Metamorphic_Rocks_notes
advertisement

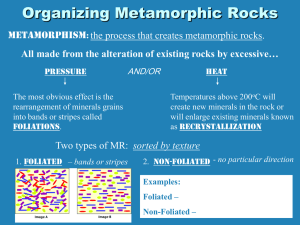
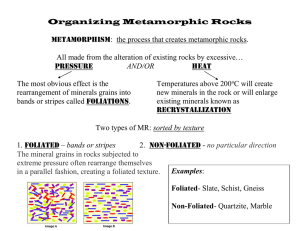
Metamorphic Rocks Meta = form Morph = change 3 Main Types Regional Metamorphism Occurs in large areas due to pressure and heat Occurs during mountain building Rocks are squeezed, making them more dense and less porous Atoms can be rearranged forming new minerals Examples: Limestone marble Sandstone quartzite Shale slate phyllite schist gneiss Contact Metamorphism Due to heat when hot magma comes in contact with other rocks (magma actually touches rock) Changes are less drastic Covers a smaller area Examples: Hornfels Hydrothermal Metamorphism Hot water reacts with rock and alters it’s mineral content o Dissolve o Break down o Deposit new minerals Occurs often near volcanoes and igneous intrusions 3 New Shapes 1. Foliated – very flat layers, sometimes light and dark a. Shale b. Slate c. Phyllite d. Schist e. Gneiss 2. Non-foliated – large, blocky crystals a. Quartz b. Marble 3. Porphyroblasts – large and small pieces, from the reorganization of atoms in solid rock during contact and regional metamorphism a. Garnet