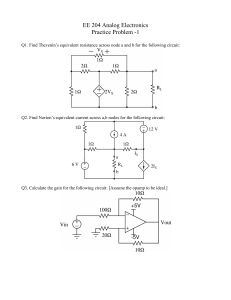
Problem 5. Find v o/vi. (Assume OpAmp is ideal). Problem 6. The
advertisement

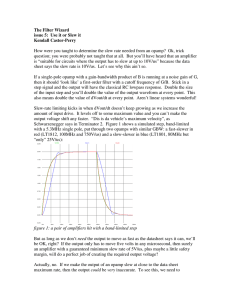
Problem 5. Find vo /vi . (Assume OpAmp is ideal). Problem 6. The circuit below is a voltage-to-current converter with IL = gVi. Find the value of g and show that it is independent of RL . (Assume OpAmp is ideal). vi + v o + − R1 − IL R1 − R2 R1 − R2 R1 + vi R3 + RL R2 R2 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7. Assume the OpAmp in the circuit below is ideal. Find the voltage transfer function H(jω) = Vo /Vi . Problem 8. Find vo in terms of v1 and v2 . (Assume OpAmp is ideal). Vi 2R R Vo − C + V1 R R2 Problem 7 R − + R1 4R − V2 2R Vo + Problem 8 Problem 9. Consider the amplifier circuit below with vi = 0.5 cos(ωt). a) what is the amplifier gain in dB? b) For what range of frequencies, does this amplifier behave as a linear amplifier? (Assume a unity-gain bandwith of 106 Hz, ISC = 100 mA, S0 = 1 V/µs and OpAmps are powered by ±15 V power supplies.) Problem 10. Consider the inverting amplifier below with RL = 500 Ω. The input signal is vi = 1 cos(106 t) V. We want the amplifier to behave linearly (i.e., output signal to be sinusoidal) and Vo /Vi = −K. What is the maximum value of K we can choose? (Assume a unity-gain bandwith of 107 Hz, ISC = 10 mA, S0 = 4 V/µs and OpAmps are powered by ±15 V power supplies.) ECE65 Lecture Notes (F. Najmabadi), Winter 2008 66