Arrhythmias - Modest Mango
advertisement

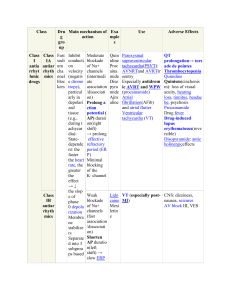
Recognizing Cardiac arrhythmias Normal anatomy Normal ECG Normal ECG Classification - tachys Atrial • AF • Atrial Flutter • PAC Junctional • • Paroxysmal SVT (PSVT) Junctional Tachycardia Ventricular • VT • VF • PVC Broad Complex Mark Henderson Classification - bradys Atrial • Sinus brady • Sick sinus syndrome Junctional • Junctional Escape Ventricular • Ventricular Escape Mark Henderson Atrial Fibrillation • Atrial dilation & decreased CO • RAAS activation • Protease stimulation • Progressive atrial fibrosis • Fragmented, asynchronous depolarizations Mark Henderson Atrial Fibrillation Mark Henderson AF - Classification AF Type Definition New-onset No previous episodes Paroxysmal Recurrent episodes of < 7 days duration Persistent Recurrent episodes of > 7 days duration • Valvular PermanentAF? • Lone AF? • Secondary AF? • Symptomatic AF? Long-term episode Mark Henderson AF - Causes Primary Cardiac Causes Other Cause Coronary artery disease Hypertension Valvular disease Lung disease Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Hyperthyroidism Congenital heart disease Medications, alcohol Pericardial disease Mark Henderson symptoms • Palpitations • Breathlessnes s • • • • Lightheaded Fatigue Chest pain Exercise intolerance DDX • Tachyarrhythmias • Flutter • Panic attack/anxiety • Drugs • Caffeine/alcohol • Symp. Agents • Stimulants Mark Henderson Diagnosis • Heart failure • Echo evidence of stroke risk • Alcohol • Regurg/stenosis • Thyroid Mark Henderson Atrial flutter Ectopic loop (reentrant pathway) of atrial electrical activity, usually precipitated by a PAC Mark Henderson Differences to AF • P waves clearly visible in characteristic ‘sawtooth’ pattern • Comment on degree of block 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 etc • More sensitive to electrical CV • Less sensitive to chemical CV. • RFA useful because of the reentrant nature. PAC • Premature Atrial Contractions • Common, not necessarily pathological • P wave is abnormal due to ectopic focus • P wave may be isolated or may have resulting QRS. Junctional tachys PSVT • Paroxysmal Supra-Ventricular Tachycardia • AVNRT and AVRT (nodal or accessory pathway) AVNRT FP SP FP SP FP SP AVRT • Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia • (Wolf Parkinson White (WPW) Syndrome) • Narrow complex • P wave may be inverted and straight after T wave. • Monomorphic • • VT Usually due to MI scarring causing an aberrant focal automaticity or a reentrant pathway like flutter Polymorphic • Usually abnormality of repolarization - prolonged QT eg. • Needs electrical cardioversion if pulseless, or progresses to VF • If < 30 seconds = non-sustained VT VF • Causes: Trauma (physical or electrical), CAD, MI, cardiomyopathies, sudden cardiac death, congenital heart disease etc... • Most have no hx of heart disease • Though often have many risk factors - smoking, hyperlipidaemia, DM. • Episodes outwith hospital have 2-25% long term survival • many survivors are comatose/permanently brain damaged. Seemingly random pattern No identifiable P or QRS rhythm Wandering baseline Heart block • 1st degree AV block (prolonged PR) • 2nd degree AV block • Mobitz I (lengthening PR til dropped QRS) • Mobitz II (intermittently dropped P waves) • 3rd degree AV block (complete) • Infranodal block • • Left BBB • Left Anterior Fascicular Block • Left Posterior Fascicular Block Right BBB mobitz ii lBBB AF PSVT - AVRT Atrial flutter 1st degree AV Block RBBB Polymorphic vt - ecg TORSADES mobitz 1 Premature Atrial Complexes 3rd degree Monomorphic vt PSVT - AVNRT VF ECG simulator http://www.skillstat.com/tools/ecg-simulator