age • Is it regular? – If it is ‘dead regular’ could it be A Fib? • Is it a broad complex? Atrial Fibrillation • Questions to ask yourself – What made it happen? – How long have they been in it? – Do they need anticoagulation? – Do I need to slow it down? – How do I slow it down? Atrial fib with LBBB How to approach a regular SVT? • • • • Is it AF, Aflutter, AVNRT, AVRT??? Valsalva? Adenosine - blocks the AV node Caution with adenosine, dig and calcium channel blockers • If they’re compromised, have some paddles on Broad complex tachycardias • Always VT until proven otherwise! • Look for concordance, evidence of AV dissociation, and very wide QRS WPW with AF Broad complex tachycardias • Electrolytes – High K, Ca++ – Low K, Mg, Ca++ • Drugs (prolong QT interval) – Methadone, amiodarone, lithium, sotalol,quinolones, Stemetil, chlorpromazine • Syndromes • Ischaemia and cardiac scarring VT with clear AV dissociation What do you need to do? • Try and work out what rhythm it is in • If it’s faster than physiologic, then it’s life threatening (220 minus age) • If there’s suggestion of ischaemia, it’s life threatening • If it’s too fast - Slow it down until • If it’s too slow – Speed it up In an arrest • Defib VF and VT only • • • • Get the paddles on! Push hard and fast! – all the way to shock Push onto a hard surface! 100% oxygen, 1 SMALL breath EVERY 30 seconds, SLOW and steady!