Chapter 9 Civilizations in Eastern Europe: Byzantium and Orthodox Europe
advertisement

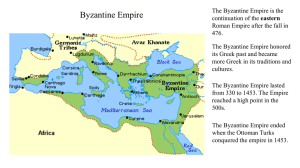
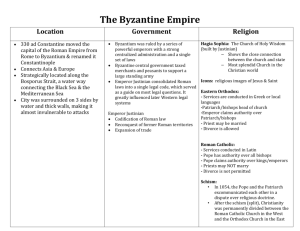
Chapter 9 Civilizations in Eastern Europe: Byzantium and Orthodox Europe The Basics • The Word Byzantine – Suggests the distinction from Rome itself • Political heir to Rome but still its own thing • Constantinople Constantinople • Constantine names capital after himself – moves capital there 340 CE • 1453 falls to Turks, renamed Istanbul – Major event in WH and the impact with be resounding • Song • One of the most important cities at the time – Located on a trading route Meet Justinian Justinian (527-565 CE) • The “sleepless emperor” • Wife Theodora as advisor – Background: circus performer • Uses army to contain tax riots, ambitious • construction program – Hagia Sophia • Law Code – Codification of Roman Law – Body of Civil Law: made Roman law coherent basis for political and economic life Meet Theodora Hagia Sophia • First built by Constantine • Rebuilt by Justinian • The greatest surviving example of Byzantine Architecture • It is an example of Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic and Islam • It was the seat of the Orthodox patriarch Byzantine Conquests • • • • General Belisarius recaptures much of western Roman Empire under Justinian Unable to consolidate control of territories Withdrew to defend empire from Sassanids, Slavs The Byzantine empire and its neighbors 527-554 C.E. The Byzantine empire and its neighbors about 1100 C.E. Islam and Arab Pressure • Constant vigilance against Muslim Invaders • The Byzantine Empire had to focus on protecting the borders • This pressure from the Muslim world is going to be one of the issues that brings about the split between east and west The Eastern Schism Split • In 1054 a longstanding disagreement came to a head, and the Christian church split into two groups. • The Western or Roman Catholic, and Eastern or Orthodox Catholic. • The Byzantine Empire goes into slow decline Disagreements • • • • • • Papal attempts to interfere over icons Charlemagne claims to be Roman Emperor Rituals in Latin not Greek Pope as first bishop Religious art Celibacy for priests Eastern Orthodox • Requires services to be in Greek • Patriarch and bishops were head of the church – The emperor was above the patriarch • Believed in a different interpretation of the Bible • Eastern Orthodox missionaries spread northward into Russia and the Balkans Cyrillic • Cyril and Methodius are the two most famous of the missionaries. • Slavic language/alphabet derived from Greek letters • Allowed for literature to be spread – HOW? Icons • Images of religious figures venerated by byzantine Christians • Iconoclasm – The breaking of images – Religious controversy of the 8th century – Byzantine emperors attempted but failed to suppress icon veneration – Believed it was the worship of idols Decline • 1071 Byzantine defeat in Asia • 1204 Constantinople sacked by Crusaders • 1453 Constantinople taken by Ottoman Turks Very Similar to China • The Byzantine political system had remarkable similarities to China. • The emperor was held to be ordained of God. • He was head of the church as well as state. • Women could and did serve as emperor. • They had an elaborate bureaucracy to administer the government. KIEVAN RUSSIA Who were the Slavs? • People who migrated from Asia – Mix with earlier populations – Family tribes, villages • Trade – with Byzantines – Trade with Northerners Scandinavian merchants • Vikings • During the 6th and 7th centuries moved into the region • c. 855, monarchy under Rurik (Danish) – Center at Kiev • Prosperous commercial center Meet Vladimir I •(980-1015) •Converts to Orthodoxy due to contact with Byzantium •Controls church Meet Yaroslav I • Issued a unifying code of laws, while not as advanced as Constantinople it still had nobles called Boyars. – Boyars: Russian landholding aristocrats • Possessed less political power than their western European counterparts (feudalism) The Tarters • The Russian name for the Mongols. The Invasion of Russia by the Mongols and the destruction of Constantinople by Muslims, isolated Russia. • The region was cut off from western contacts, stifling economic, political, and cultural sophistication.