Document 15957535
advertisement
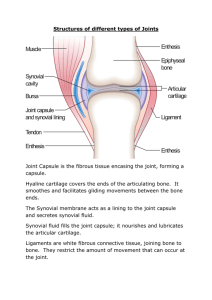
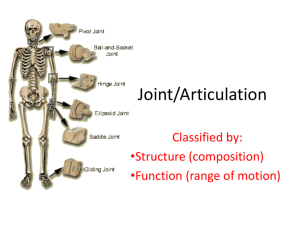
A. Functions 1. gives skeleton mobility and holds it together still is “weakest link” in skeleton. B. When joints are classified according to structure, they are named for material binding bones together 1. Fibrous 2. Cartilagenous 3. Synovial a.are immovable (synarthrotic) joined by fibrous connective with no joint cavity. Ex: sutures b.Gomphoses in Gum c.Distal tibiofibular joint 1. Articulating bones joined by bar or plate of hyaline cartilage; no joint cavity. Two types: a. Synchrondroses b. Symphyses 1. Synchrondroses- bar or plate of hyaline cartilage joins bones. Joint is immoveable (synarthrotic). Ex. epiphyseal plate 2. Symphyseshyaline cartilage of articulating bone end is fused to pad or plate of fibrocartilage Ex. Pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs. Slightly moveable a. definition: articulating bones are joined by fluid - filled joint capsule. They are diarthrotic, or freely moveable, include most joints of body, i.e., hinge, ball and socket, plane, condyloid, pivot and saddle joints. b. General structure of synovial joint (1) Articular cartilage (2) Joint cavity (3) Articular capsule (4). Synovial fluid (5) Reinforcing ligaments (6) Other parts associated with synovial joints (a)fatty pads (b)bursae (c)menisci (d)tendon sheath d. Type of movement - Angular movement at hinge joints, elbow shown • Flexion (decreases angle) • Extension (increases angle) Angular movement at ball and socket joints • Adduction movement toward the body center • Abduction movement away from body center Rotational movement around an axis at hip, shoulder and C1 and C2. • Circumduction, movement in a small circle at ball and socket (shoulder & hip) and saddle joint Metacarpal/thumb e. Origin and insertions of muscles (1)the origin is the end of muscle attached to immoveable end (2)insertion end of the muscle that is attached to moveable end d. More Movement at synovial joints •g.Gliding movement at Plane Movements at synovial joints joints (intercarpal & intertarsal joints) flat surfaces glide across each other @ Js • flexion/extension at condyloid joint, interphalangeal joint • Rotational movement at Pivot joint, radioulnar joint one bone pivots around another stationary bone,