Chapter 7 Membrane Structure & Function
advertisement
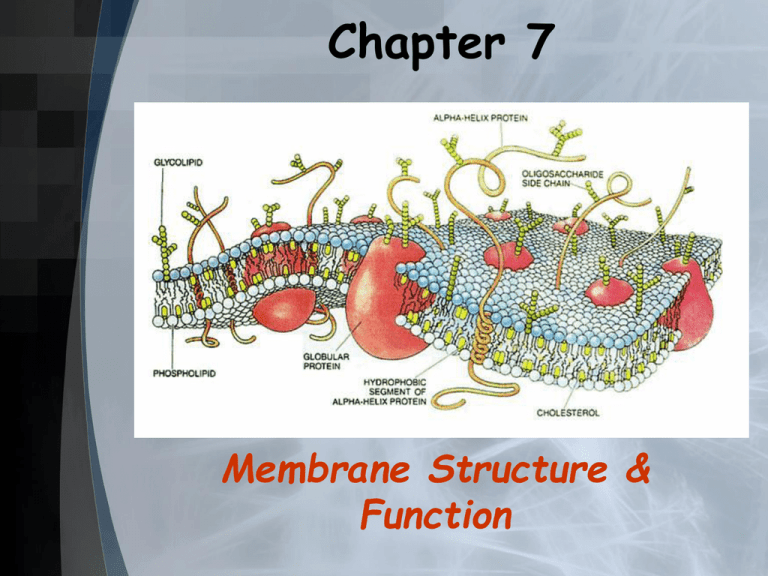
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure & Function Membrane Structure, I Shows Selective permeability Known as the plasma membrane Amphipathic - hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions Singer-Nicolson developed the fluid mosaic model Membrane Structure, II Phospholipids - membrane fluidity Cholesterol - membrane stabilization “Mosaic” Structure due to: Integral proteins - transmembrane proteins Peripheral proteins - surface of membrane Membrane carbohydrates -~ cell to cell recognition; oligosaccharides (cell markers); glycolipids; glycoproteins Membrane Structure, III Membrane protein functions: Transport Enzymatic activity Signal transduction Intercellular joining Cell-cell recognition ECM attachment Membrane Traffic Diffusion - tendency of any molecule to spread out into available space Concentration gradient – moves from high to low Passive transport - diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane Osmosis - the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane; DOWN the concentration gradient Water Balance Osmoregulation - control of water balance Hypertonic - higher concentration of solutes Hypotonic - lower concentration of solutes Isotonic - equal concentrations of solutes Water Balance Cells with Walls (plants, bacteria): Require hypotonic external environments to keep their turgor pressure (water pressure pushing cell membrane out against cell wall) Become limp or flaccid when lose turgor pressure Plasmolysis - plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall Water Balance Cells without Walls (animals, most protist): Require isotonic external environments Hypertonic environments – cells swell & may burst with too much water pressure (Cytolysis) May have contractile vacuoles (some protists) to control internal water pressure Specialized Transport Transport proteins (with or without channels) Facilitated diffusion - passage of molecules and ions with transport proteins across a membrane down the concentration gradient Active transport - movement of a substance against its concentration gradient with the help of cellular energy Types of Active Transport Sodium-potassium pump Exocytosis - secretion of macromolecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane Endocytosis - import of macromolecules by forming new vesicles with the plasma membrane Phagocytosis –cell “eating” Pinocytosis – cell “drinking” Receptor-mediated endocytosis (ligands)








