Introduction to Simulation
using EDWinXP
Introduction to Simulation using EDWinXP
First Edition
© Copyright Notice
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Any unauthorized reprint or use of this material is prohibited.
No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage
and retrieval system without express written permission from the author / publisher.
Published by
Visionics India Pvt Ltd, Technopark, Trivandrum
Preface
This book is compiled for the easier illustration of SPICE simulation and PCB designing to
cater the syllabus of various Universities for the undergraduate level of Engineering. Each
section has experiments described in a step by step manner.
This book is divided into five sections.
Introduction to EDWinXP, Introduction to EDSpice Simulator and the types of analysis that
can be performed in EDSpice Simulator, EDSpice simulation experiments, SPICE circuit
files, VHDL code samples, examples of 8051, AVR, PIC and Motorola microcontrollers and
PCB design.
The EDSpice simulation experiments describes the Aim, Components required for the
simulation, the circuit diagram, procedure, steps for the simulation and finally the result of
the simulation. The Components required for the experiment is given as Type of Component
– EDWinXP Component Name (Number of Components). The procedure section describes
the method of simulating the circuit with the values to be assigned to each component in the
circuit and the steps for simulating the circuit for the specified analysis. The result is obtained
in the Waveform viewer.
SPICE section lists the *.cir files for the circuits that can be simulated in EDWinXP CIR file
Editor.
VHDL simulation illustrates the list of experiments written in VHDL. The VHDL Editor in
EDWinXP can be used for its simulation.
The microcontroller section give the real time simulation of the projects using different
microcontrollers.
The PCB section describes the procedure of designing of PCB in EDWinXP.
Contents
•
•
About EDWinXP
EDSpice Simulator
Introduction
Type of Analysis
1. EDSpice Simulation
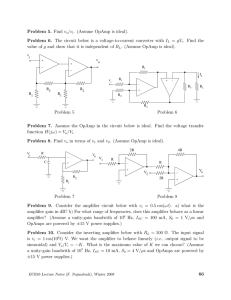
1. RC Coupled Amplifier
2. Diode Characteristics
3. V.I. Characteristics Of Zener Diode
4. BJT Input Characteristics – Common Emitter Configuration
5. BJT Input Characteristics – Common Base Configuration
6. BJT Output Characteristics – Common Base Configuration
7. FET Input Characteristics
8. FET Output Characteristics
9. MOSFET Input Characteristics
10. MOSFET Output Characteristics
11. Positive Clipper
12. Negative Clipper
13. Biased Double Limiter
14. Differentiator
15. Integrator (Triangle Output)
16. Integrator
17. Half Wave Rectifier
18. Positive Clamper
19. Negative Clamper
20. Biased Positive Clamper
21. Emitter Follower
22. Astable Multivibrator
23. Monostable Multivibrator
24. Bistable Multivibrator
25. Schmitt Trigger
26. Sweep Generator
27. Bootstrap Sweep Circuit
28. UJT Relaxation Oscillator
29. Series Voltage Generator
30. JFET Amplifier
31. Series Voltage Regulator
32. Class A Power Amplifier
33. Class C Power Amplifier
34. Complementary Symmetry Push Pull Amplifier
35. Cascode Amplifier
36. Current Time Base Generator
37. Opamp Differentiator
38. Opamp Integrator
39. Opamp Integrator with feedback
40. 741 Non-Inverting Summing Amplifier
41. 741 Non-Inverting Averaging Amplifier
1
3
3
4
7
8
22
24
25
27
29
32
34
36
38
40
41
43
45
47
49
51
53
55
56
58
60
62
64
66
68
70
72
74
76
78
80
82
84
86
88
90
92
94
96
98
42. First order active low pass filter
43. First order active notch filter
44. Opamp Asymmetric Astable Multivibrator
45. Opamp Current To Voltage Converter
46. Differential Amplifier
47. Opamp Monostable Multivibrator
48. Opamp Schmitt Trigger
49. Opamp Voltage Limiter
50. Opamp Peak Detector
51. Opamp Precision Half Wave Rectifier
52. Opamp Precision Full Wave Rectifier
53. Square Wave Generator
54. Window Detector
55. Saw tooth wave generator
56. RC Phase Shift Oscillator
57. Hartely Oscillator
58. Colpitts Oscillator
100
102
104
106
108
110
112
114
116
118
120
122
124
126
128
130
132
1. RC Differentiator Sine
2. RC Differentiator with Pulse
3. RC Differentiator with Sine
4. Full Wave W/O Filter
5. Full Wave With filter
6. Bridge Rectifier
7. Clipper
8. Clipper DC Characteristics
9. Clamper
10. Bias clamper
11. Diode Characteristics – Forward
12. Diode Characteristics – Reverse
13. Transistor Output Characteristics
14. Transistor Input Characteristics
15. FET IDS vs VGS Characteristics
16. FET Characteristics
17. Amplifier DC Bias
18. RC coupled Amplifier
19. RC Coupled Amplifier Response
20. RC Phase Shift Oscillator
21. Astable Multivibrator
22. JFET Amplifier
23. Frequency Response
24. Op Amp Integrator
25. Op Amp Differentiator
26. Filter
134
135
135
135
135
135
136
136
136
136
136
137
137
137
137
137
137
138
138
138
138
139
139
140
140
140
141
2. SPICE
3. VHDL Simulation
1. Adder 4 Bit
2. Adder Subtractor
3. BCD 7 Segment Decoder
142
143
143
144
4. Binary BCD Converter
5. Binary Counter 8 Bit
6. Binary Gray Converter
7. Comparator 3 Bit Easiest
8. Comparator 4 Bit
9. Multiplexer 16 Bit
10. Priority Encoder
11. Rom 16x8
12. Serial In Serial Out Shift Register
13. Parallel In Serial Out Shift Register
14. Johnson Counter
15. Decade Counter
144
145
147
147
148
148
149
150
150
151
152
153
4. 8051 Microcontroller
1. 8 bit Addition
2. 8 bit Subtraction
3. 8 bit Multiplication
4. 8 bit Division
5. 16 bit Addition
6. 16 bit Subtraction
7. Factorial
8. HCF
9. LCM
10. Matrix Addition
11. RAM Sort
12. Sorting
13. Squareroot of a Number
14. Square of a Number
15. Sawtooth waveform generation
16. Triangle waveform generation
17. Stepper motor
18. ADC
19. Add Sub
20. Biggest Number
21. Counter 255
22. Count Num
23. DAC
24. Division Multiplication
154
156
158
160
162
164
166
168
170
172
174
176
178
180
182
184
186
188
190
192
193
194
195
196
197
5. AVR Microcontroller
1. 4052 Analog Mux Demux
2. Binary to Graycode
3. Encryption
199
201
202
202
6. PIC Microcontroller
1. Addition
2. Subtraction
3. Multiplication
4. Division
5. BCD to Binary Converter
203
205
206
208
210
212
6. Multiplication and Division using PIC Microcontroller
217
7. Motorola Microcontroller
1. Pulse Counter
2. Voltage Reader
225
226
228
8. PCB Design
233