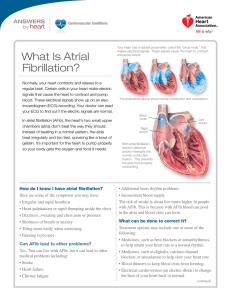
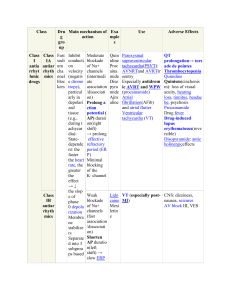
❤ Afib Case Study Student Name: Adrian Sese Case Description: You are the nurse in the cardiac care rehabilitation unit. Mr. Jones is a 68-year-old male who was recently diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. He has the following questions regarding his condition. Answer his questions using terminology appropriate for patient education. Question 1: What is the cause of my dysrhythmia? The heart has two functions to work as a pump and a battery because there are electrical components in there, and the failure of those two functions is what’s causing the rapid and irregular heart rhythms you are having right now. This can be caused from a heart attack, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and any physical stress from surgeries. Question 2: How will my atrial fibrillation be treated? We will continue monitoring you with ECG, blood tests, stress tests, and chest x-rays, and vital signs to measure your baseline. Your atrial fibrillation will be treated with antidysrhythmic medications such as amiodarone, which is known to be one of the most effective drugs to treat Afib. Your doctor can discuss any more further treatment options for you and give you more details. Question 3: What are the risks involved in treating my dysrhythmia? Amiodarone has side effects such as headache, fatigue, hypotension, and bradycardia. There is high risk of toxicity from amiodarone if not managed properly, so we need to Afib Case Study 1 constantly and carefully monitor you and choose the most appropriate dosing and checks to uphold safety. There is also a risk of toxicity if you drink grapefruit juices, or if you take other drugs such as warfarin and digoxin. There is also a risk if having a dangerously low heart rate if amiodarone is taken with beta blockers, because they both have a synergistic relationship in lowering heart rate. We ask that you report any adverse effects, take the drug with meals, and to follow and prescribed regimen while not stopping the drug abruptly. This will be a team effort from all of us to get through this therapy. Afib Case Study 2