Acids-Chemistry Regents Review
advertisement

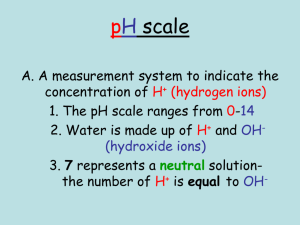
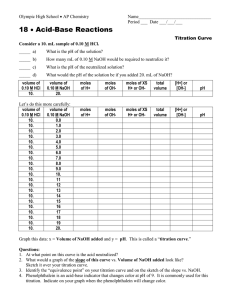
Acids, Bases and Salts Tables K, L and M MAVA = MBVB M1V1=M2V2 Electrolytes – substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water Salts NaCl(s) Na+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) Acids HCl(s) H+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) Bases NaOH(s) Na+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) Indicators Use reference table Indicator only works for the ranges listed If pH falls between the range it is a MIX of the two colors If pH is below the range it will be color on left If pH is above the range it will be color on right Acids: Arrhenius - H+ is ONLY positive (+) ion in solution H+ is same as H3O+ Alternate theory – Donates a proton (H+) Organic acids end in –COOH Turn Litmus Red and Phenolphthalein Colorless React with metals to produce H2(g) Sour taste HCl, H2SO4, CH3COOH, HNO3 Bases: Arrhenius – OH- s ONLY negative (-) ion in solution OH- MUST be IONICALLY bonded to a positive ion (NOT CH3OH) Alternate theory – Accepts a proton (H+) NO Organic Bases!!!!!!! Turn Litmus Blue and Phenolphthalein Pink Slippery, soapy, and caustic PH NaOH, NH3, LiOH, Ca(OH)2 Salts: Ionically Bonded Metal + Nonmetal Ionize in H2O NaCl, CaCl2, LiBr Neutralization HCl(s) + NaOH(s) NaCl(aq) + H2O(aq) Acid + Base Salt + Water Double Replacement Reaction Exothermic Power of Hydrogen Below 7 = acid Above 7 = base Each step is 10X more or less o 2 steps = 100X o 3 steps = 1000X o Ex: pH 4-7 is 1000X more BASIC!!! + [H ] = 1X 10-9 has a pH of 9 [OH-] = 1 X 10-9 had a pH of 5 Titration Molarity of an acid (or base) of unknown concentration can be determined by adding it to a measured volume of base (or acid) until neutralization occurs MAVA = MBVB or M1V1=M2V2 If more than 1 mol of acid or base use: MA VA (# of H+) = MB VB (# of OH-) End point – where neutralization occurs