Metamorphic Rocks
advertisement

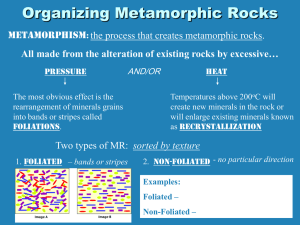
Metamorphic Rocks “Metamorphic” “Metamorphic” means Change! Biochemical Limestone Marble Metamorphic Rock Sources Metamorphic rocks are formed when: 1.Igneous 2. Sedimentary or 3. Pre-existing Metamorphic rocks are Metamorphic Rock Classification Metamorphic Rocks are classified based on: 1. Formation Conditions (where formed) 2. Texture 3. Parent Rock (what rock, or rock type, it came from) Quartzite- Fine Grained Gneiss- Foliated Common Metamorphic Rocks Rock Name Parent Rock Slate Shale or Mud Mica Shale or Mud Gneiss Granite Quartzite Sandstone Marble Limestone Temp C Temp F Coal Limestone Sandstone Basalt Shale Index Minerals Slate Chlorite Phyllite Biotite Schist Garnet Lignite Bituminous 300 500 Anthracite 600 Graphite Marble 700 800 500 1100 1200 700 Quartzite 900 1000 600 Greenstone Amphibolite Staurolite Gneiss Kyanite Sillimanite Melting Begins Slate Mica Gneiss Quartzite Marble Schist What Causes Metamorphic Rocks to Form? Metamorphic Rocks are formed when preexisting rocks are changed by: And Sources of Heat •Increase in Temperature due to Deep Burial (2030 degrees Celsius per kilometer below the surface). Due to radioactive decay.----RegionalMetamorphism •Increase in Temperature due to Plate Friction (100-300 degree Celsius per km below the surface). -----Dynamic Metamorphism •Intrusion by hot Magma. ----Contact Metamorphism Sources of Pressure • Weight of Overlying Rocks (1 cubic foot of granite weighs 167 pounds) •Created by converging plates (ConvergingBoundaries) or those •Transform Boundaries (side-by-side movement) Effects of Metamorphism on Rocks • Impurities such as holes and fossils destroyed. Effects of Metamorphism on Rocks • Pore Space between grains is lost due to Compression. • Rock density increases. Effects of Metamorphism on Rocks •Mineral Grains are flattened, enlarged and elongated. Types of Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism •Occurs in large areas. •Occurs in response to deep burial by large areas of rock. •Occurs with Mountain Building (Collision Boundary). Regional Metamorphism Regional Metamorphism Foliated Metamorphic Rocks Increasing metamorphic grade Increasing foliation slate phyllite schist gneiss migmatite (partially melted) (low grade) (high grade) Dynamic Metamorphism • Occurs between moving plates (very localized and happens quickly). Thermal or Contact Metamorphism •Occurs when rock comes into contact with Magma or hot Pore Fluids (Geysers and Hot Springs). Thermal or Contact Metamorphism