Chap 14: ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
advertisement

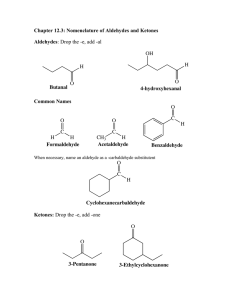
Chap 14: ALDEHYDES AND KETONES • The carbonyl group: • Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl group. • Ketones have two carbons attached to the carbonyl group. 1 NAMING ALDEHYDES • Find the longest carbon chain that contains the aldehyde group. • Change ending of the root hydrocarbon name by dropping –e and adding –al. • All other branches and groups are named and located using standard IUPAC system. Examples: 2 NAMING KETONES • Find the longest chain that contains C=O. • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. Examples: 3 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES • The carbonyl group is moderately polar, but it doesn’t have any hydrogen atoms attached, so it cannot hydrogen bond between molecules. 4 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, cont. • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen bonding. • This makes the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones higher than alkanes, but lower than alcohols. 5 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, cont. • The C=O group can hydrogen bond with water molecules. H O || R-C-R O H • This makes low molecular weight aldehydes and ketones water soluble (they have small hydrophobic sections). 6 ALDEHYDE AND KETONE REACTIONS • Recall the oxidation of alcohols to produce aldehydes and ketones: 7 REACTIONS, cont. • The addition of H2 in the presence of catalysts. 8 Examples: 9 REACTIONS, cont. • The addition of alcohols to aldehydes produces an unstable hemiacetal intermediate. 10 REACTIONS, cont. • General formulas for: Hemiacetals Acetals 11 REACTIONS, cont. • The addition of alcohol to ketones produces an unstable hemiketal intermediate. 12 REACTIONS, cont. • General formula for: Hemiketal Ketal 13 REACTIONS, cont. • Cyclical hemiacetals and hemiketals are more stable than open chains and are important in carbohydrate chemistry. 14 REACTIONS, cont. • Acetals and ketals are stable, but may be converted back to aldehydes and ketones through acid catalyzed hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is the breakage of a bond by reaction with water. • Acetal hydrolysis: 15 REACTIONS, cont. • Ketal hydrolysis: Specific Example: 16 IMPORTANT ALDEHYDES AND KETONES • Formaldehyde Gas at room temperature Formalin – 37% aqueous solution Sterilizer Embalming fluid Starting material for plastics such as Formica and Bakelite 17 IMPORTANT ALDEHYDES AND KETONES, cont. • Acetone (propanone) Important organic solvent Used in such things as nail polish remover Miscible with water 18 IMPORTANT ALDEHYDES AND KETONES, cont. • Progesterone and testosterone (female and male sex hormones) are ketones. • Some aldehydes and ketones are very fragrant and are used in flavorings. Vanillin (vanilla) Cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon) Citral (citrus flavoring) Camphor (medicinal odor) 19