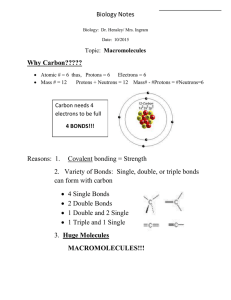
Nutrition Q & A for Bingo
advertisement
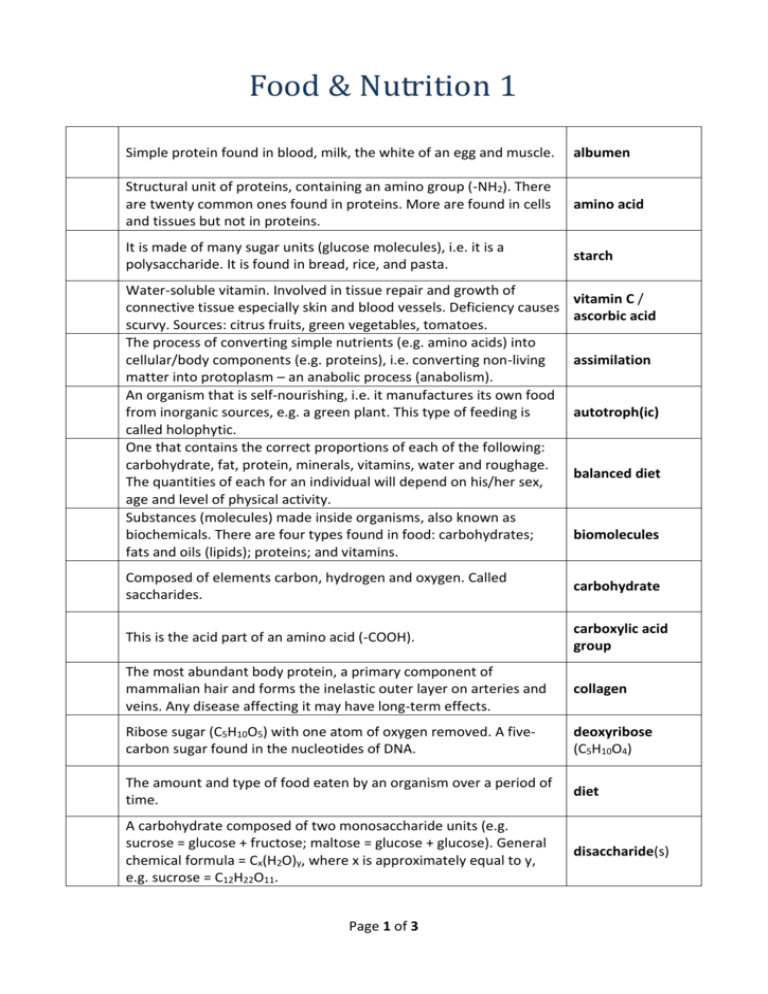
Food & Nutrition 1 Simple protein found in blood, milk, the white of an egg and muscle. albumen Structural unit of proteins, containing an amino group (-NH2). There are twenty common ones found in proteins. More are found in cells and tissues but not in proteins. amino acid It is made of many sugar units (glucose molecules), i.e. it is a polysaccharide. It is found in bread, rice, and pasta. starch Water-soluble vitamin. Involved in tissue repair and growth of connective tissue especially skin and blood vessels. Deficiency causes scurvy. Sources: citrus fruits, green vegetables, tomatoes. The process of converting simple nutrients (e.g. amino acids) into cellular/body components (e.g. proteins), i.e. converting non-living matter into protoplasm – an anabolic process (anabolism). An organism that is self-nourishing, i.e. it manufactures its own food from inorganic sources, e.g. a green plant. This type of feeding is called holophytic. One that contains the correct proportions of each of the following: carbohydrate, fat, protein, minerals, vitamins, water and roughage. The quantities of each for an individual will depend on his/her sex, age and level of physical activity. Substances (molecules) made inside organisms, also known as biochemicals. There are four types found in food: carbohydrates; fats and oils (lipids); proteins; and vitamins. vitamin C / ascorbic acid assimilation autotroph(ic) balanced diet biomolecules Composed of elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Called saccharides. carbohydrate This is the acid part of an amino acid (-COOH). carboxylic acid group The most abundant body protein, a primary component of mammalian hair and forms the inelastic outer layer on arteries and veins. Any disease affecting it may have long-term effects. collagen Ribose sugar (C5H10O5) with one atom of oxygen removed. A fivecarbon sugar found in the nucleotides of DNA. deoxyribose (C5H10O4) The amount and type of food eaten by an organism over a period of time. diet A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharide units (e.g. sucrose = glucose + fructose; maltose = glucose + glucose). General chemical formula = Cx(H2O)y, where x is approximately equal to y, e.g. sucrose = C12H22O11. disaccharide(s) Page 1 of 3 Any amino acid that must be in the diet as it cannot be made by the body. essential (amino acid) Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, but in a different ratio to carbohydrates. It is solid at room temperature. fat An acid occurring in or derived from natural fats, waxes, etc. Component of fats or lipids. The smallest lipid is a triglyceride. It is made from three molecules of these and one glycerol molecule. Food containing a large content of indigestible material (cellulose), e.g. vegetables. Provides bulk. Eating it makes you feel full and can prevent you overeating as part of a balanced diet. Gives the muscles of the gut wall something to push against. Keeps the contents of the gut moving. Absorbs water, keeps faeces soft and easier to egest. Prevents constipation. Helps prevent bowel (colon) cancer. Water soluble, essential for the formation of RNA and DNA and the normal production of red blood cells. Deficiency causes anaemia during pregnancy and certain birth defects, e.g. spina bifida. Source: liver, green vegetables and yeast. Substances that are required by all living organisms and provide them with energy and materials for growth and repair of cells, tissues and organs. fatty acid fibre folic acid food A monosaccharide sugar found naturally in fruit juices, honey, etc. Chemical formula = C6H12O6. fructose Naturally occurring monosaccharide found in milk and other dairy products. Chemical formula = C6H12O6. galactose A hormone released by the pancreas. In humans glycogen is broken down to glucose through the action of hormones (adrenaline and this hormone), as more glucose is demanded for respiration. This hormone and insulin work together to control the level of sugar in the blood. A six-carbon single sugar, monosaccharide, hexose sugar. Formed in plants during photosynthesis and is the end product of the digestion of carbohydrates. Most living organisms need it for respiration. glucagon glucose (C6H12O6) Fats are formed from one of these molecules attached to three fatty acids. glycerol Animal storage polysaccharide found in muscles, liver and brain. glycogen An organism that cannot make its own food. Depends on other organisms as sources of food, e.g. all animals, saprophytes and parasites. This type of feeding is called holozoic. heterotroph(ic) A monosaccharide sugar with six carbon atoms in each molecule. hexose Page 2 of 3 A compound containing hydrogen and carbon. hydrocarbon Tough, fibrous protein with a high sulphur content forming structures such as horns, nails, hair, feathers, etc keratin Page 3 of 3