Byzantine Empire: Location, Government, Religion, Culture
advertisement

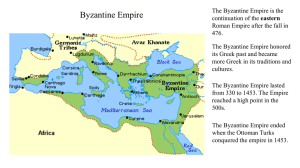
The Byzantine Empire Location 330 ad Constantine moved the capital of the Roman Empire from Rome to Byzantium & renamed it Constantinople Connects Asia & Europe Strategically located along the Bosporus Strait, a water way connecting the Black Sea & the Mediterranean Sea City was surrounded on 3 sides by water and thick walls, making it almost invulnerable to attacks Government Byzantium was ruled by a series of powerful emperors with a strong centralized administration and a single set of laws Byzantine central government taxed merchants and peasants to support a large standing army Emperor Justinian consolidated Roman laws into a single legal code, which served as a guide on most legal questions. It greatly influenced later Western legal systems Emperor Justinian Codification of Roman law Reconquest of former Roman territories Expansion of trade Religion Hagia Sophia: The Church of Holy Wisdom (built by Justinian) – Shows the close connection between the church and state – Most splendid Church in the Christian world Icons: religious images of Jesus & Saint Eastern Orthodox: - Services are conducted in Greek or local languages -Patriarch/bishops head of church -Emperor claims authority over Patriarch/bishops - Priest may be married - Divorce is allowed Roman Catholic: - Services conducted in Latin - Pope has authority over all bishops - Pope claims authority over kings/emperors - Priests may NOT marry - Divorce is not permitted Schism: • In 1054, the Pope and the Patriarch excommunicated each other in a dispute over religious doctrine. • After the schism (split), Christianity was permanently divided between the Roman Catholic Church in the West and the Orthodox Church in the East The Byzantine Empire Culture Decline The Byzantines preserved the rich cultural heritage of classical civilization, including Greek philosophy and science and Roman engineering. Copies of ancient texts were saved despite destruction in the West Plagues: bubonic plague spread through the city during Justinian’s reign. Plague broke every 8-12 years. -Smaller population left empire exposed to its enemies Byzantines were renowed for their mosaics, painted icons, gold jewelry, & skills. Attacks: Enemies pressed on all sides. -Slavs, Avars, Bulgars, Persians, Arabs, Russians, Turks - Crusades brought armies into the city who pillaged Constantinople Byzantium benefited from a rich infusion of Greek, Roman, Christian and Middle Eastern cultures Decline: Byzantines used bribes, diplomacy, political marriages to help prop up shaky empire - Province (military districts) were set up and run by a general who reported back to the emperor - Shrank under impact of attacks - Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453 Influences Early Russian cities carry on a brisk trade with the Byzantine Empire. Orthodox Christianity Cyrillic alphabet developed by Saint Methodius and Saint Cyril Byzantine crafts & products Converted Slavic peoples & Bulgars to Christianity