Alcohol Substitution Reactions: SN1 & SN2 Mechanisms
advertisement

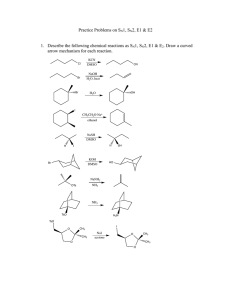
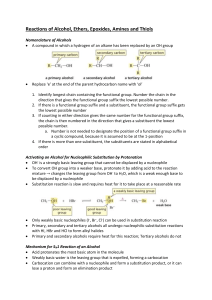
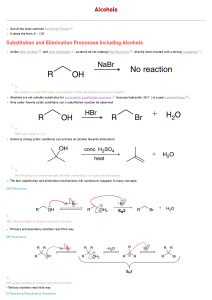
CH 11-2 - Substitution Reactions of Alcohols: Halogenation by HX R OH alcohol + HX R X + acid Points about Mechanism: •Why do we need “HX” instead of “NaX”? •For 3o and 2o alcohols the mechanism is SN1. •For 1o alcohols the mechanism is SN2 only. •Is the reaction acid catalyzed or is the acid a stoichiometric reagent? H2O weak base SN1 Alcohol Substitution. Write a complete mechanism for the balanced equation shown below. Your mechanism must consist of a series of numbered, balanced equations for each chemical step, and curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs. SN2 Alcohol Substitution. Write a complete mechanism for the balanced equation shown below. Your mechanism must consist of a series of numbered, balanced equations for each chemical step, and curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs. CH 11-2 - Substitution Reactions of Alcohols: Halogenation by HX R OH alcohol + HX R X + acid Points about Mechanism: •Why do we need “HX” instead of “NaX”? •For 3o and 2o alcohols the mechanism is SN1. •For 1o alcohols the mechanism is SN2 only. •Is the reaction acid catalyzed or is the acid a stoichiometric reagent? H2O weak base