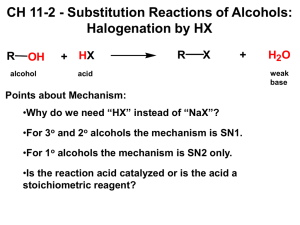CHM 234: Worksheet #13 Spring 2011 Chapter 10 Dr. Halligan The
advertisement

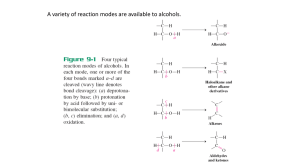
CHM 234: Worksheet #13 Chapter 10 Spring 2011 Dr. Halligan The “-OH” group makes a “lousy LG” and so we use the following regents to convert an alcohol to a more reactive substrate for future substitution and elimination reactions. HI, HBr or HCl with ZnCl (SN1 mech for 2° and 3° ROH, SN2 mech for 1° ROH) PBr3, PCl3 or SOCl2 (all with pyridine) (Used with 1° and 2° ROH, SN2 mech, get RX product) TsCl, MsCl, or TfCl (all with pyridine) (Used with 1° and 2° ROH, Results in an OTs, OMs or OTf LG, then subsequent SN2 reactions provide substitution products). 1. Write a mechanism leading to the major product of each of the following reactions. Keep in mind that 1° alcohols undergo SN2 reactions and 2° and 3° alcohols proceed by the SN1 mechanism. 2. PCl3, PBr3, PI3 and SOCl2 are used to convert 1° and 2° alcohols to alkyl halides. Write a mechanism and give the major product of each of the following reactions. 3. Show how to convert trans-4-methylcyclohexanol to cis-1-iodo-4-methylcyclohexane via a tosylate. Write a mechanism for this transformation and use the chair form of the cyclohexane derivatives. 4. Design a synthesis for the following compounds from 1-butanol. Show all reagents and intermediates. In order to maximize yields, first convert the alcohols to either alkyl halides by PCl3, PBr3, PI3 and SOCl2 or convert them to sulfonate esters by TsCl, MsCl or trifluoromethanesulfonyl chloride. 5. Alcohols can be dehydrated by concentrated acid to give alkenes (prone to carbocation rearrangements). However, 1° and 2° alcohols are especially problematic since side since side reactions occur so we typically use POCl3 to convert OH to a better LG and then conduct an E2 reaction with pyridine as the base. Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions. 6. Predict the products of the following oxidation reactions. 7. Ethers are typically cleaved by an SN1 mechanism unless a stable carbocation cannot be formed, then they proceed via an SN2 mechanism. Write mechanisms for the following reactions that involve ethers and 1 equiv. of HI.