Acids 2018
advertisement
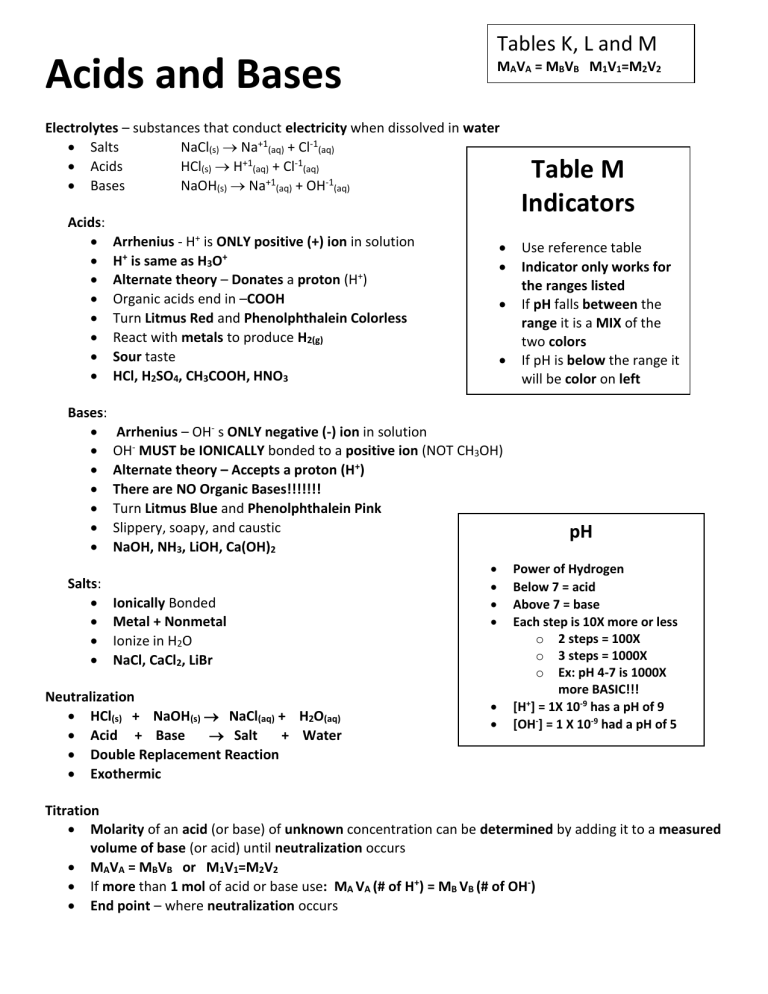
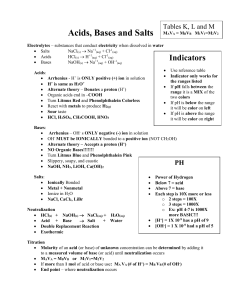
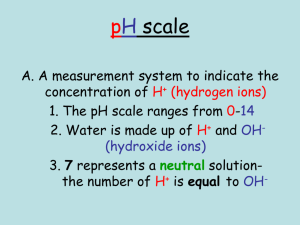
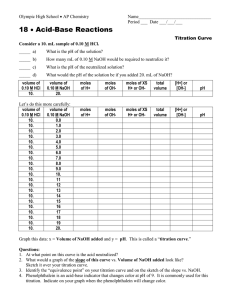
Tables K, L and M Acids and Bases MAVA = MBVB M1V1=M2V2 Electrolytes – substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water Salts NaCl(s) Na+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) Acids HCl(s) H+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) Bases NaOH(s) Na+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) Acids: Arrhenius - H+ is ONLY positive (+) ion in solution H+ is same as H3O+ Alternate theory – Donates a proton (H+) Organic acids end in –COOH Turn Litmus Red and Phenolphthalein Colorless React with metals to produce H2(g) Sour taste HCl, H2SO4, CH3COOH, HNO3 Bases: Salts: Arrhenius – OH- s ONLY negative (-) ion in solution OH- MUST be IONICALLY bonded to a positive ion (NOT CH3OH) Alternate theory – Accepts a proton (H+) There are NO Organic Bases!!!!!!! Turn Litmus Blue and Phenolphthalein Pink Slippery, soapy, and caustic NaOH, NH3, LiOH, Ca(OH)2 Ionically Bonded Metal + Nonmetal Ionize in H2O NaCl, CaCl2, LiBr Neutralization HCl(s) + NaOH(s) NaCl(aq) + H2O(aq) Acid + Base Salt + Water Double Replacement Reaction Exothermic Table M Indicators Use reference table Indicator only works for the ranges listed If pH falls between the range it is a MIX of the two colors If pH is below the range it will be color on left If pH is above the range it will be color on right pH Power of Hydrogen Below 7 = acid Above 7 = base Each step is 10X more or less o 2 steps = 100X o 3 steps = 1000X o Ex: pH 4-7 is 1000X more BASIC!!! [H+] = 1X 10-9 has a pH of 9 [OH-] = 1 X 10-9 had a pH of 5 Titration Molarity of an acid (or base) of unknown concentration can be determined by adding it to a measured volume of base (or acid) until neutralization occurs MAVA = MBVB or M1V1=M2V2 If more than 1 mol of acid or base use: MA VA (# of H+) = MB VB (# of OH-) End point – where neutralization occurs