Metamorphic Rock Notes
advertisement

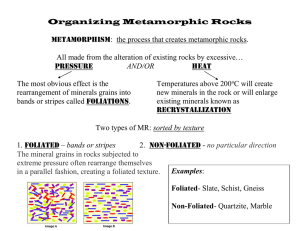
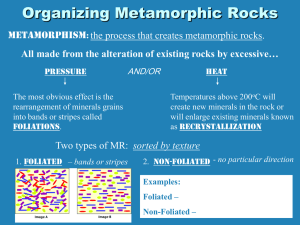
Which type of igneous rock forms on the surface of Earth from lava? Intrusive OR Extrusive Metamorphic rocks form from other rocks due to intense heat and pressure***. There can be NO melting! Metamorphic rocks are from recrystallization of unmelted material over a long period of time. This forms larger, denser crystals. 1. Regional – formed by forces acting over large areas, at great depth where extreme temperature*** and pressure exist. High Pressure: caused by collisions of plates A great region to find metamorphic rock is in mountains! Foliation: reorientation of mineral grains Banding: concentration of minerals into zones of light and dark colors Contact – occurs at regions where magma comes into contact with pre-existing rock. 2. High temperature changes the rock without melting 1. 2. Foliated Examples: Slate, Gneiss, Schist, Phyllite Non-Foliated Examples: Hornfels, Marble, Quartzite 1. 2. 3. 4. Check for foliation Check for grain size Check composition Use ESRT (page 7) 1. Marble – metamorphic form of limestone 2. Quartzite – from sandstone 3. Slate – usually from metamorphism of shale Phyllite – further metamorphism of slate Schist – foliated – contains layering, is easily broken Gneiss – highly distorted – contains banding 6. Usually from granite Science Review Game- Mixed Rock