Time Use Statistics in the Context of Social Statistics
advertisement

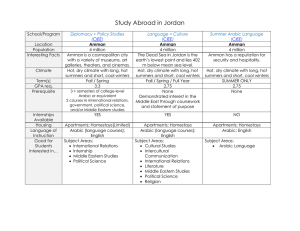
Time Use Statistics in the Context of Social Statistics Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Definition Time – part of the fundamental structure of the universe, a dimension in which events occur in sequence Different measurement of time around the world Time – measure of activities Daily activities - regulated by the clock In principle, every activity “costs” time – and that time can be measured Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Definition Time use surveys – quantitative summaries of how individuals “spend” or allocate their time over a specified period Typically over 24 hours of the day Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Origin and history Originated in early 20th century Use of labor force Industrialization Effects on society Applied in USSR until 1960’s In 1960’s Alexandre Szalai First attempt at international comparison – 12 countries - harmonization Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Origin and history In 1980’s focus on paid work Productivity Small samples Various government agencies – not statistical offices Low interest Commercial purposes – use of leisure time Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Origin and history In 1990’s sharp increase in interest – focus on gender and unpaid work Beijing Platform for action – suitable means to recognize and make visible the full extent of the work of women Human Development Report 1995 – GenderRelated Development Index Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Meeting data needs Economic – quantifying household production and not-for profit activities Satellite accounts Energy consumption – patterns of consumption Leisure and recreation Culture and identity Paid work Social connectedness Knowledge and skills Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Meeting data needs Standard of living - wellbeing Older people Youth Children Second hand tobacco exposure Exercise and sedentary activity Occupational health and safety Infectious disease transmission Intra-household decision-making and division of labor Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Meeting data needs In developing countries Netting economic work of the poor Improving estimates of national income Policy guidelines Example: Philippines - unpaid work adds 66% to the GDP - women’s share in GDP rose from 39% to 47% - women account for 60% of all unpaid work Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Meeting data needs Contribution of women is often overlooked Global Gender Statistics Programme focuses on time use statistics Informal sector Unpaid work Caring for family members Intra-household balance Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Methodological issues Three types of units of enumeration Household Household member Time Seasonality Workweek vs. weekends Rare events Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Methodological issues Data collection methods Short form/long form Self-administered (real time) Recollection method Obstacles: Watches not common Literacy Interviewers Background information Sampling Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Methodological issues Context variables What for? For whom? With whom? Paid or non-paid activity? Location of the activity? Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Classification of time use Trial International Classification of Activities for Time Use Statistics (ICATUS) Designed to Collect data on time use Measure unpaid work Type of activity complemented by the purpose of activity (what, with whom and what for) Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Classification of time use Harmonized European Time Use Surveys (HETUS) Gainful work, study Domestic work Travel Sleep Meals, personal care Free time, unspecified time use Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Concluding remarks Powerful statistical instrument Measure paid and unpaid work Measure host of other phenomena Division of labor within family Characteristics of family life Social connectedness Civic participation Wellbeing Happiness? Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Concluding remarks Complete diary vs. light form Further experiments necessary “Long form/Short form” paradigm? Advantages and disadvantages – need for evaluation Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan Concluding remarks International Programme on Time use Surveys Conduct such a survey at least once in ten years Implement international guidelines and statistical standards Disseminate results in timely manner Procedures for exchanging experiences and training Time Use Statistics Workshop for Arabic Speaking Countries 25 – 28 April 2011, Amman, Jordan